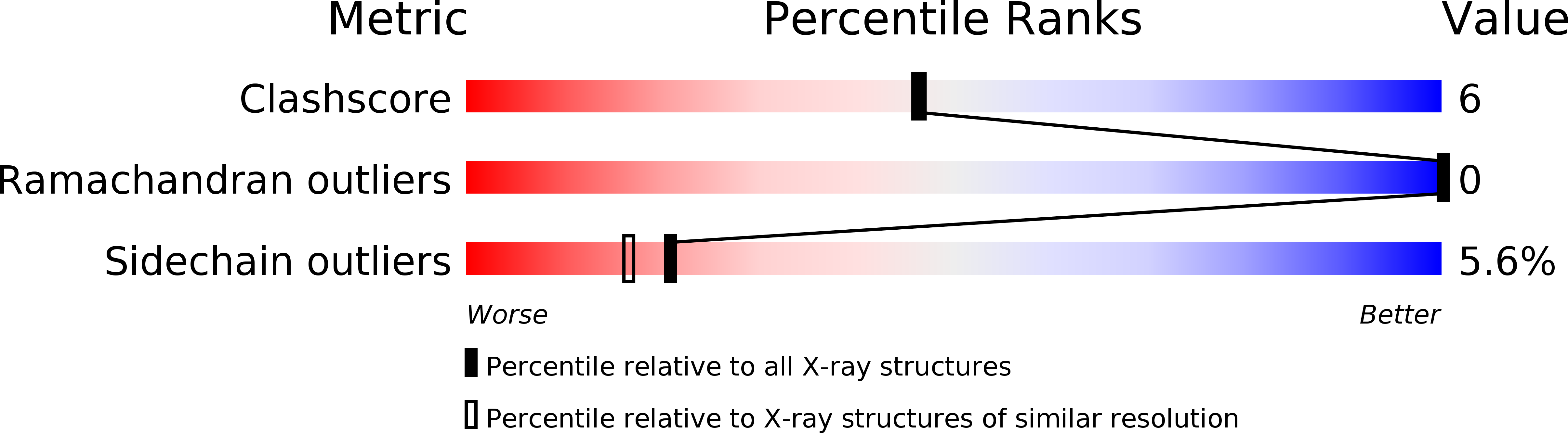
Deposition Date
1994-10-24
Release Date
1995-02-14
Last Version Date
2024-10-23
Entry Detail
PDB ID:
1ELE
Keywords:
Title:
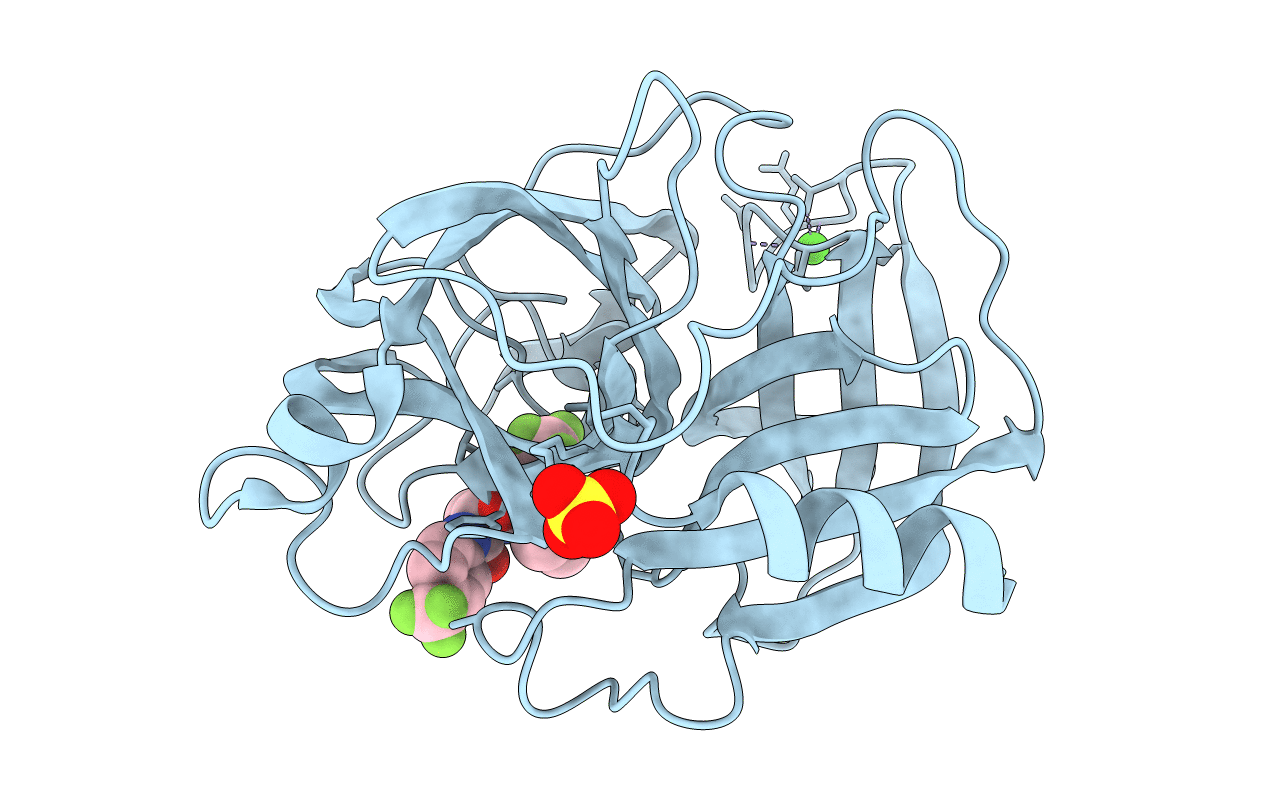
STRUCTURAL ANALYSIS OF THE ACTIVE SITE OF PORCINE PANCREATIC ELASTASE BASED ON THE X-RAY CRYSTAL STRUCTURES OF COMPLEXES WITH TRIFLUOROACETYL-DIPEPTIDE-ANILIDE INHIBITORS
Biological Source:
Source Organism(s):
Sus scrofa (Taxon ID: 9823)
Method Details:
Experimental Method:
Resolution:
2.00 Å
R-Value Work:
0.17
R-Value Observed:
0.17
Space Group:
P 21 21 21