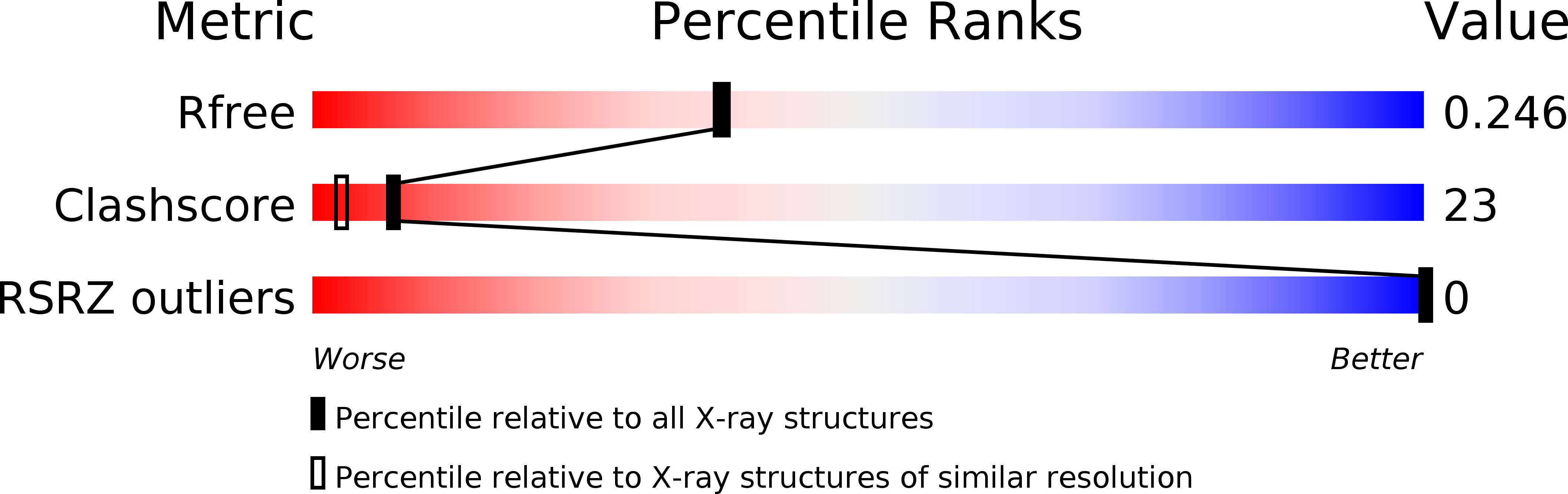Deposition Date
2002-11-27
Release Date
2003-02-25
Last Version Date
2024-02-14
Entry Detail
PDB ID:
1NAB
Keywords:
Title:
The crystal structure of the complex between a disaccharide anthracycline and the DNA hexamer d(CGATCG) reveals two different binding sites involving two DNA duplexes
Method Details:
Experimental Method:
Resolution:
2.15 Å
R-Value Free:
0.23
R-Value Work:
0.22
R-Value Observed:
0.22
Space Group:
P 43 21 2