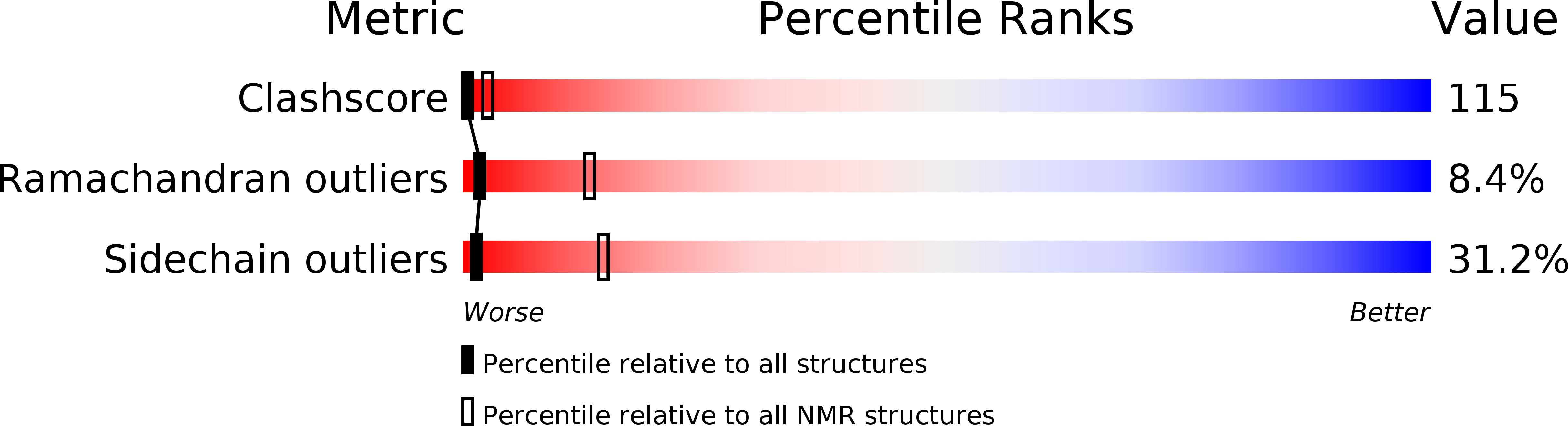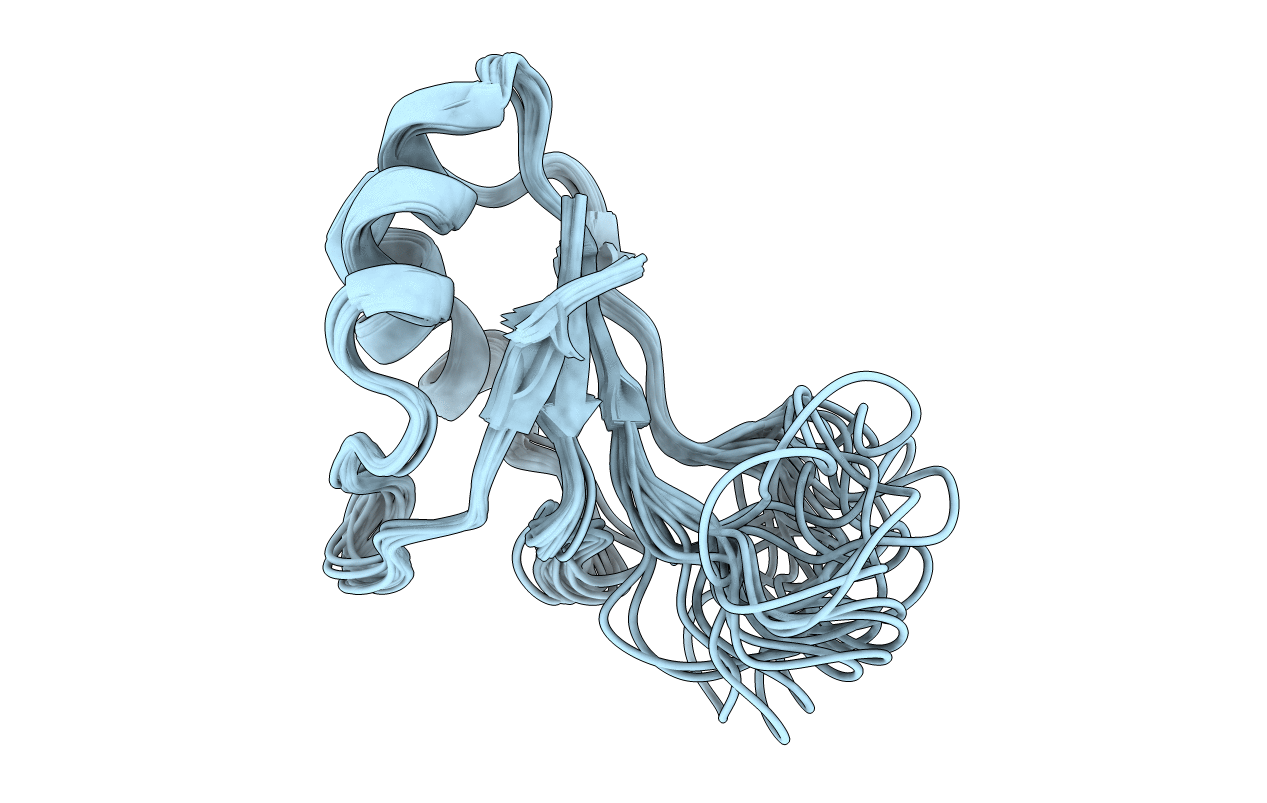
Deposition Date
2001-08-01
Release Date
2002-08-07
Last Version Date
2023-12-27
Entry Detail
PDB ID:
1IQT
Keywords:
Title:
Solution structure of the C-terminal RNA-binding domain of heterogeneous nuclear ribonucleoprotein D0 (AUF1)
Biological Source:
Source Organism(s):
Homo sapiens (Taxon ID: 9606)
Expression System(s):
Method Details:
Experimental Method:
Conformers Calculated:
200
Conformers Submitted:
20
Selection Criteria:
structures with the lowest energy