Deposition Date
1995-02-09
Release Date
1996-01-01
Last Version Date
2024-10-23
Entry Detail
PDB ID:
1LSP
Keywords:
Title:
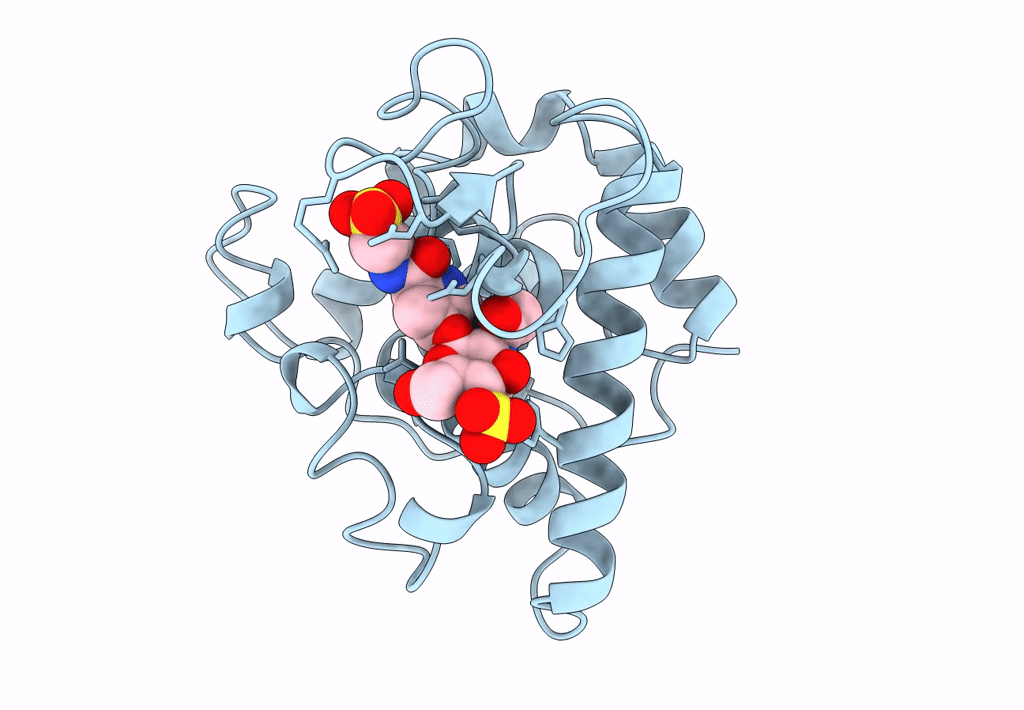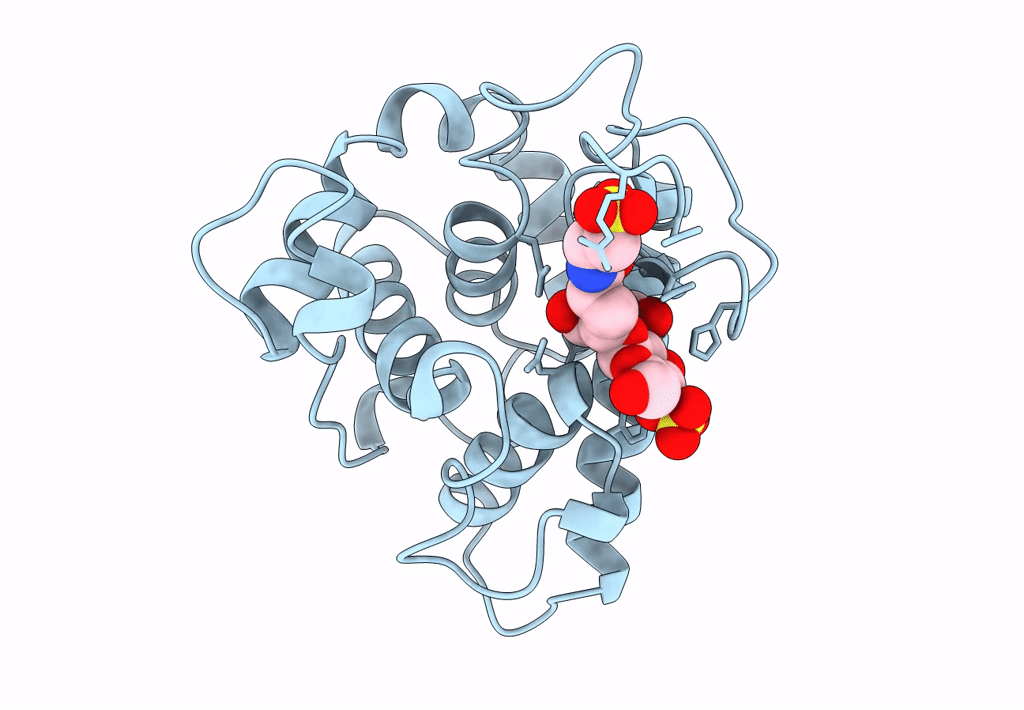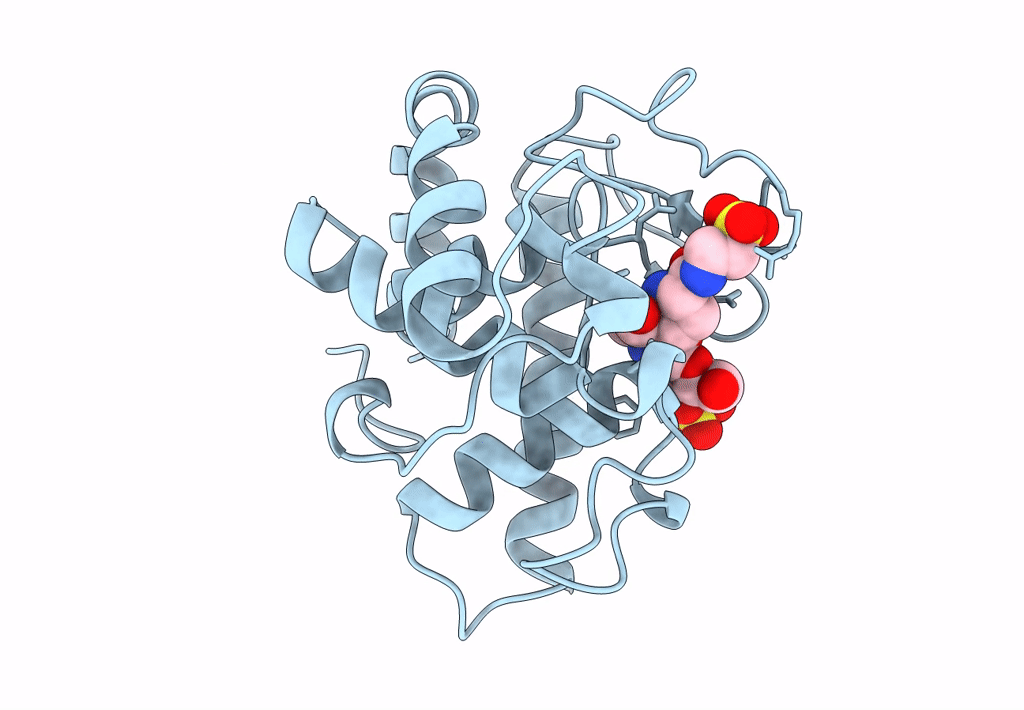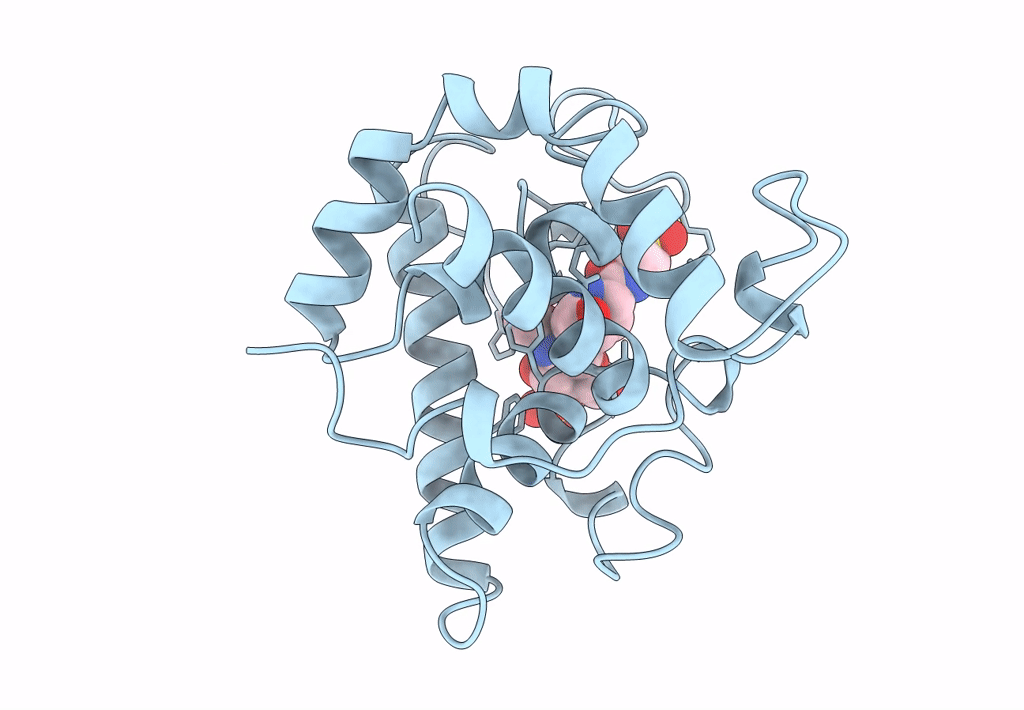
THE CRYSTAL STRUCTURE OF A BULGECIN-INHIBITED G-TYPE LYSOZYME FROM THE EGG-WHITE OF THE AUSTRALIAN BLACK SWAN. A COMPARISON OF THE BINDING OF BULGECIN TO THREE MURAMIDASES
Biological Source:
Source Organism(s):
Cygnus atratus (Taxon ID: 8868)
Method Details:
Experimental Method:
Resolution:
2.45 Å
R-Value Observed:
0.17
Space Group:
P 21 21 2


