Abstact
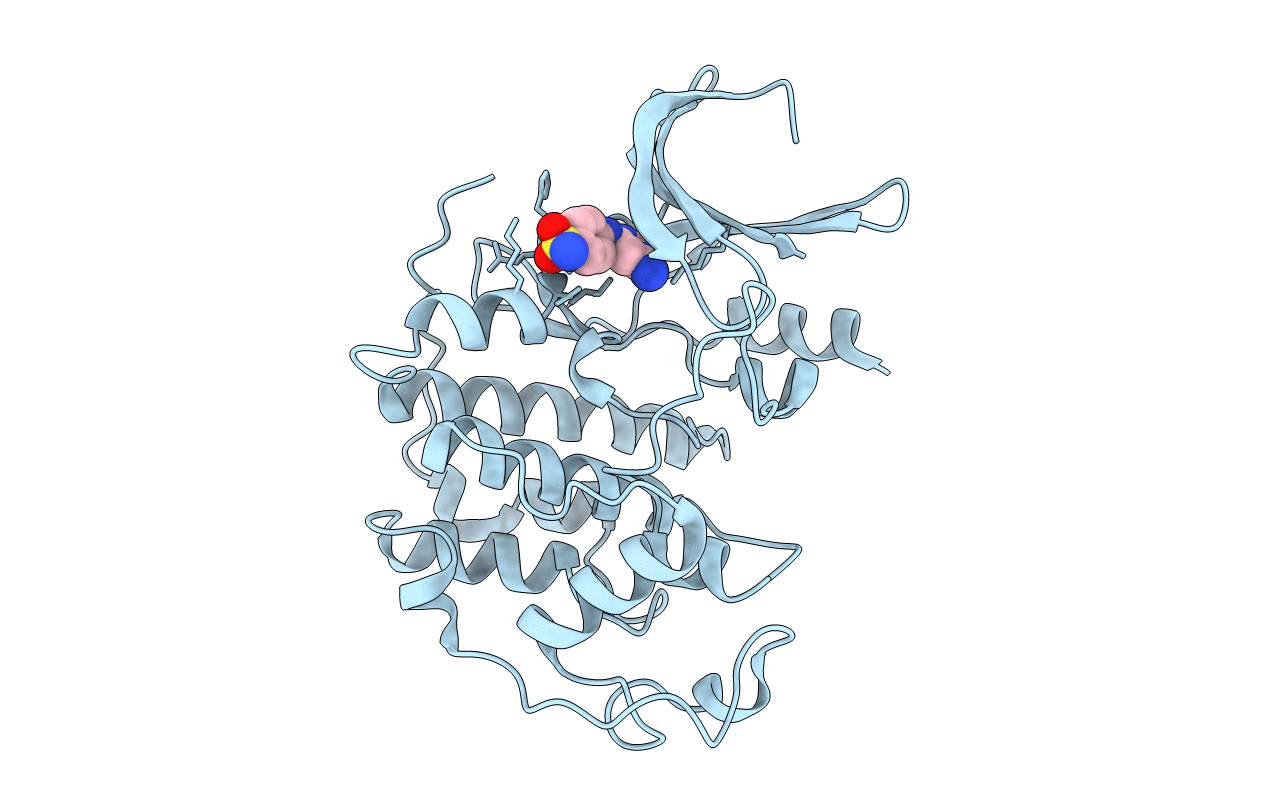
cdk2.cyclin E and cdk5.p25 are two members of the cyclin-dependent kinase family that are potential therapeutic targets for oncology and Alzheimer's disease, respectively. In this study we have investigated the mechanism for these enzymes. Kinases catalyze the transfer of phosphate from ATP to a protein acceptor, thus utilizing two substrates, ATP and the target protein. For a two-substrate reaction, possible kinetic mechanisms include: ping-pong, sequential random, or sequential ordered. To determine the kinetic mechanism of cdk2.GST-cyclin E and cdk5.GST-p25, kinase activity was measured in experiments in which concentrations of peptide and ATP substrates were varied in the presence of dead-end inhibitors. A peptide identical to the peptide substrate, but with a substitution of valine for the phosphoacceptor threonine, competed with substrate with a K(i) value of 0.6 mm. An aminopyrimidine, PNU 112455A, was identified in a screen for inhibitors of cdk2. Nonlinear least squares and Lineweaver-Burk analyses demonstrated that the inhibitor PNU 112455A was competitive with ATP with a K(i) value of 2 microm. In addition, a co-crystal of PNU 112455A with cdk2 showed that the inhibitor binds in the ATP binding pocket of the enzyme. Analysis of the inhibitor data demonstrated that both kinases use a sequential random mechanism, in which either ATP or peptide may bind first to the enzyme active site. For both kinases, the binding of the second substrate was shown to be anticooperative, in that the binding of the first substrate decreases the affinity of the second substrate. For cdk2.GST-cyclin E the kinetic parameters were determined to be K(m, ATP) = 3.6 +/- 1.0 microm, K(m, peptide) = 4.6 +/- 1.4 microm, and the anticooperativity factor, alpha = 130 +/- 44. For cdk5.GST-p25, the K(m, ATP) = 3.2 +/- 0.7 microm, K(m, peptide) = 1.6 +/- 0.3 microm, and alpha = 7.2 +/- 1.8.