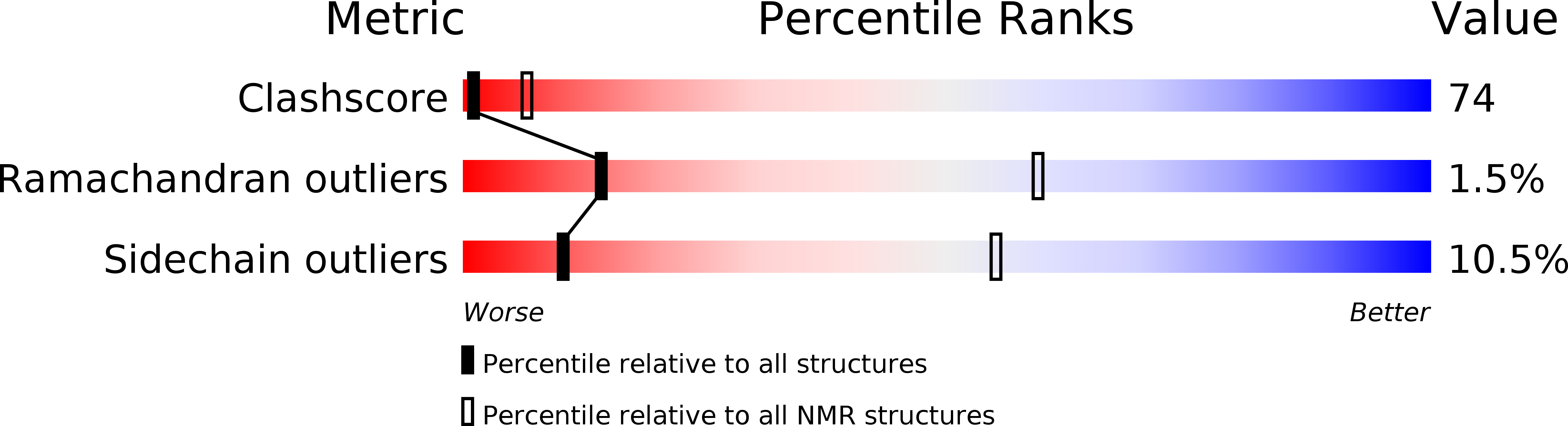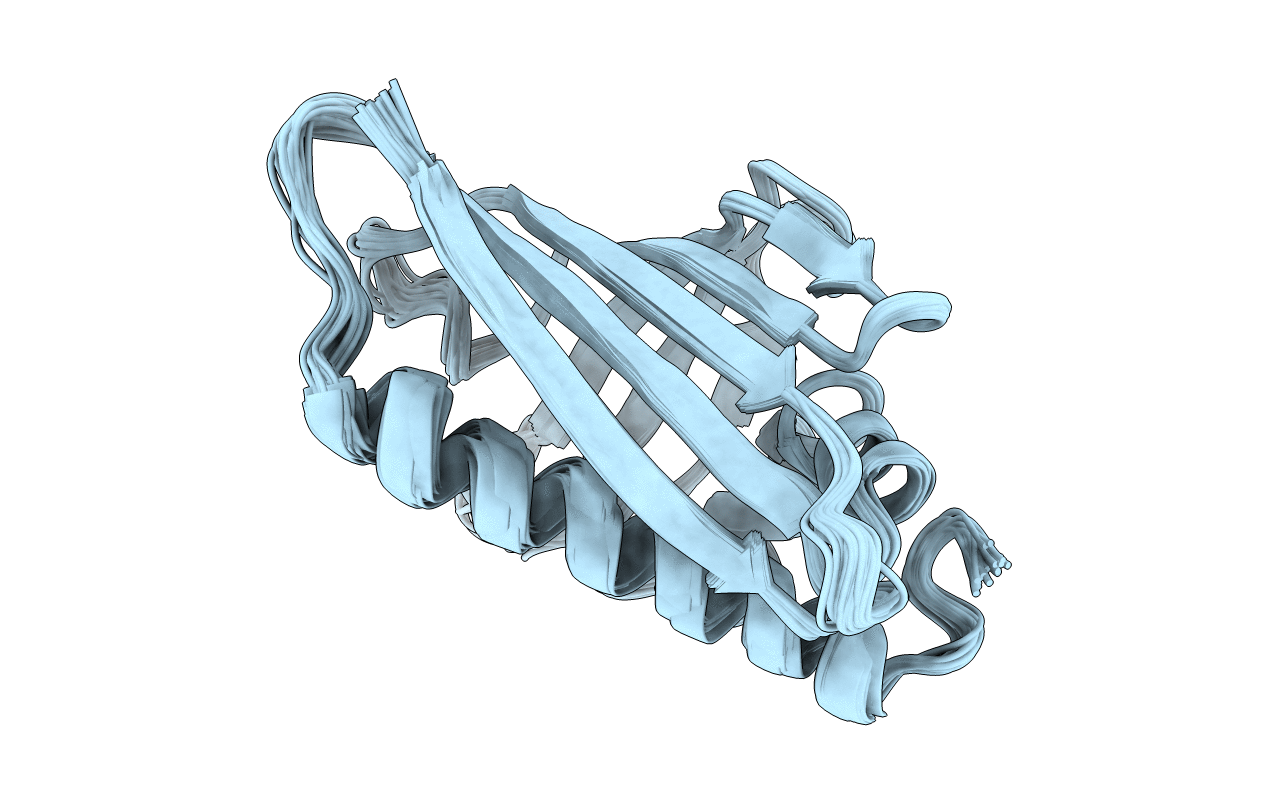
Deposition Date
2002-08-12
Release Date
2003-08-28
Last Version Date
2024-05-15
Entry Detail
PDB ID:
1H2O
Keywords:
Title:
SOLUTION STRUCTURE OF THE MAJOR CHERRY ALLERGEN PRU AV 1 MUTANT E45W
Biological Source:
Source Organism(s):
PRUNUS AVIUM (Taxon ID: 42229)
Expression System(s):
Method Details:
Experimental Method:
Conformers Calculated:
60
Conformers Submitted:
24
Selection Criteria:
LOWEST ENERGY