Deposition Date
1990-08-27
Release Date
1991-10-15
Last Version Date
2024-11-20
Entry Detail
PDB ID:
1FDL
Keywords:
Title:
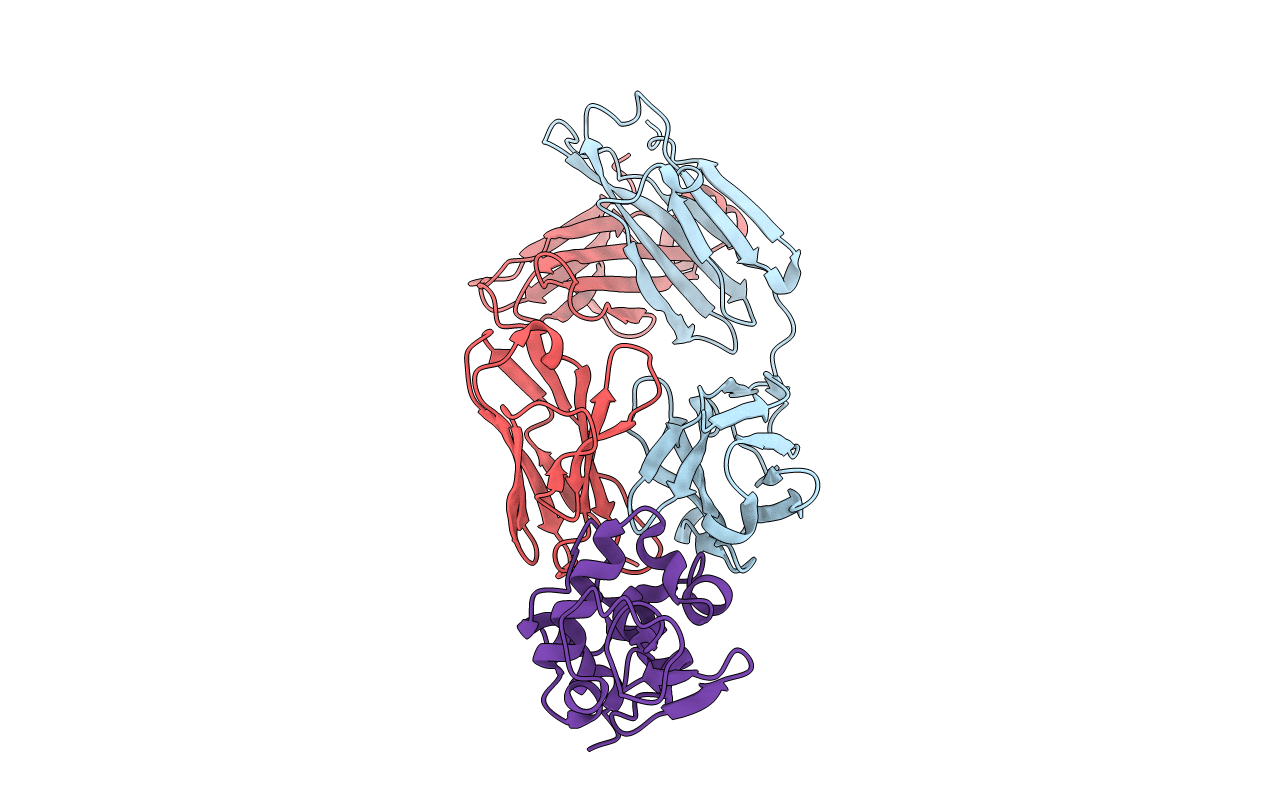
CRYSTALLOGRAPHIC REFINEMENT OF THE THREE-DIMENSIONAL STRUCTURE OF THE FAB D1.3-LYSOZYME COMPLEX AT 2.5-ANGSTROMS RESOLUTION
Biological Source:
Source Organism(s):
Mus musculus (Taxon ID: 10090)
Gallus gallus (Taxon ID: 9031)
Gallus gallus (Taxon ID: 9031)
Expression System(s):
Method Details: