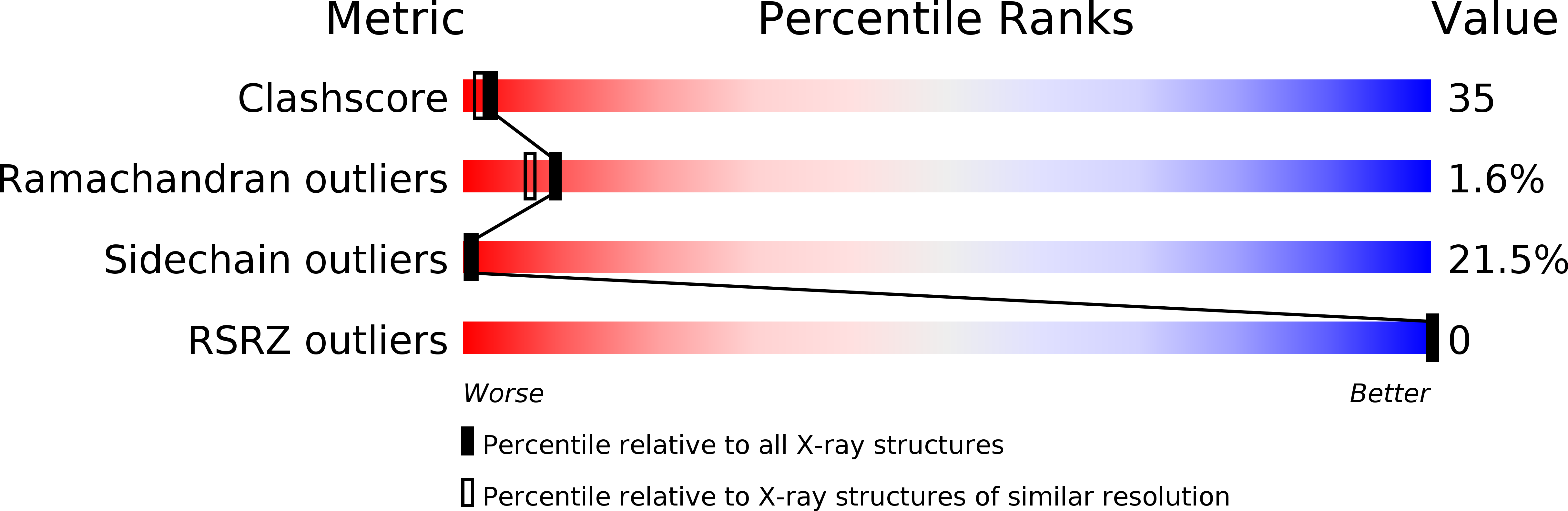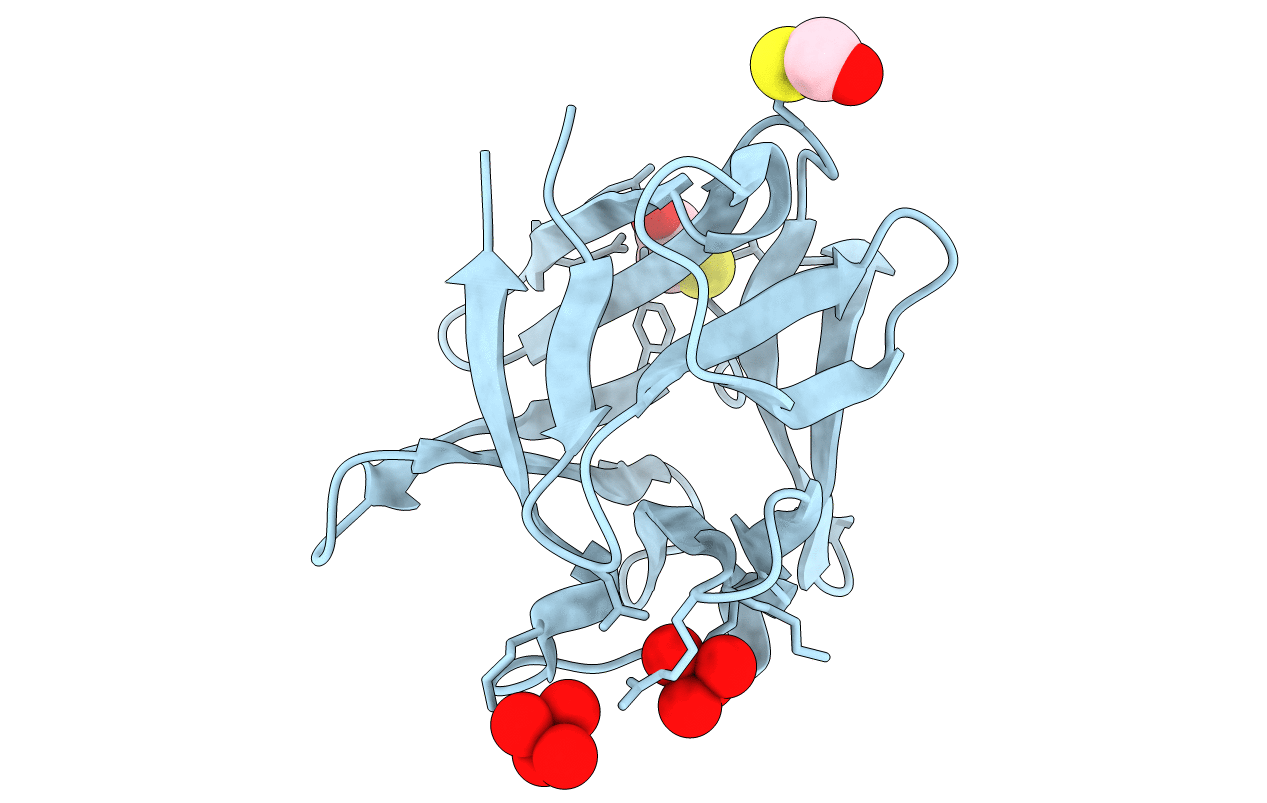
Deposition Date
1993-02-26
Release Date
1993-07-15
Last Version Date
2025-03-26
Entry Detail
PDB ID:
1FGA
Keywords:
Title:
REFINEMENT OF THE STRUCTURE OF HUMAN BASIC FIBROBLAST GROWTH FACTOR AT 1.6 ANGSTROMS RESOLUTION AND ANALYSIS OF PRESUMED HEPARIN BINDING SITES BY SELENATE SUBSTITUTION
Biological Source:
Source Organism(s):
Homo sapiens (Taxon ID: 9606)
Method Details: