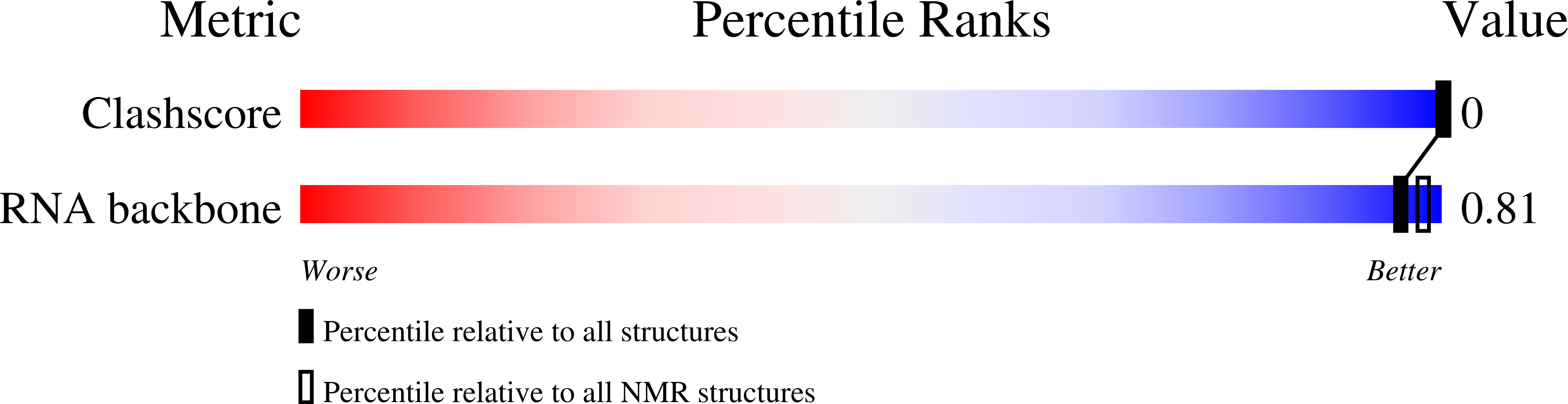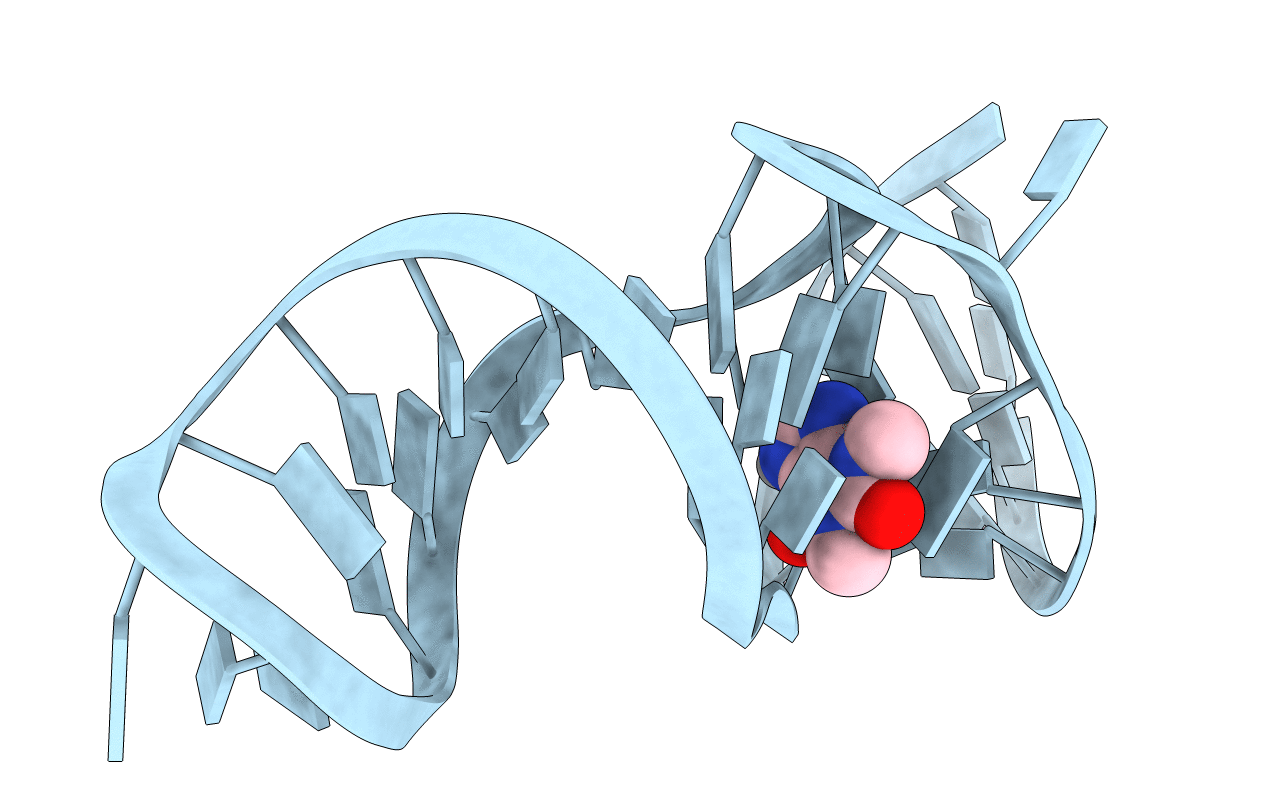
Deposition Date
2002-10-21
Release Date
2003-02-18
Last Version Date
2023-12-27
Entry Detail
PDB ID:
1O15
Keywords:
Title:
THEOPHYLLINE-BINDING RNA IN COMPLEX WITH THEOPHYLLINE, NMR, REGULARIZED MEAN STRUCTURE, REFINEMENT WITH TORSION ANGLE AND BASE-BASE POSITIONAL DATABASE POTENTIALS AND DIPOLAR COUPLINGS
Method Details:
Experimental Method:
Conformers Calculated:
250
Conformers Submitted:
1
Selection Criteria:
RESTRAINED REGULARIZED MEAN STRUCTURE