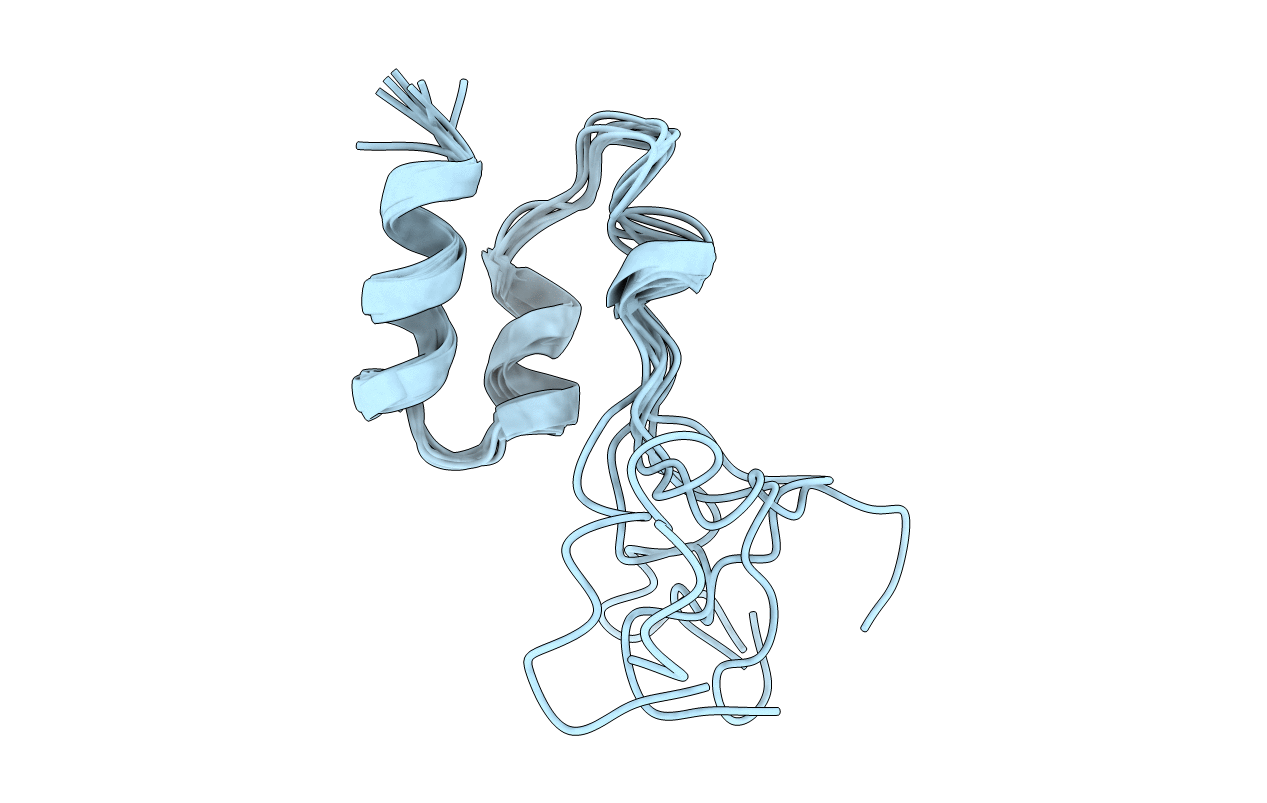
Deposition Date
1995-06-21
Release Date
1996-11-08
Last Version Date
2025-03-26
Entry Detail
PDB ID:
1MGX
Keywords:
Title:
COAGULATION FACTOR, MG(II), NMR, 7 STRUCTURES (BACKBONE ATOMS ONLY)
Biological Source:
Source Organism:
Homo sapiens (Taxon ID: 9606)
Method Details:
Experimental Method:
Conformers Submitted:
7


