Deposition Date
2003-01-24
Release Date
2005-10-13
Last Version Date
2023-12-13
Entry Detail
PDB ID:
1OB5
Keywords:
Title:
T. aquaticus elongation factor EF-Tu complexed with the antibiotic enacyloxin IIa, a GTP analog, and Phe-tRNA
Biological Source:
Source Organism(s):
THERMUS AQUATICUS (Taxon ID: 271)
SACCHAROMYCES CEREVISIAE (Taxon ID: 4932)
SACCHAROMYCES CEREVISIAE (Taxon ID: 4932)
Expression System(s):
Method Details:
Experimental Method:
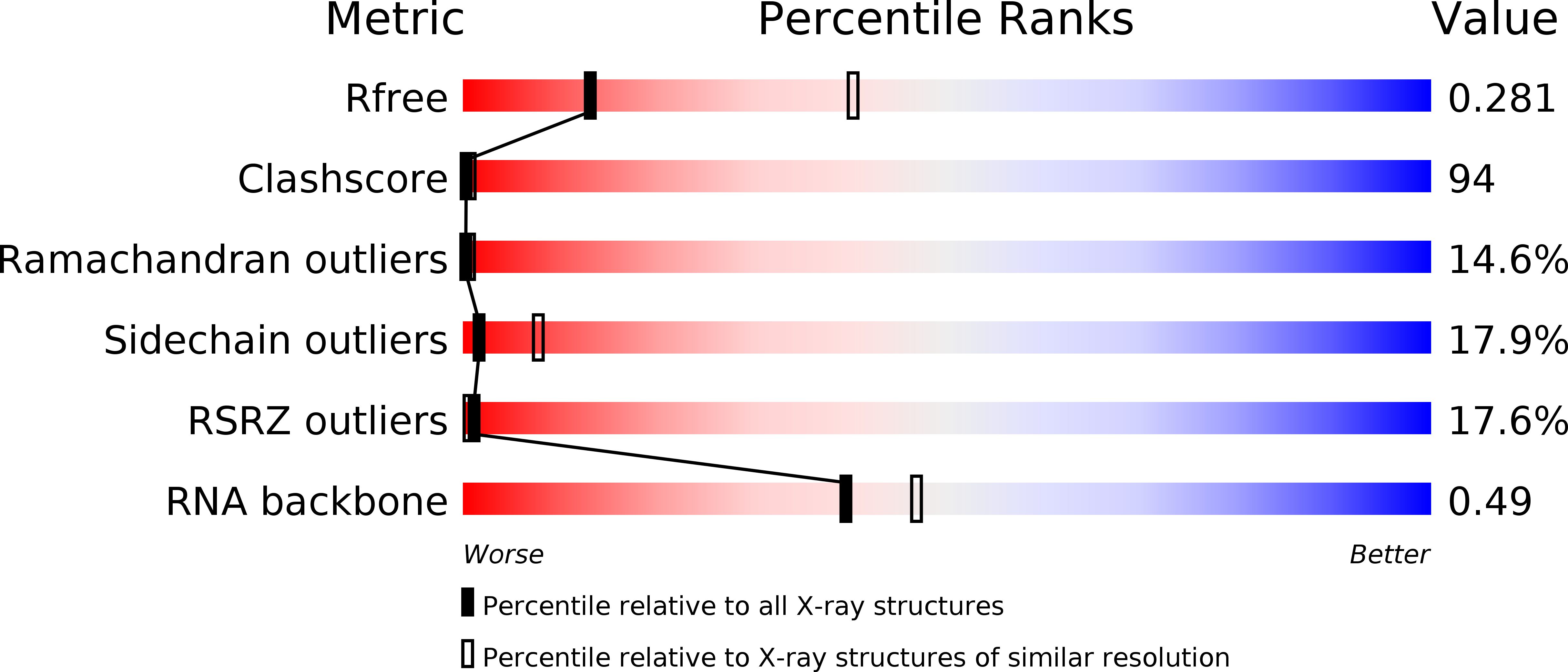
Resolution:
3.10 Å
R-Value Free:
0.29
R-Value Work:
0.27
R-Value Observed:
0.27
Space Group:
C 1 2 1