Deposition Date
2001-10-22
Release Date
2001-12-05
Last Version Date
2024-10-16
Entry Detail
PDB ID:
1J4Q
Keywords:
Title:
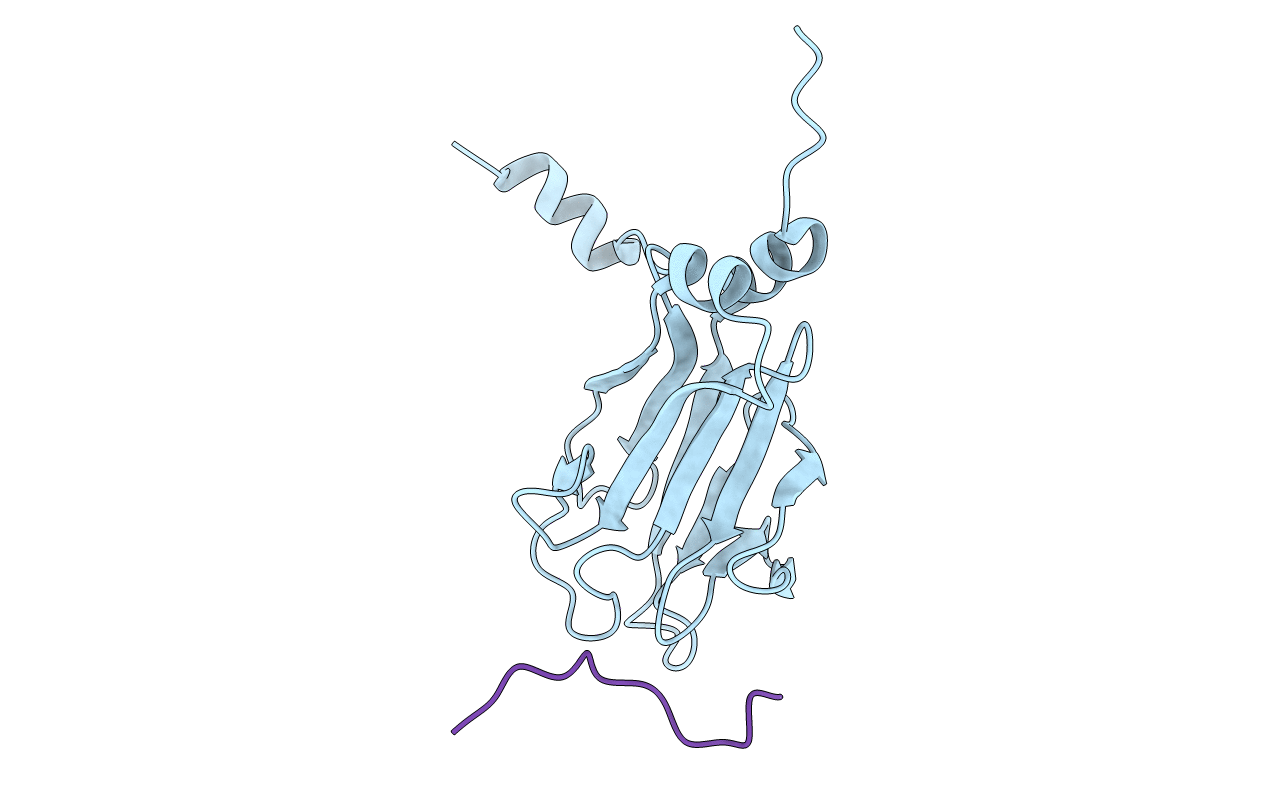
NMR STRUCTURE OF THE FHA1 DOMAIN OF RAD53 IN COMPLEX WITH A RAD9-DERIVED PHOSPHOTHREONINE (AT T192) PEPTIDE
Biological Source:
Source Organism(s):
Saccharomyces cerevisiae (Taxon ID: 4932)
Expression System(s):
Method Details:
Experimental Method:
Conformers Submitted:
1


