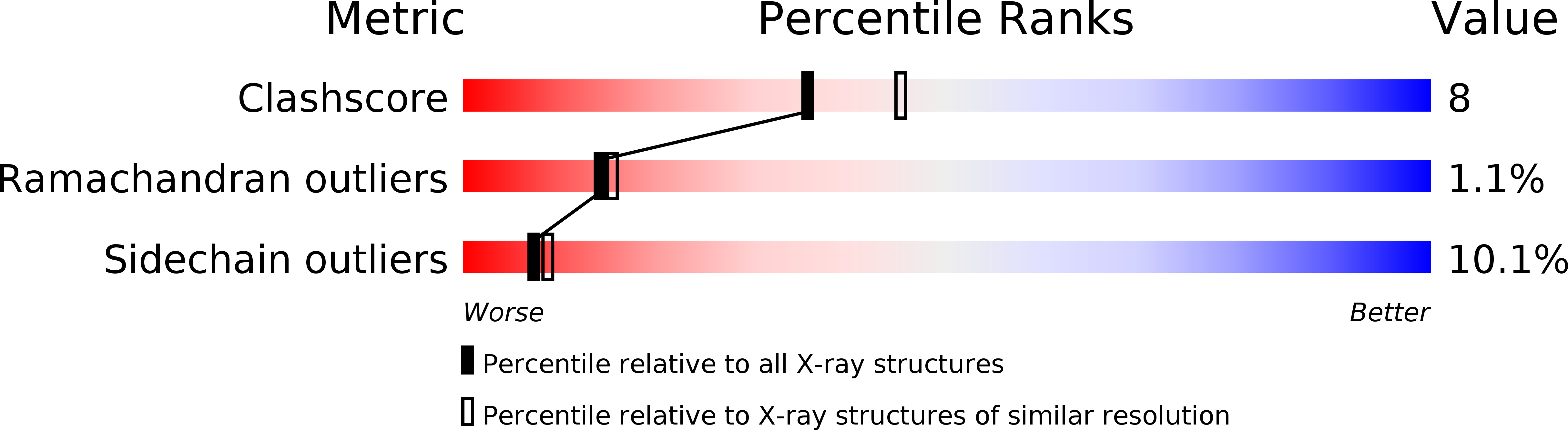
Deposition Date
2000-05-12
Release Date
2001-05-16
Last Version Date
2024-10-23
Entry Detail
PDB ID:
1EZV
Keywords:
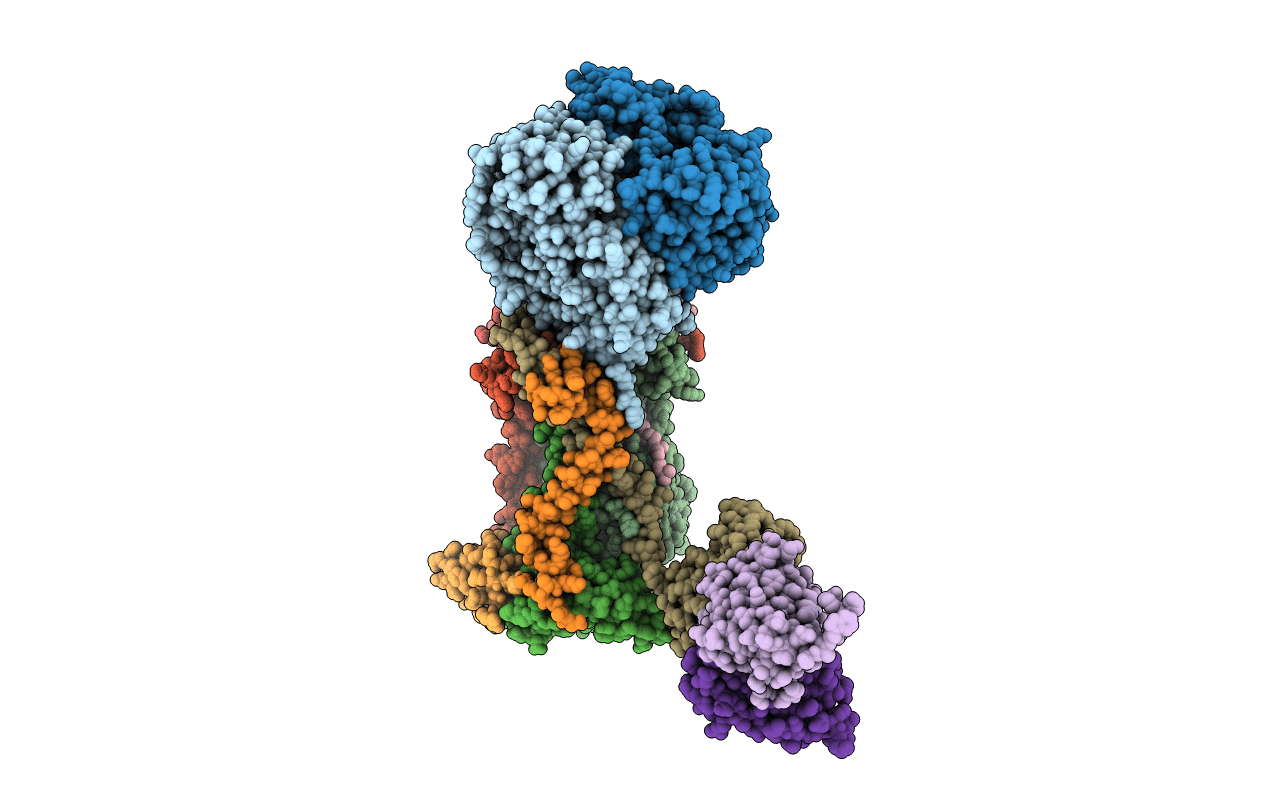
Title:
STRUCTURE OF THE YEAST CYTOCHROME BC1 COMPLEX CO-CRYSTALLIZED WITH AN ANTIBODY FV-FRAGMENT
Biological Source:
Source Organism:
Saccharomyces cerevisiae (Taxon ID: 4932)
Mus musculus (Taxon ID: 10090)
Mus musculus (Taxon ID: 10090)
Method Details:
Experimental Method:
Resolution:
2.30 Å
R-Value Free:
0.25
R-Value Work:
0.22
R-Value Observed:
0.25
Space Group:
C 1 2 1