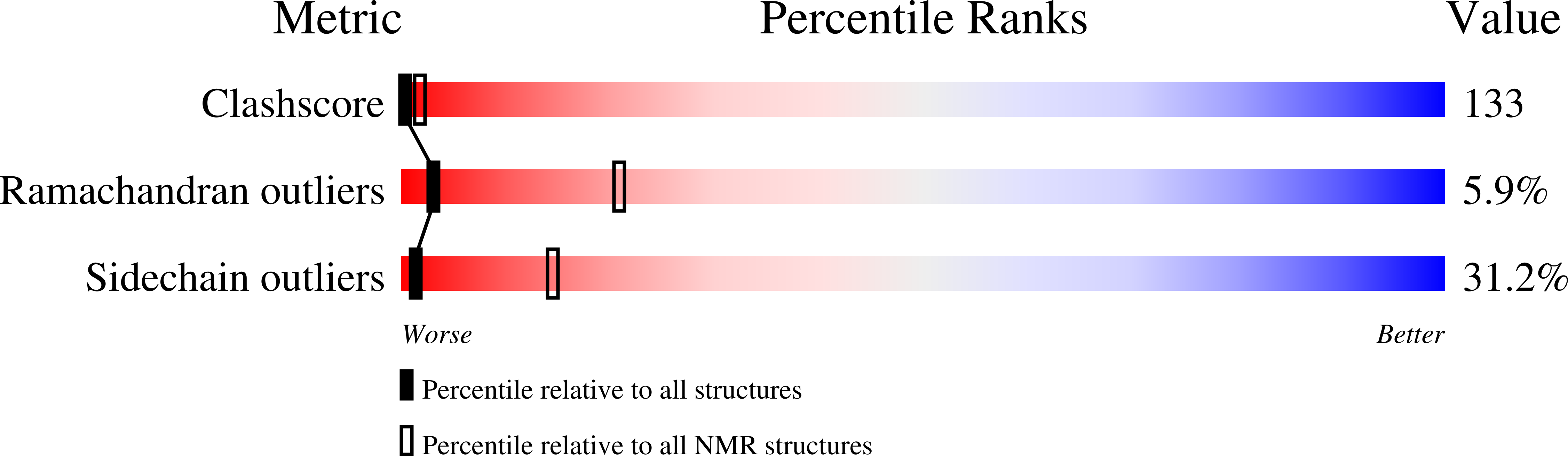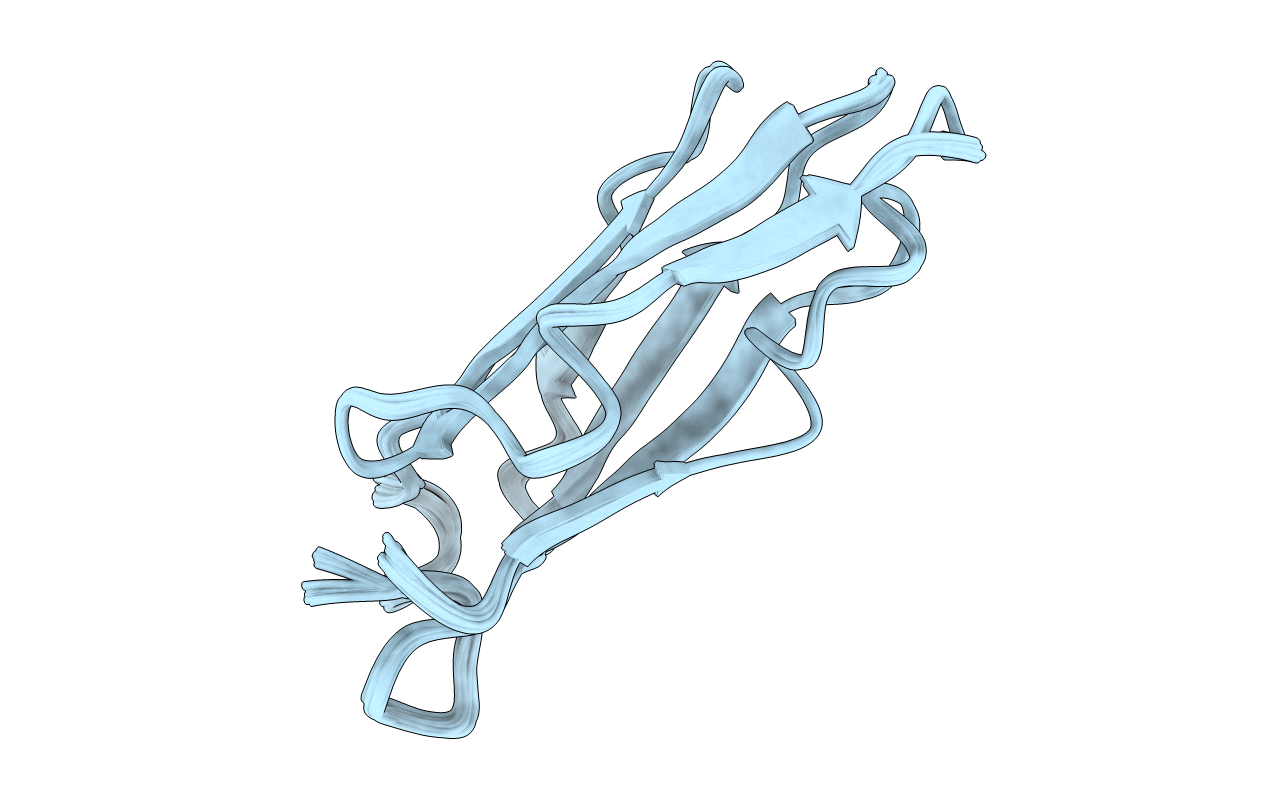
Deposition Date
1997-02-07
Release Date
1997-08-20
Last Version Date
2024-05-22
Entry Detail
PDB ID:
1KSR
Keywords:
Title:
THE REPEATING SEGMENTS OF THE F-ACTIN CROSS-LINKING GELATION FACTOR (ABP-120) HAVE AN IMMUNOGLOBULIN FOLD, NMR, 20 STRUCTURES
Biological Source:
Source Organism(s):
Dictyostelium discoideum (Taxon ID: 44689)
Expression System(s):
Method Details:
Experimental Method:
Conformers Calculated:
45
Conformers Submitted:
20
Selection Criteria:
NUMBER (0) OF RESIDUAL CONSTRAINS VIOLATION (THRESHOLDS: 0.45 A FOR NOES AND 10.0 DEGREE FOR ANGLES)