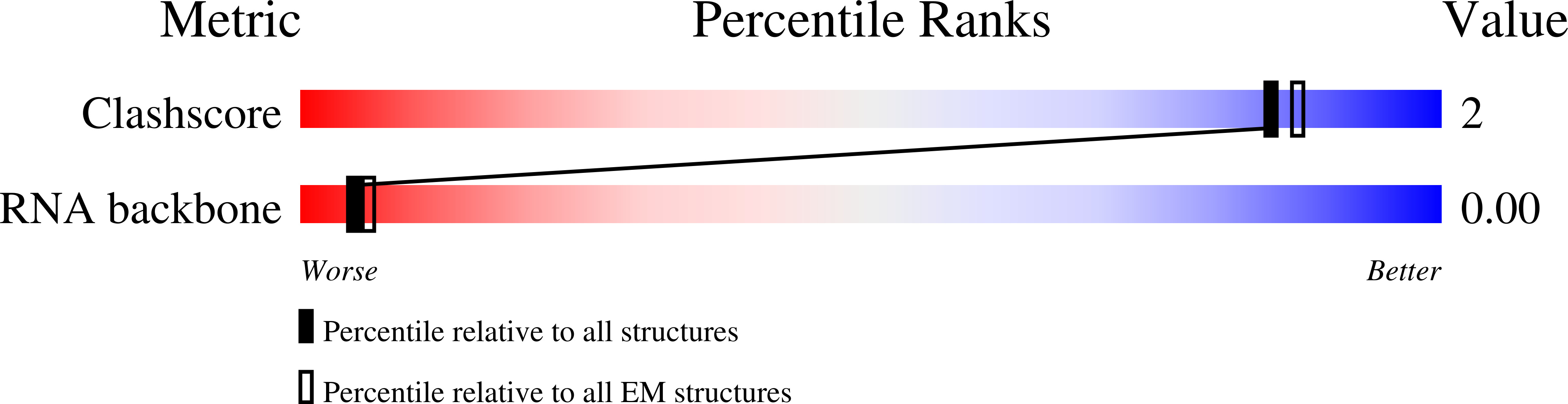
Deposition Date
2002-05-16
Release Date
2002-06-26
Last Version Date
2024-02-14
Entry Detail
PDB ID:
1LS2
Keywords:
Title:
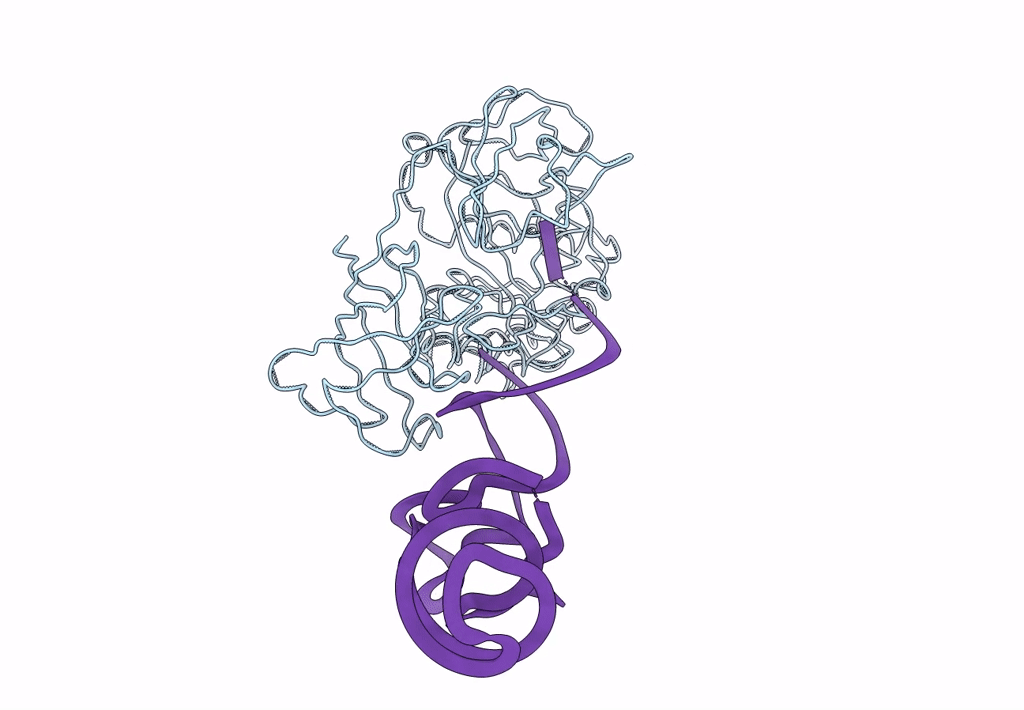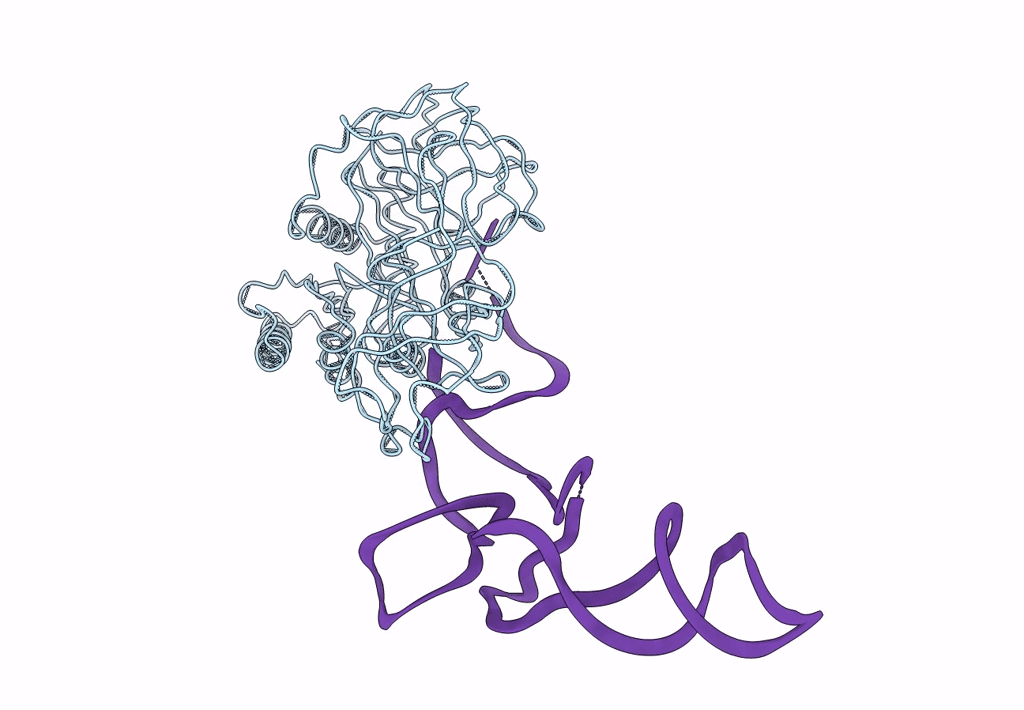