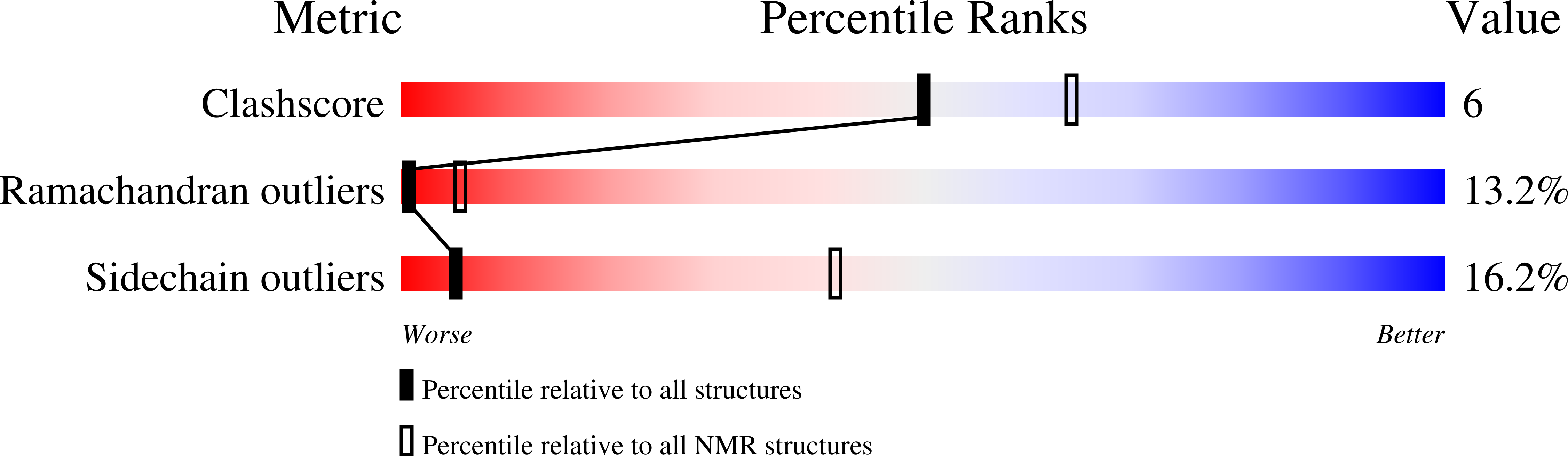Deposition Date
1994-12-16
Release Date
1995-07-10
Last Version Date
2024-10-09
Entry Detail
PDB ID:
1ICA
Keywords:
Title:
REFINED THREE-DIMENSIONAL STRUCTURE OF INSECT DEFENSIN A
Biological Source:
Source Organism(s):
Protophormia terraenovae (Taxon ID: 34676)
Method Details:
Experimental Method:
Conformers Submitted:
10