Deposition Date
2002-05-28
Release Date
2002-11-27
Last Version Date
2024-11-06
Entry Detail
PDB ID:
1LVB
Keywords:
Title:
CATALYTICALLY INACTIVE TOBACCO ETCH VIRUS PROTEASE COMPLEXED WITH SUBSTRATE
Biological Source:
Source Organism:
Tobacco etch virus (Taxon ID: 12227)
Host Organism:
Method Details:
Experimental Method:
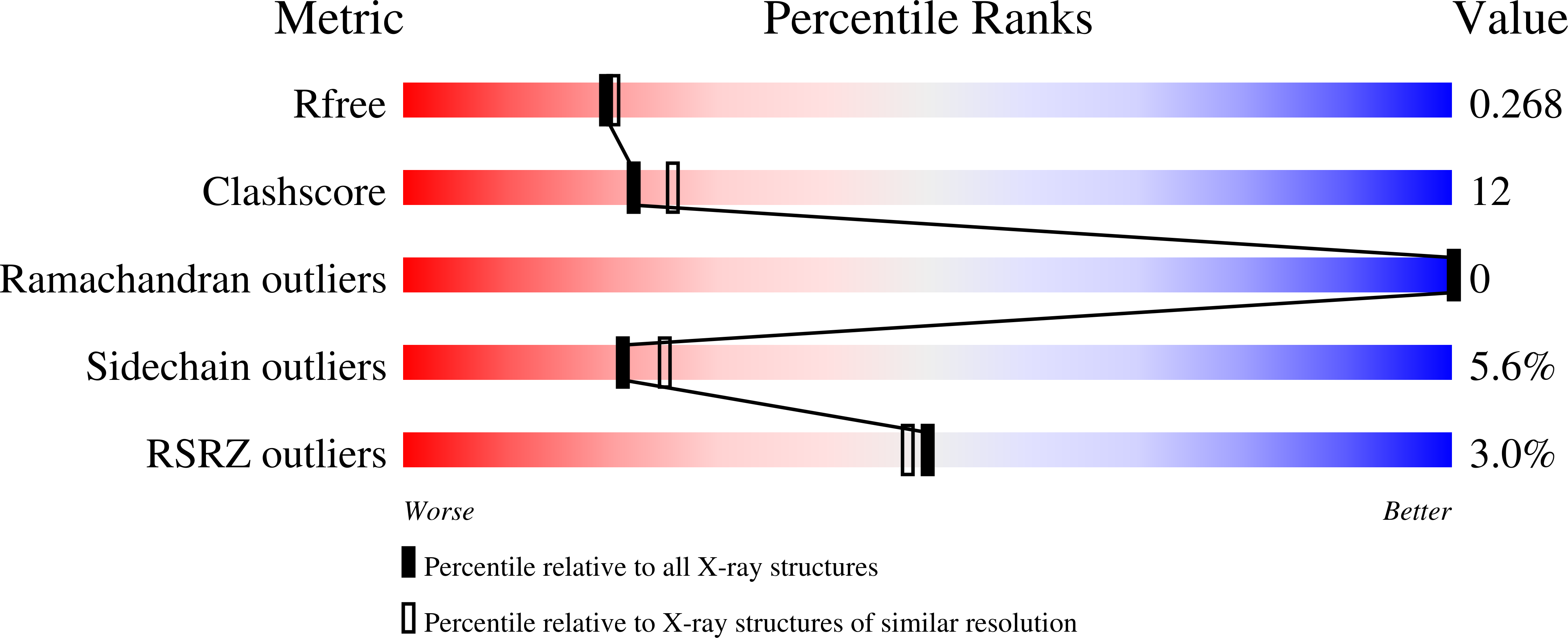
Resolution:
2.20 Å
R-Value Free:
0.26
R-Value Work:
0.23
Space Group:
P 42 21 2