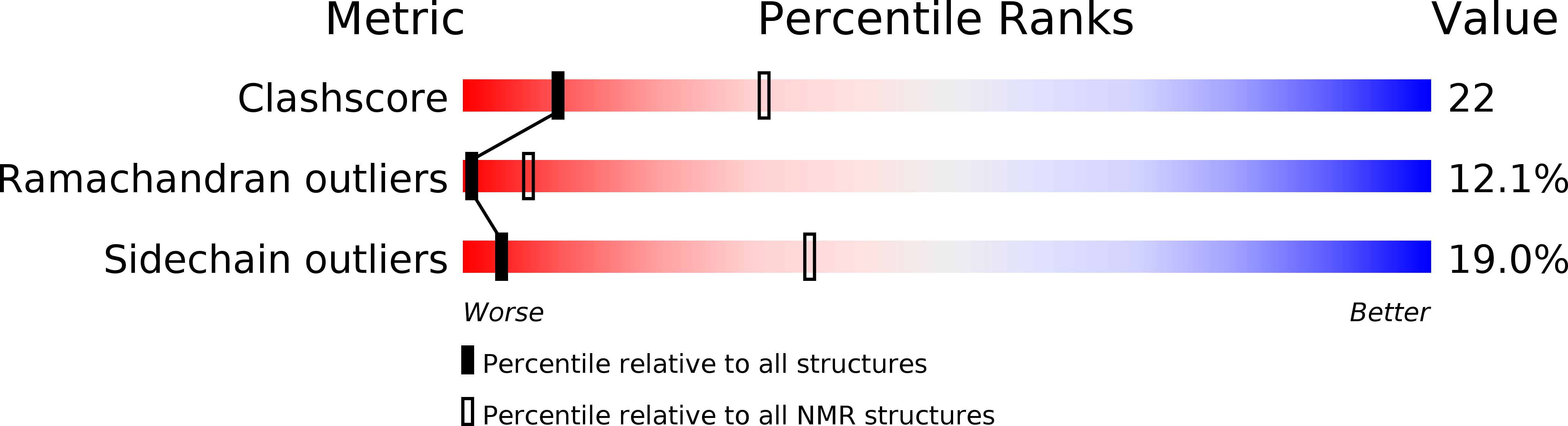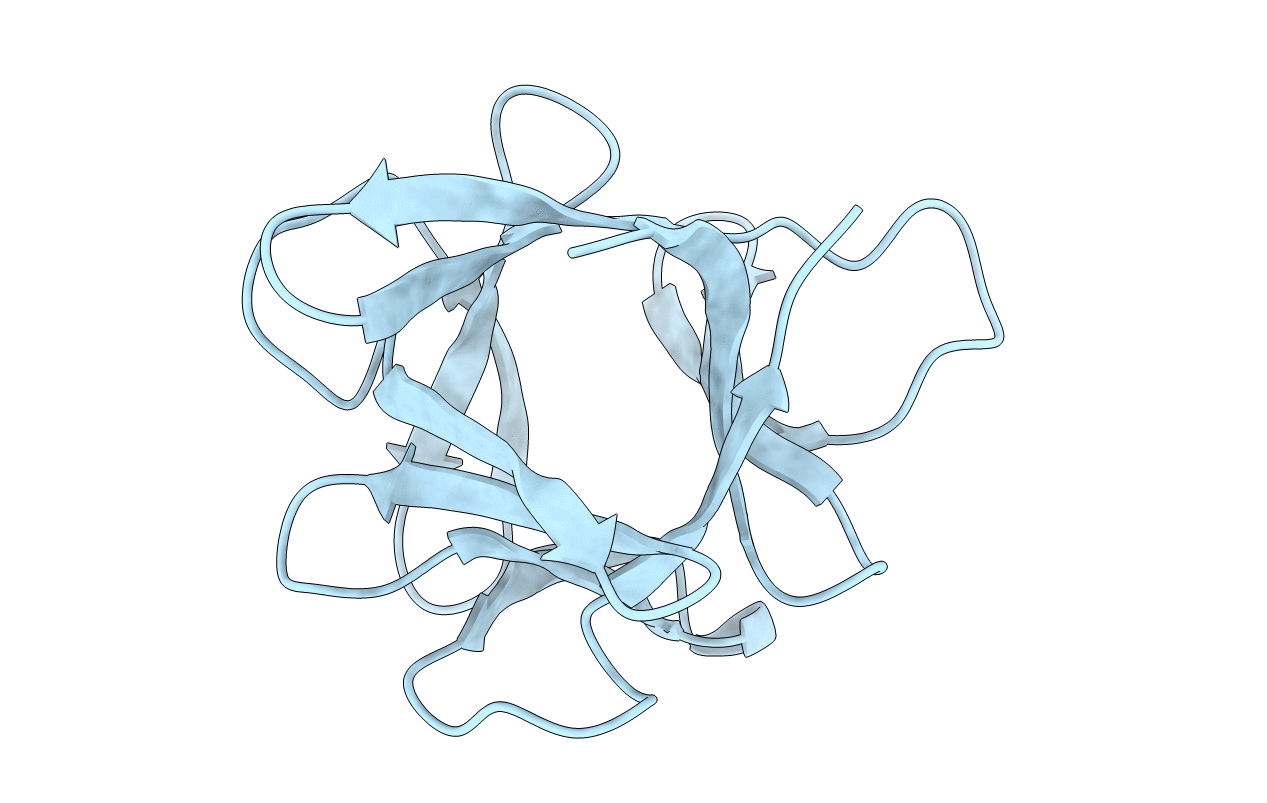
Deposition Date
1994-05-03
Release Date
1994-10-15
Last Version Date
2024-05-01
Entry Detail
PDB ID:
1HCD
Keywords:
Title:
STRUCTURE OF HISACTOPHILIN IS SIMILAR TO INTERLEUKIN-1 BETA AND FIBROBLAST GROWTH FACTOR
Biological Source:
Source Organism(s):
Dictyostelium discoideum (Taxon ID: 44689)
Method Details:
Experimental Method:
Conformers Submitted:
1