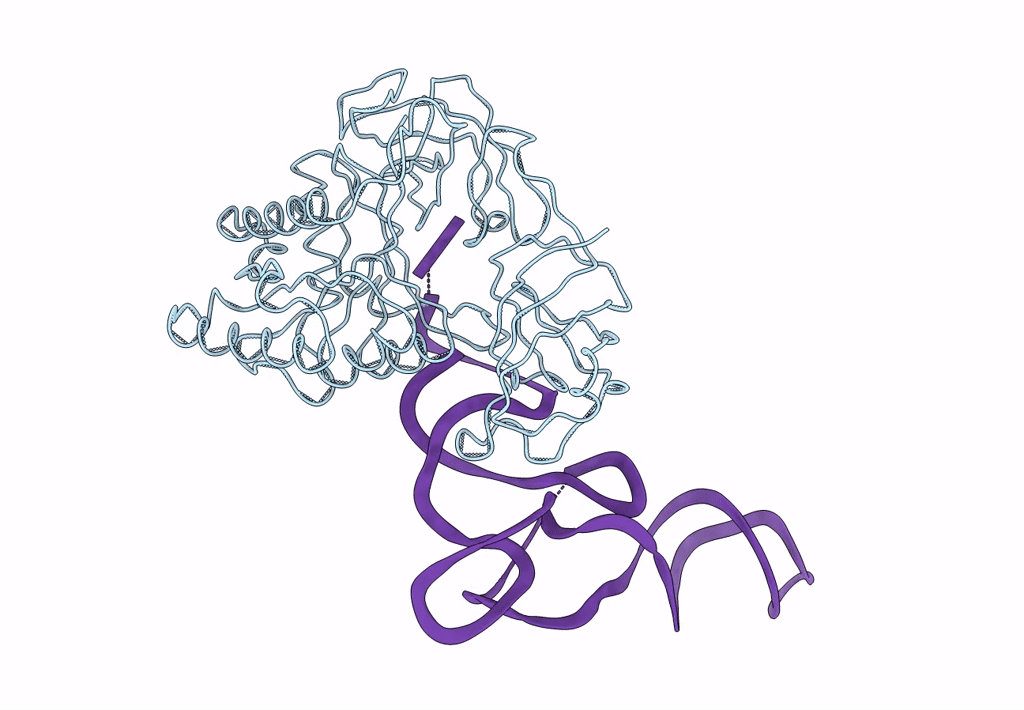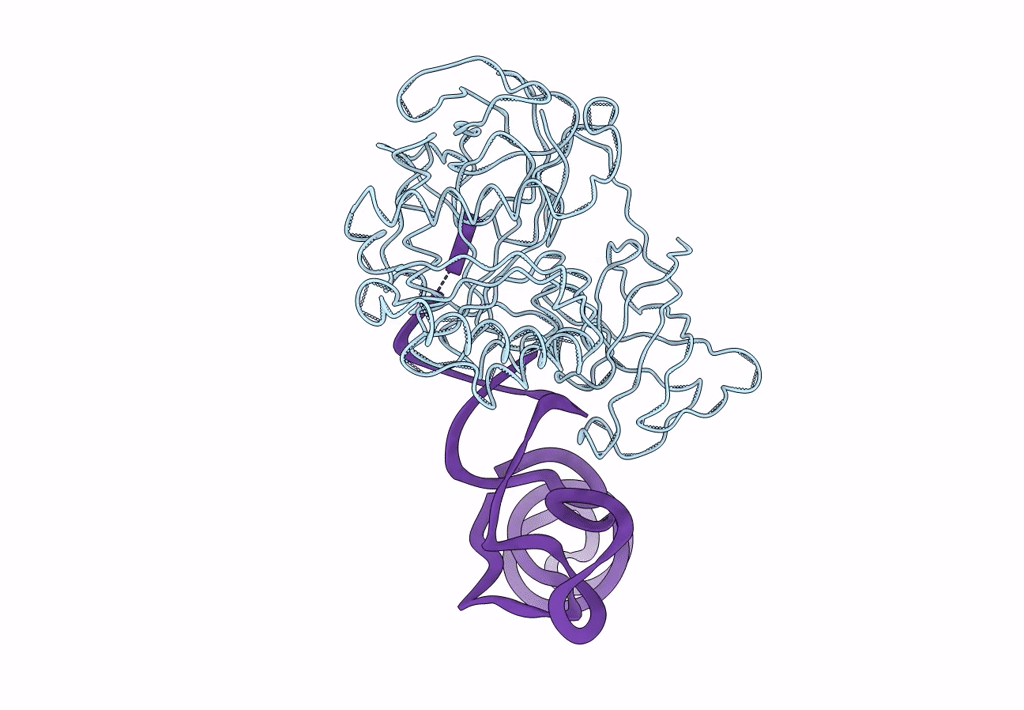
Fitting of EF-Tu and tRNA in the Low Resolution Cryo-EM Map of an EF-Tu Ternary Complex (GDP and Kirromycin) Bound to E. coli 70S Ribosome
Biological Source:
Source Organism(s):
Saccharomyces cerevisiae (Taxon ID: 4932)
Escherichia coli (Taxon ID: 562)
Escherichia coli (Taxon ID: 562)
Method Details:
Experimental Method:
Resolution:
16.80 Å
Aggregation State:
PARTICLE
Reconstruction Method:
SINGLE PARTICLE