Deposition Date
2001-04-30
Release Date
2001-07-11
Last Version Date
2024-10-30
Entry Detail
PDB ID:
1IJX
Keywords:
Title:
CRYSTAL STRUCTURE OF THE CYSTEINE-RICH DOMAIN OF SECRETED FRIZZLED-RELATED PROTEIN 3 (SFRP-3;FZB)
Biological Source:
Source Organism:
Mus musculus (Taxon ID: 10090)
Host Organism:
Method Details:
Experimental Method:
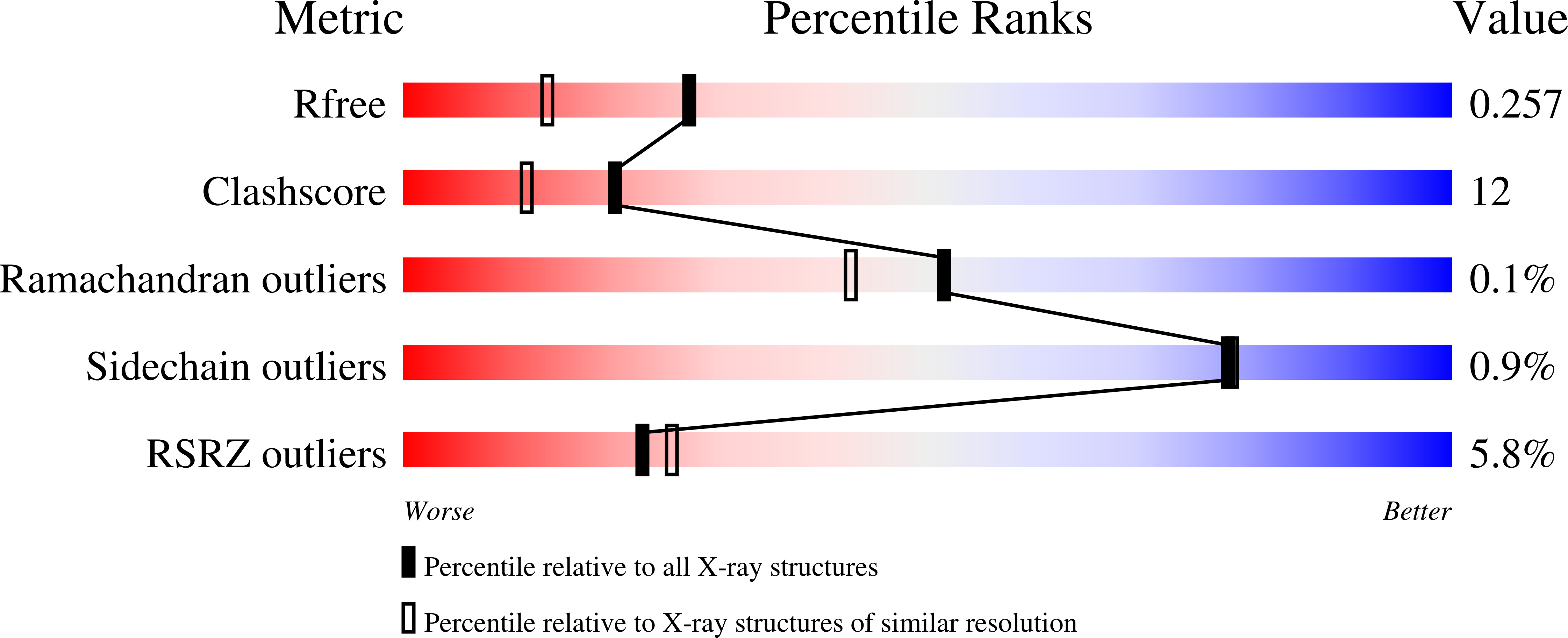
Resolution:
1.90 Å
R-Value Free:
0.25
R-Value Work:
0.22
Space Group:
P 1 21 1