Deposition Date
2001-04-25
Release Date
2003-02-11
Last Version Date
2024-03-13
Entry Detail
PDB ID:
1IJ6
Keywords:
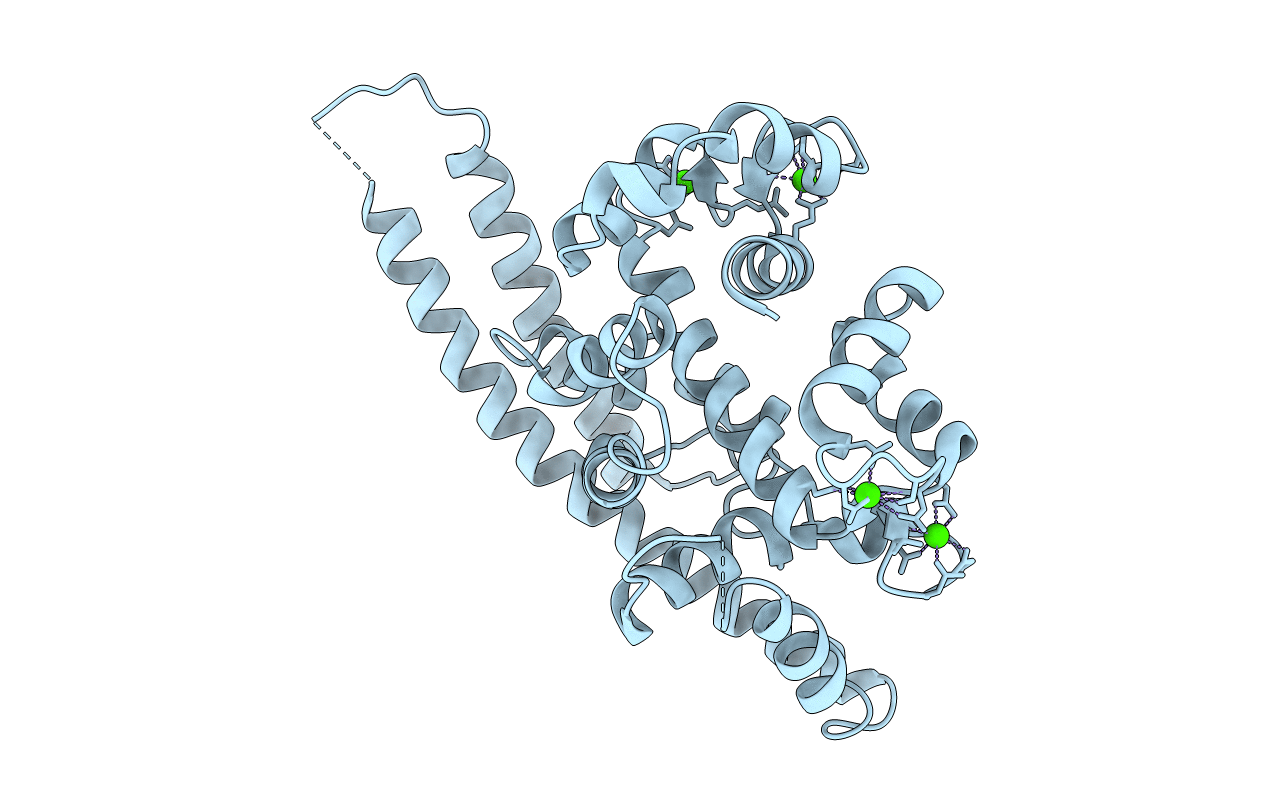
Title:
CA2+-BOUND STRUCTURE OF MULTIDOMAIN EF-HAND PROTEIN, CBP40, FROM TRUE SLIME MOLD
Biological Source:
Source Organism(s):
Physarum polycephalum (Taxon ID: 5791)
Expression System(s):
Method Details:
Experimental Method:
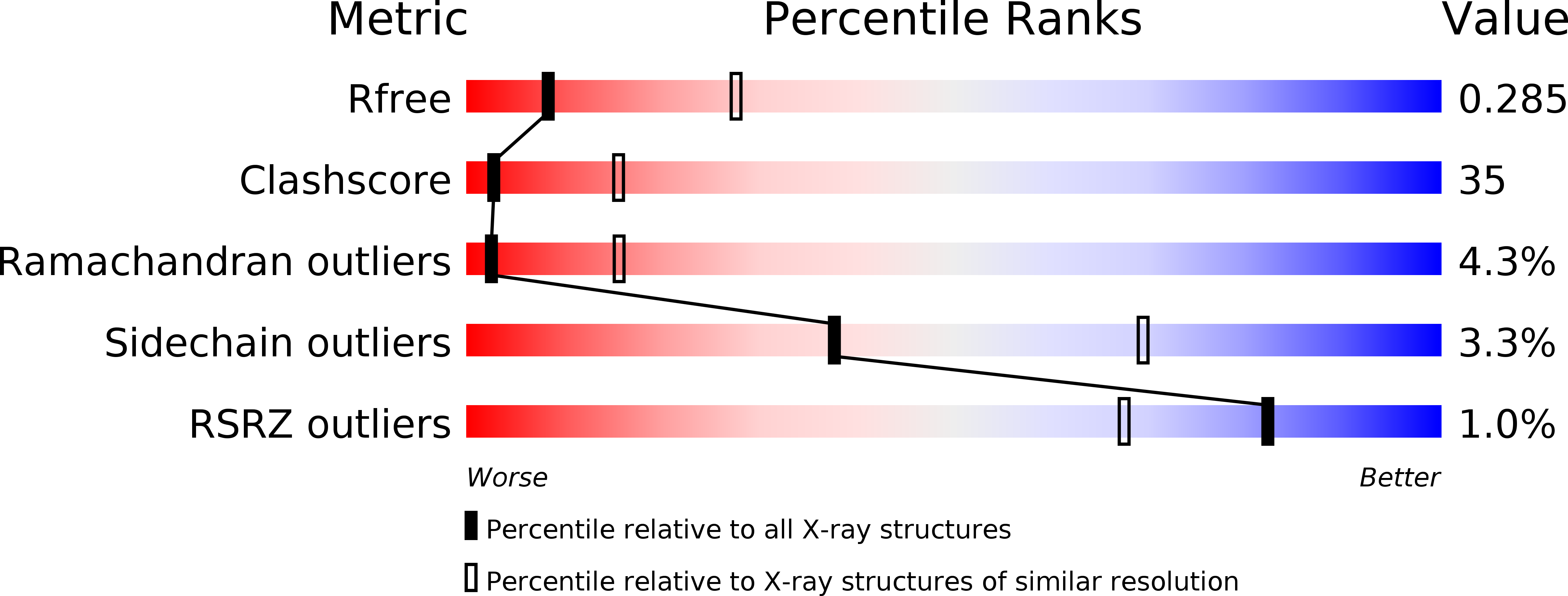
Resolution:
3.10 Å
R-Value Free:
0.29
R-Value Work:
0.24
Space Group:
P 32 2 1