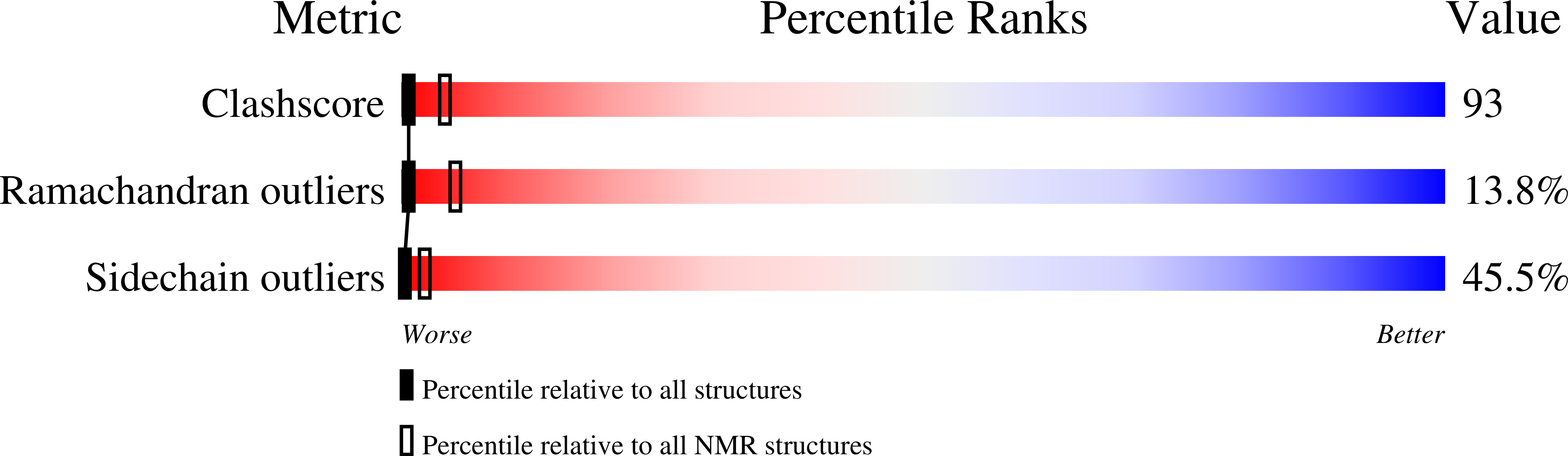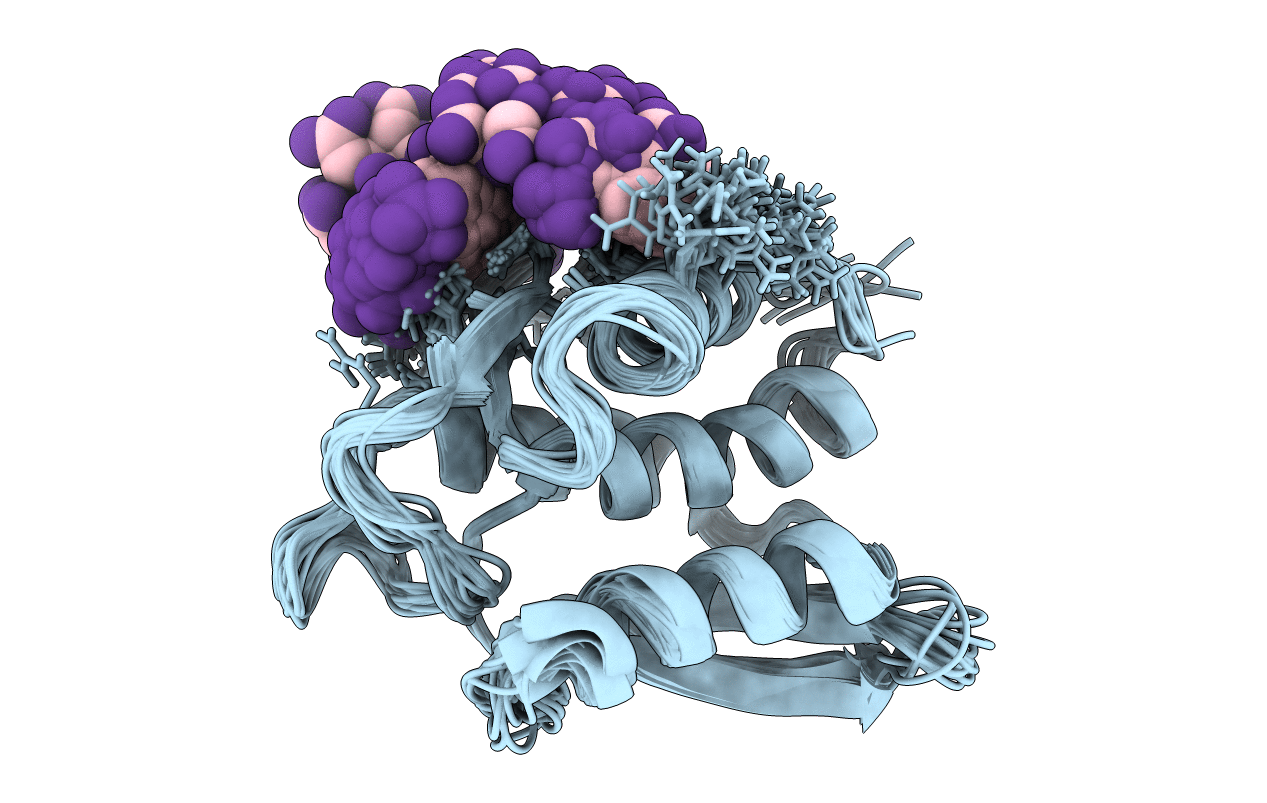
Deposition Date
2002-06-14
Release Date
2002-07-24
Last Version Date
2024-11-20
Entry Detail
PDB ID:
1M0V
Keywords:
Title:
NMR STRUCTURE OF THE TYPE III SECRETORY DOMAIN OF YERSINIA YOPH COMPLEXED WITH THE SKAP-HOM PHOSPHO-PEPTIDE N-acetyl-DEpYDDPF-NH2
Biological Source:
Source Organism(s):
Yersinia pseudotuberculosis (Taxon ID: 633)
Expression System(s):
Method Details:
Experimental Method:
Conformers Calculated:
360
Conformers Submitted:
20
Selection Criteria:
structures with the least restraint violations