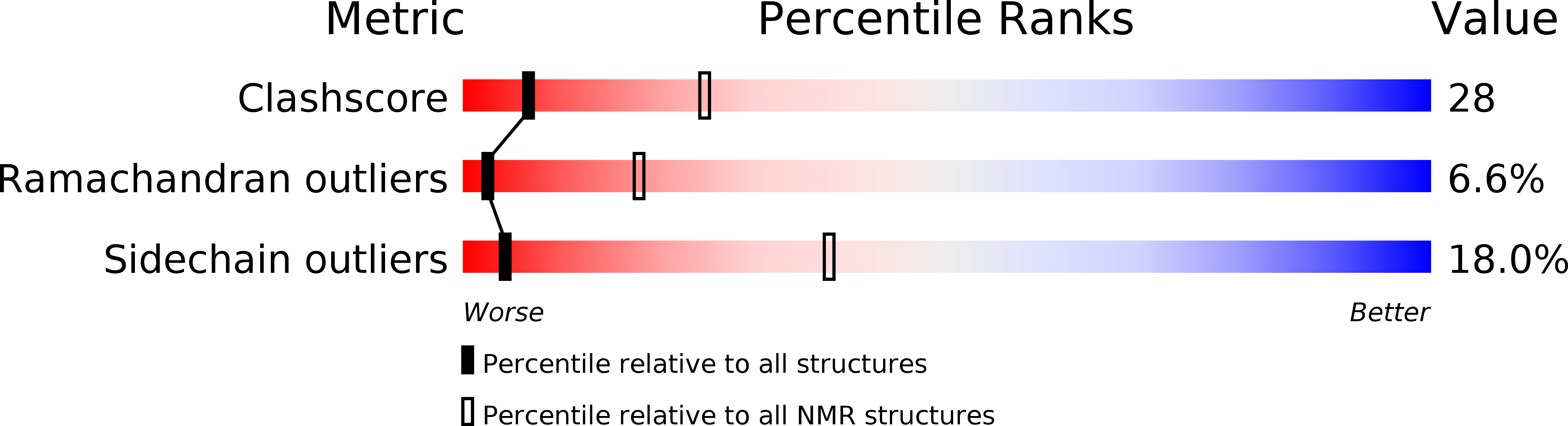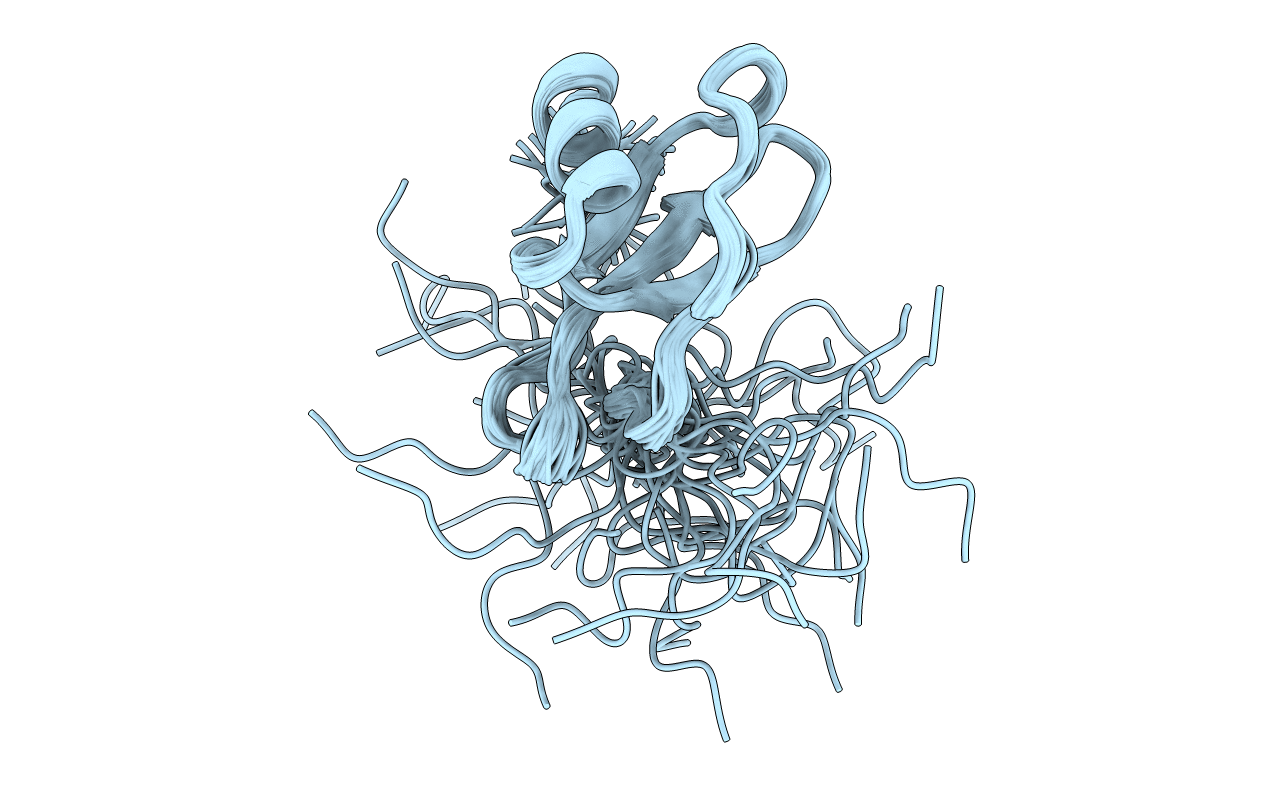
Deposition Date
2000-12-07
Release Date
2001-01-07
Last Version Date
2024-10-23
Entry Detail
PDB ID:
1HFN
Keywords:
Title:
NMR solution structures of vMIP-II 1-71 from Kaposi's sarcoma-associated herpesvirus.
Biological Source:
Source Organism(s):
HUMAN HERPESVIRUS 8 (Taxon ID: 37296)
Method Details:
Experimental Method:
Conformers Calculated:
38
Conformers Submitted:
38
Selection Criteria:
LEAST RESTRAINT VIOLATION