Deposition Date
2002-04-05
Release Date
2003-04-08
Last Version Date
2023-08-16
Entry Detail
PDB ID:
1LC4
Keywords:
Title:
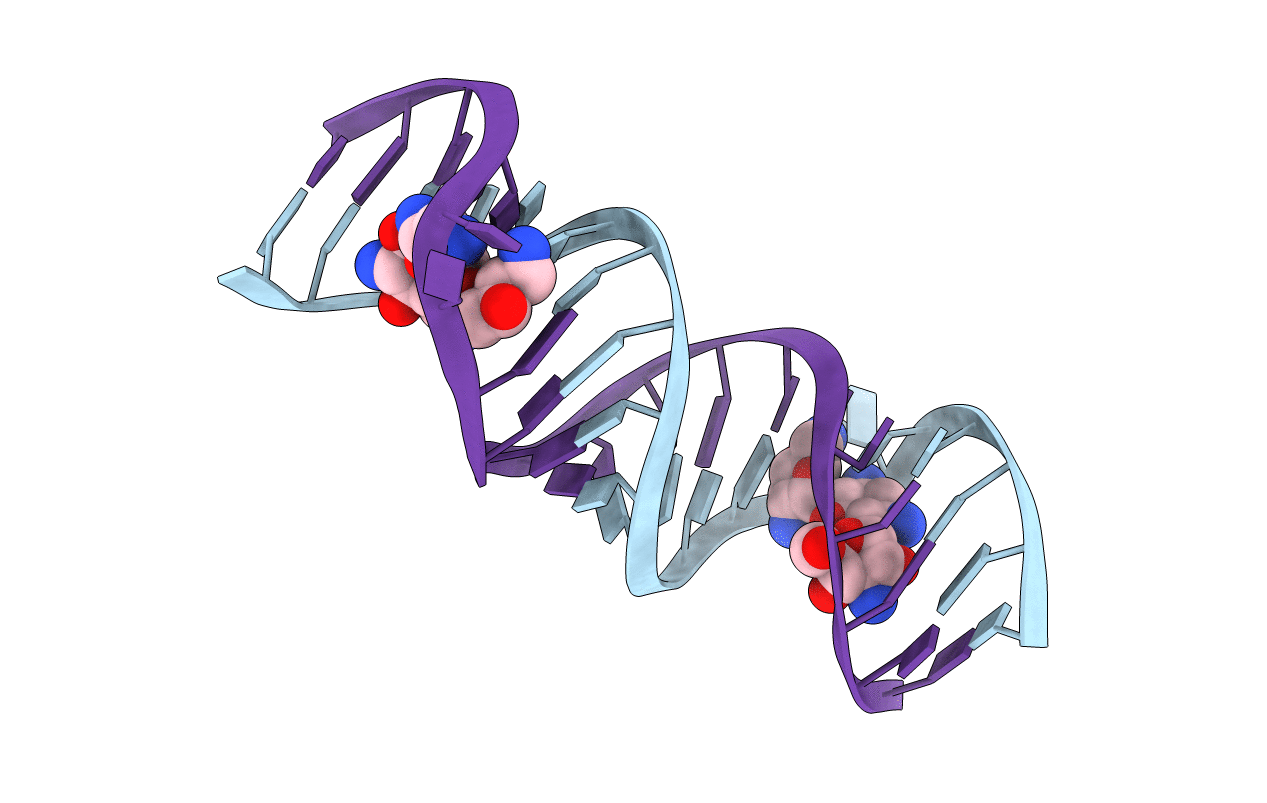
Crystal Structure of Tobramycin Bound to the Eubacterial 16S rRNA A Site
Method Details:
Experimental Method:
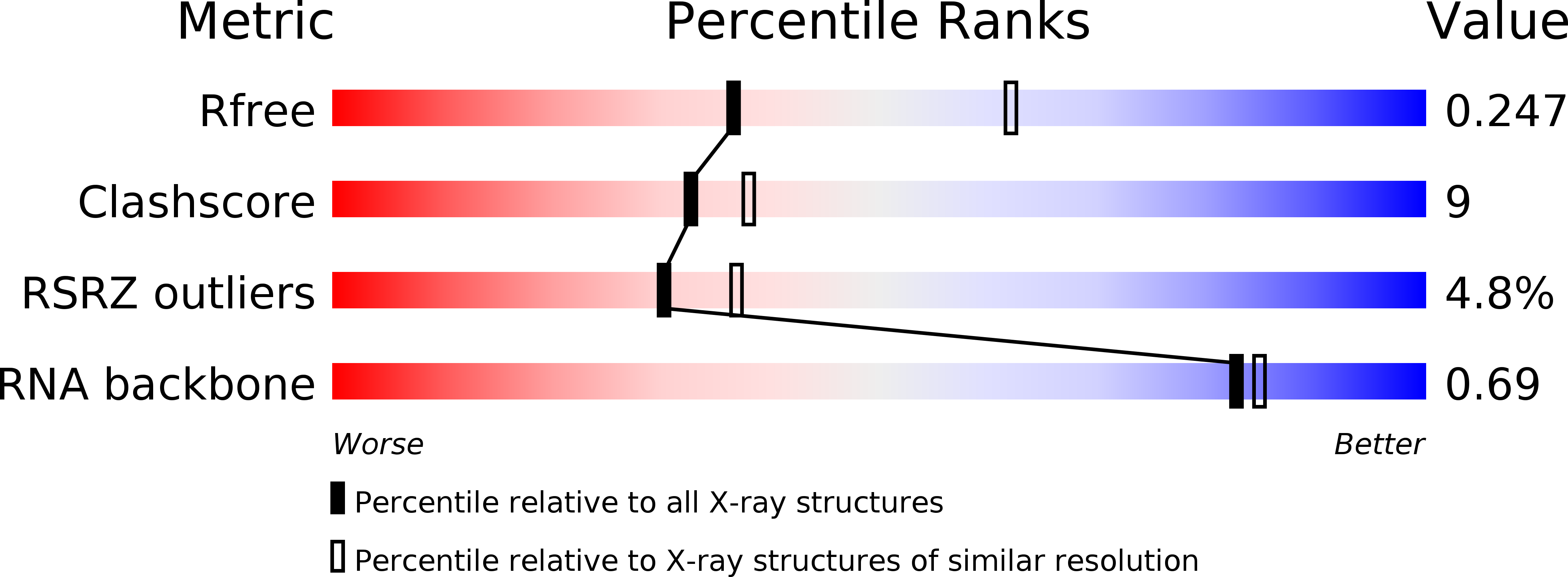
Resolution:
2.54 Å
R-Value Free:
0.26
R-Value Work:
0.21
Space Group:
P 1 21 1