Deposition Date
2001-07-27
Release Date
2001-11-16
Last Version Date
2024-05-22
Entry Detail
PDB ID:
1JO6
Keywords:
Title:
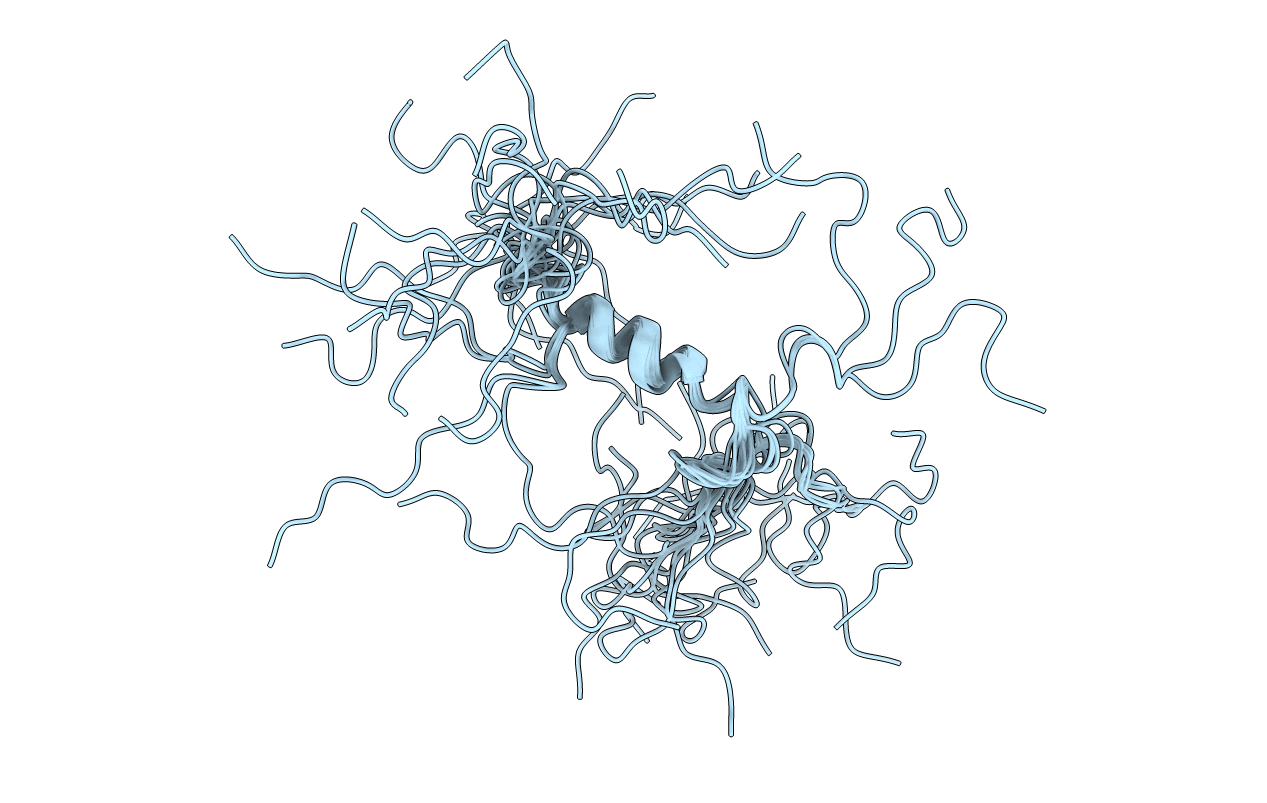
Solution structure of the cytoplasmic N-terminus of the BK beta-subunit KCNMB2
Method Details:
Experimental Method:
Conformers Calculated:
30
Conformers Submitted:
24
Selection Criteria:
structures with the least restraint violations,target function


