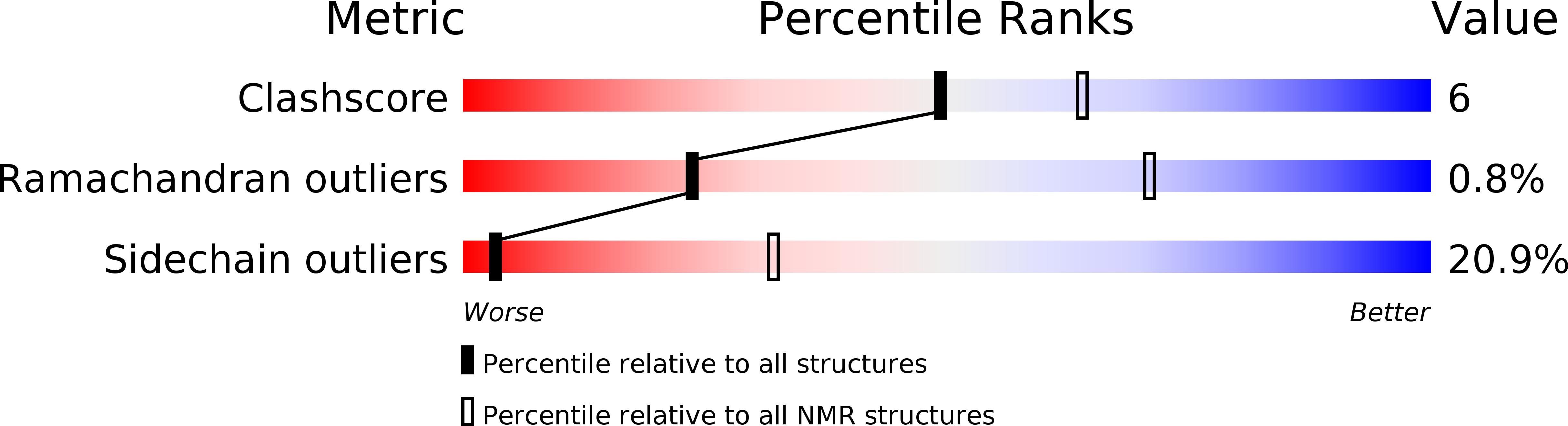
Deposition Date
2002-12-30
Release Date
2003-01-14
Last Version Date
2024-10-30
Entry Detail
PDB ID:
1NIY
Keywords:
Title:
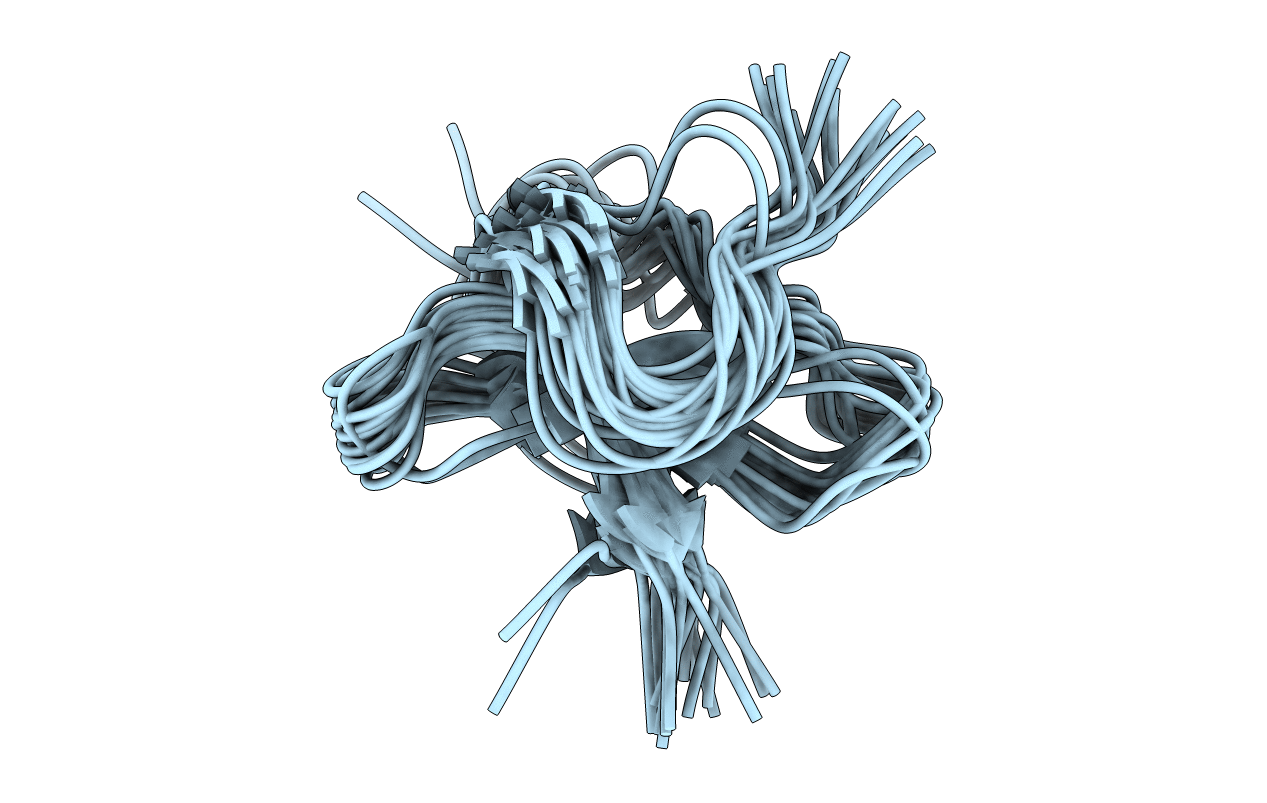
THREE DIMENSIONAL SOLUTION STRUCTURE OF HAINANTOXIN-IV BY 2D 1H-NMR
Biological Source:
Source Organism:
Ornithoctonus hainana (Taxon ID: 209901)
Method Details:
Experimental Method:
Conformers Calculated:
50
Conformers Submitted:
20
Selection Criteria:
structures with the lowest energy