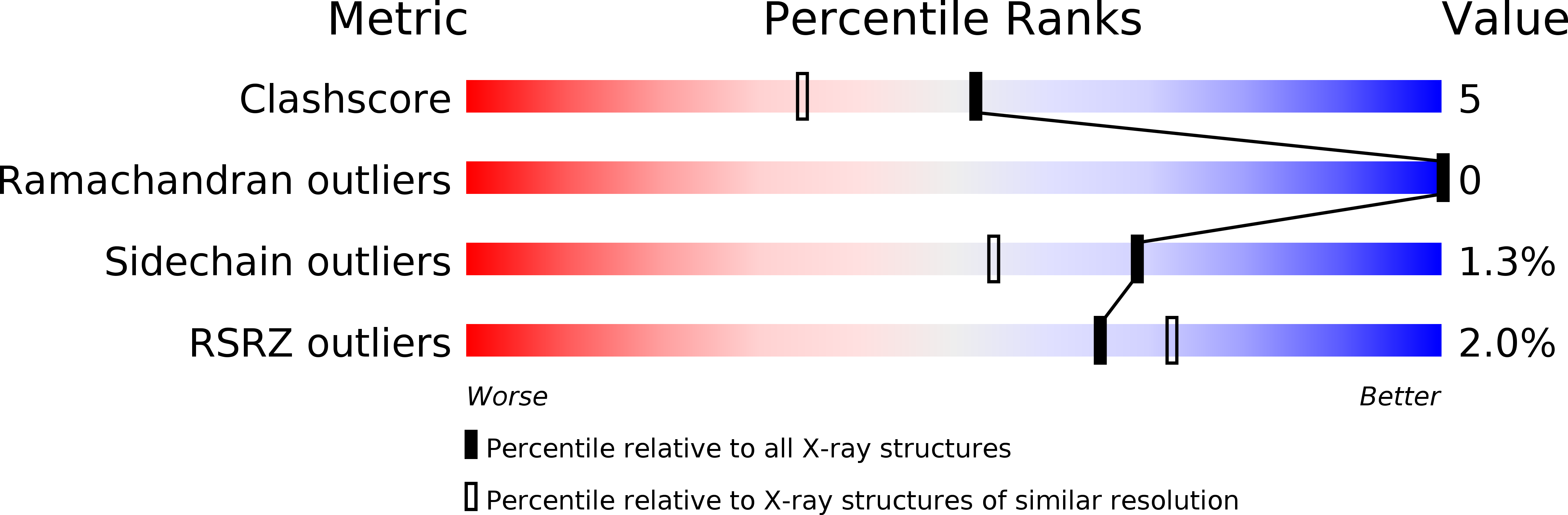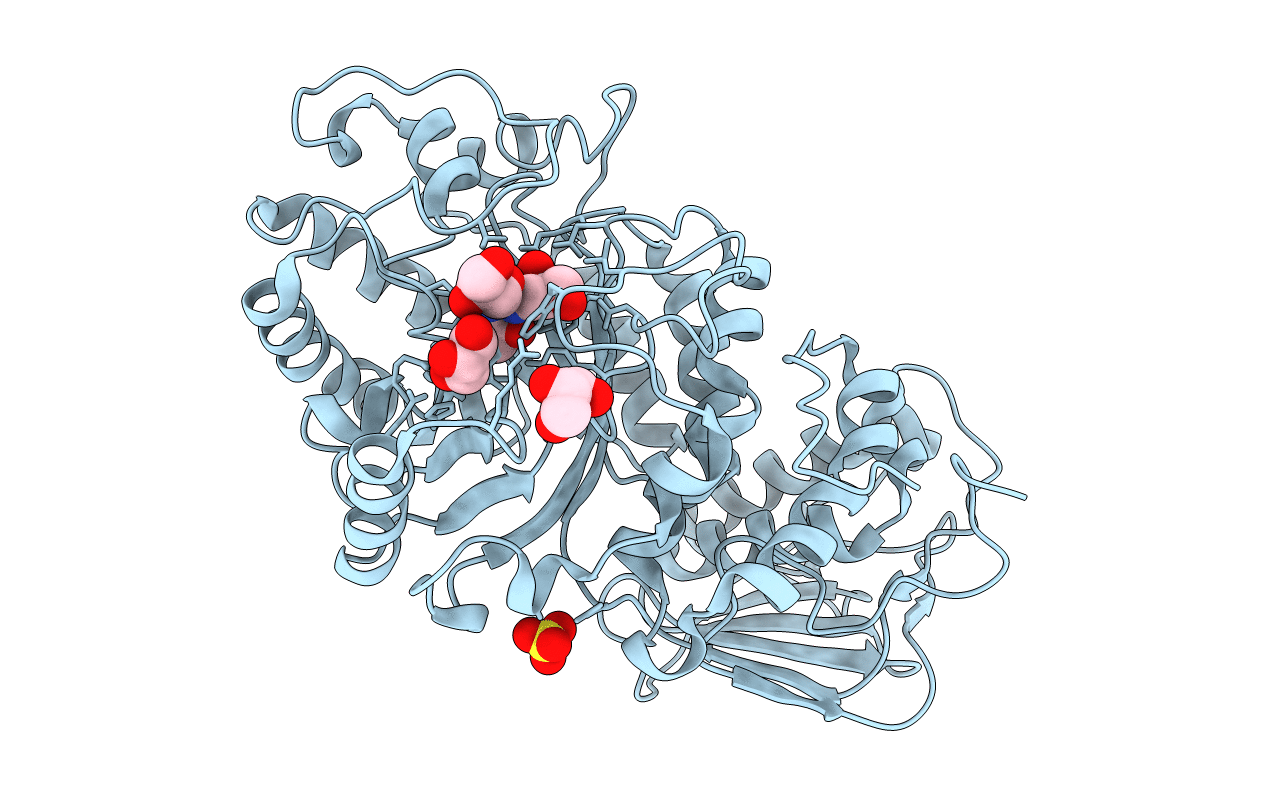
Deposition Date
2001-05-30
Release Date
2001-11-21
Last Version Date
2024-10-30
Entry Detail
PDB ID:
1JAK
Keywords:
Title:
Streptomyces plicatus beta-N-acetylhexosaminidase in Complex with (2R,3R,4S,5R)-2-acetamido-3,4-dihydroxy-5-hydroxymethyl-piperidinium chloride (IFG)
Biological Source:
Source Organism:
Streptomyces plicatus (Taxon ID: 1922)
Host Organism:
Method Details:
Experimental Method:
Resolution:
1.75 Å
R-Value Free:
0.19
R-Value Work:
0.17
R-Value Observed:
0.17
Space Group:
P 61 2 2