Deposition Date
2002-07-19
Release Date
2003-07-17
Last Version Date
2024-05-08
Entry Detail
PDB ID:
1H1O
Keywords:
Title:
Acidithiobacillus ferrooxidans cytochrome c4 structure supports a complex-induced tuning of electron transfer
Biological Source:
Source Organism:
THIOBACILLUS FERROOXIDANS (Taxon ID: 920)
Method Details:
Experimental Method:
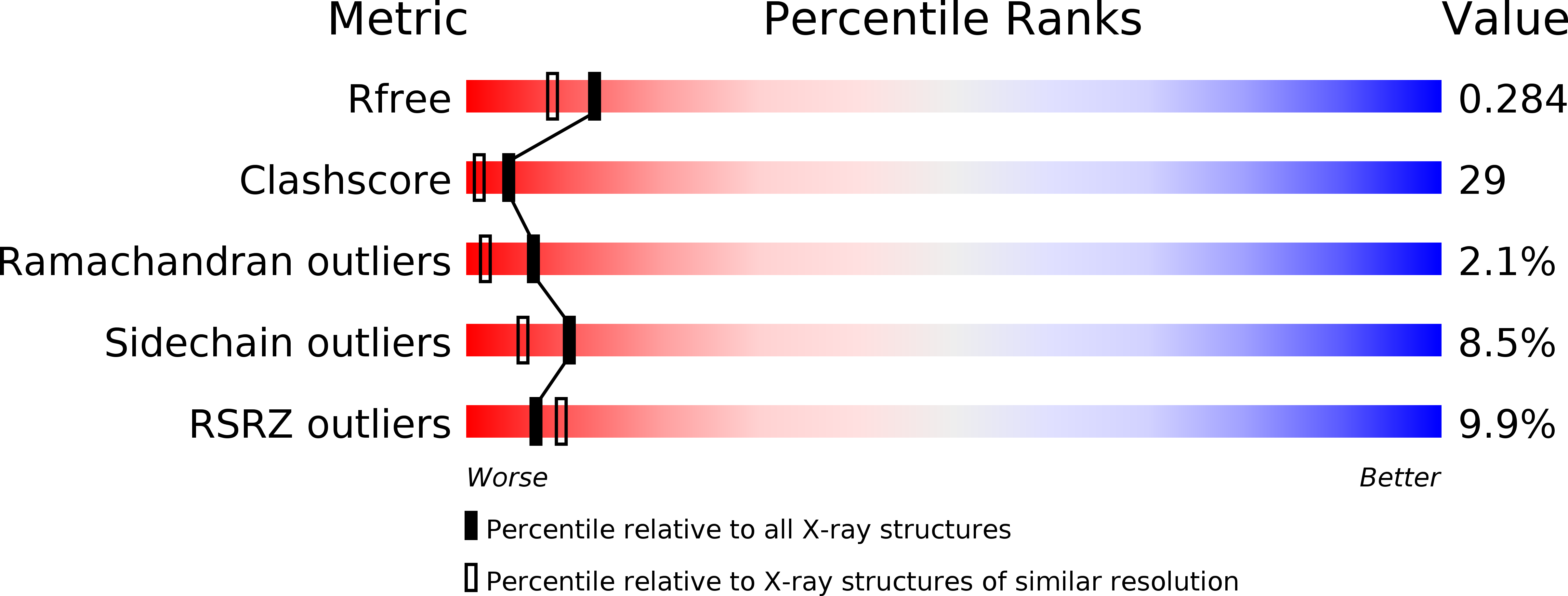
Resolution:
2.13 Å
R-Value Free:
0.28
R-Value Work:
0.23
R-Value Observed:
0.23
Space Group:
P 64 2 2