Deposition Date
2003-03-14
Release Date
2004-03-30
Last Version Date
2024-11-13
Entry Detail
PDB ID:
1HL7
Keywords:
Title:
Gamma lactamase from an Aureobacterium species in complex with 3a,4,7,7a-tetrahydro-benzo [1,3] dioxol-2-one
Biological Source:
Source Organism(s):
MICROBACTERIUM SP. (Taxon ID: 51671)
Expression System(s):
Method Details:
Experimental Method:
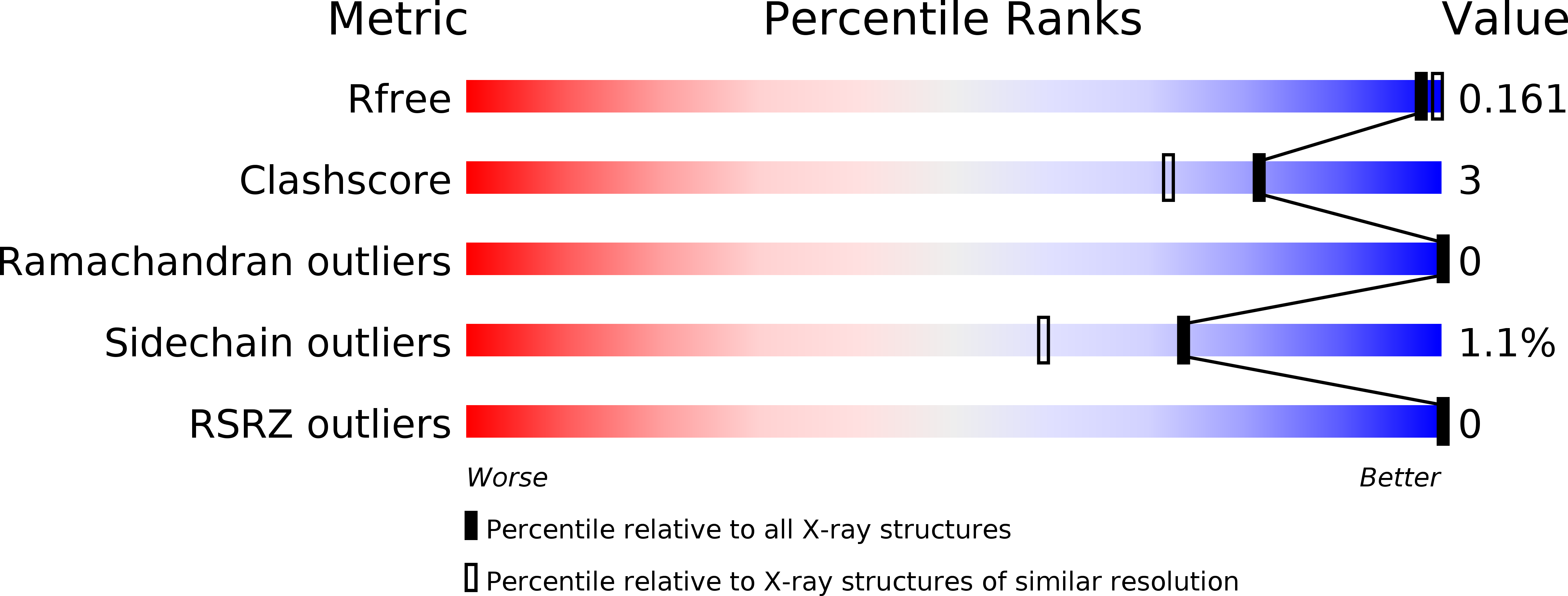
Resolution:
1.73 Å
R-Value Free:
0.16
R-Value Work:
0.15
Space Group:
F 2 3