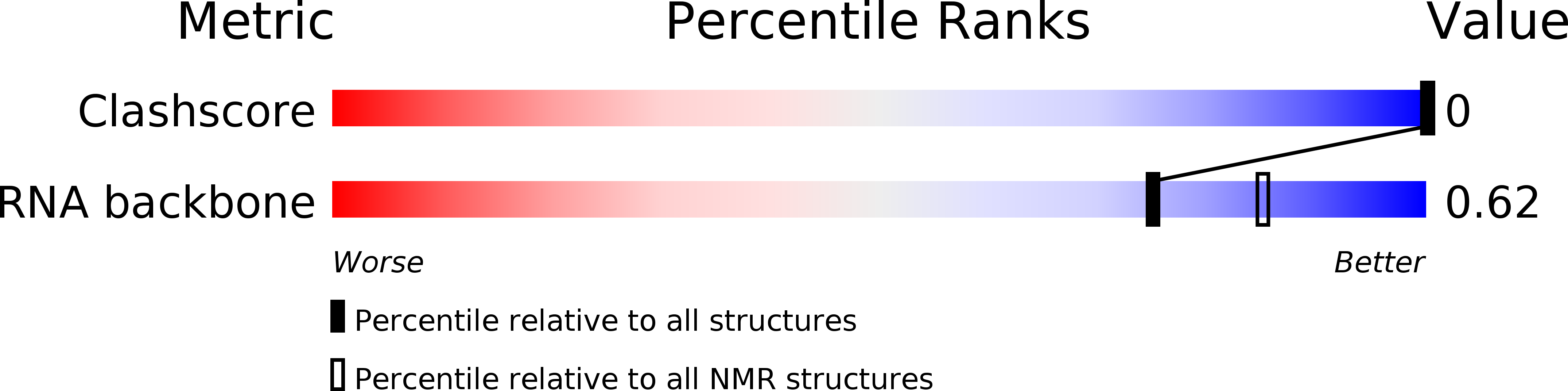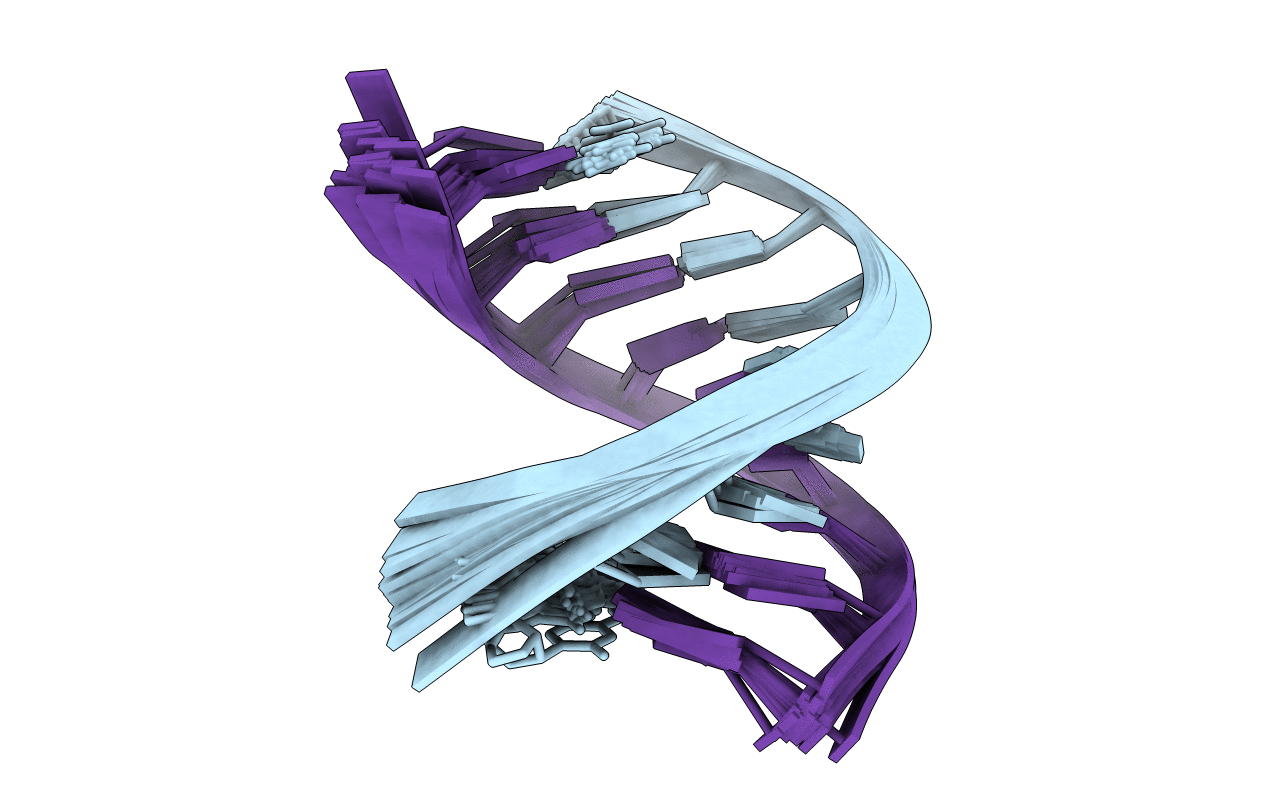
Deposition Date
2002-06-27
Release Date
2003-07-17
Last Version Date
2024-05-15
Entry Detail
PDB ID:
1H0Q
Keywords:
Title:
NMR solution structure of a fully modified locked nucleic acid (LNA) hybridized to RNA
Method Details: