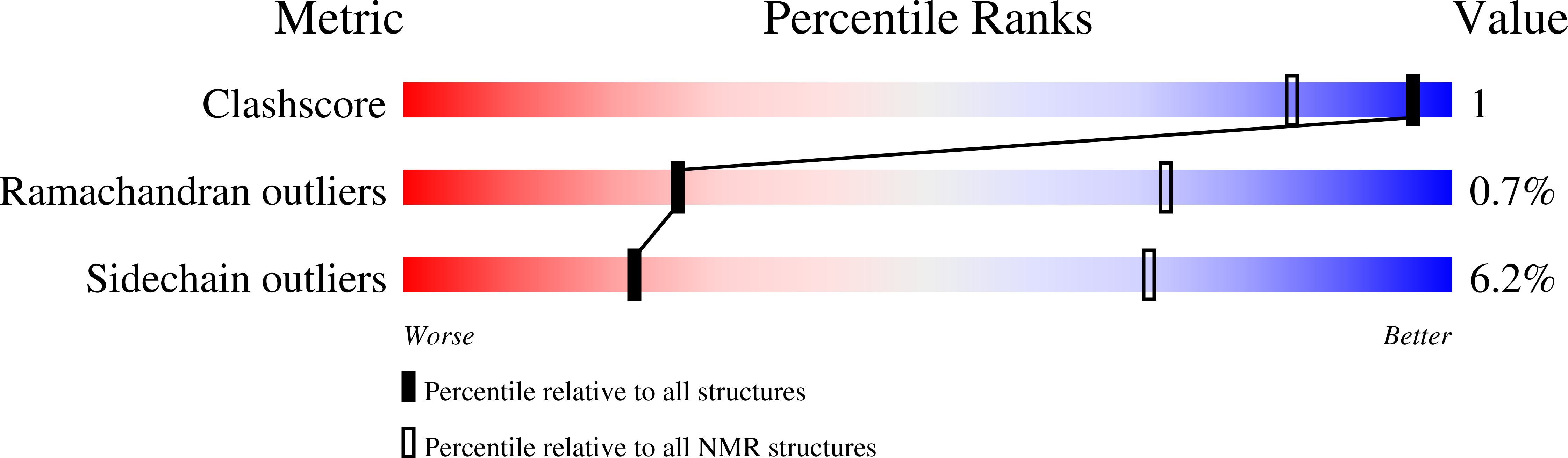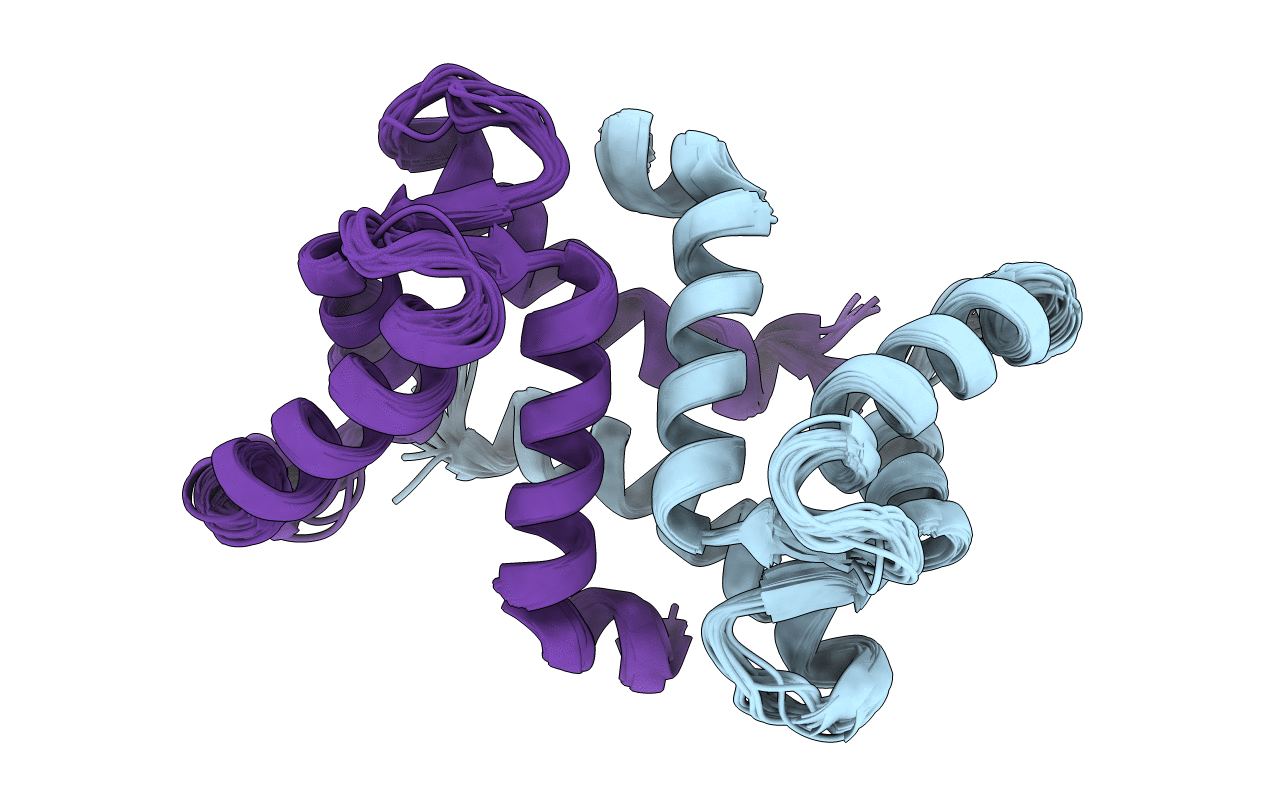
Deposition Date
2001-09-04
Release Date
2002-03-27
Last Version Date
2024-05-22
Entry Detail
PDB ID:
1JWD
Keywords:
Title:
Ca2+-induced Structural Changes in Calcyclin: High-resolution Solution Structure of Ca2+-bound Calcyclin.
Biological Source:
Source Organism(s):
Oryctolagus cuniculus (Taxon ID: 9986)
Expression System(s):
Method Details:
Experimental Method:
Conformers Calculated:
100
Conformers Submitted:
22
Selection Criteria:
The program Findfam was used to establish that the number of structures required to accurately represent the ensemble was less than 22 (the number selected to represent previous S100A6 ensembles). Structures were ordered by lowest restraint violations, then accepted if total molecular energy and each contributing term was within two standard deviations of the mean. The 22 structures with least restraint violations (energy penalty and magnitude of largest violation) all met these criteria.