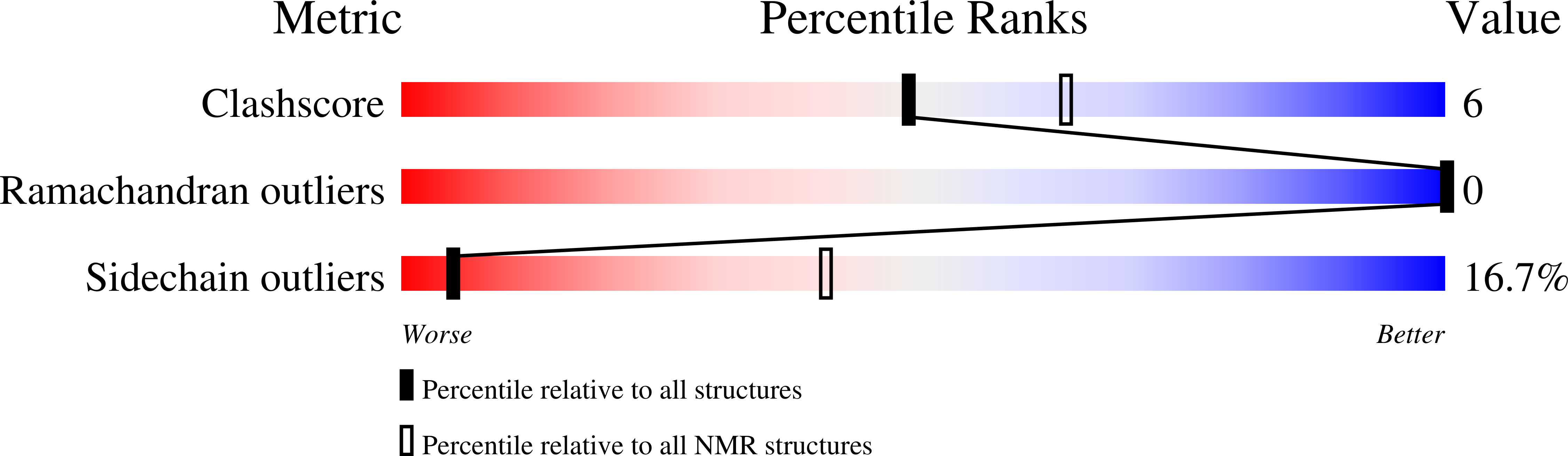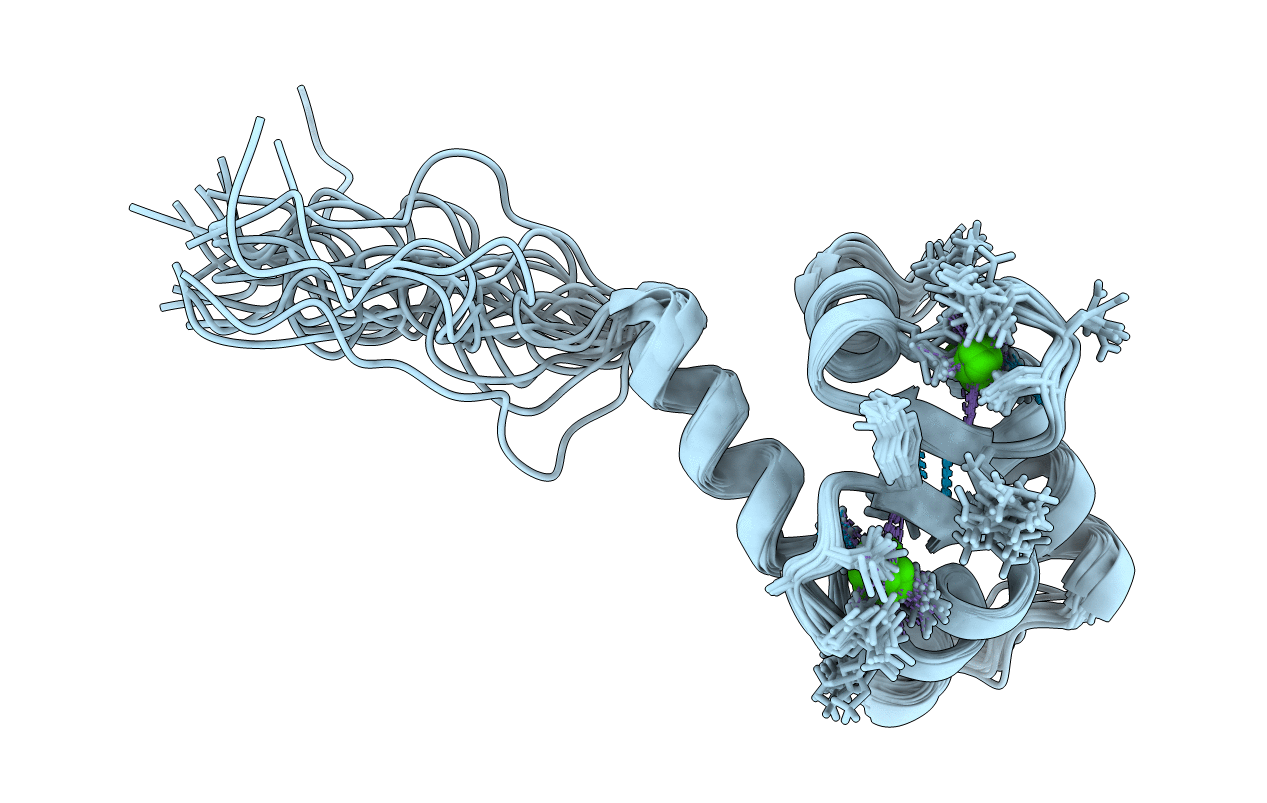
Deposition Date
2000-08-03
Release Date
2000-08-23
Last Version Date
2024-05-22
Entry Detail
PDB ID:
1FI5
Keywords:
Title:
NMR STRUCTURE OF THE C TERMINAL DOMAIN OF CARDIAC TROPONIN C BOUND TO THE N TERMINAL DOMAIN OF CARDIAC TROPONIN I.
Biological Source:
Source Organism(s):
Gallus gallus (Taxon ID: 9031)
Expression System(s):
Method Details:
Experimental Method:
Conformers Calculated:
500
Conformers Submitted:
20
Selection Criteria:
SMALLEST RMSD TO AVERAGE STRUCTURE