Deposition Date
2000-06-22
Release Date
2000-10-03
Last Version Date
2024-05-15
Entry Detail
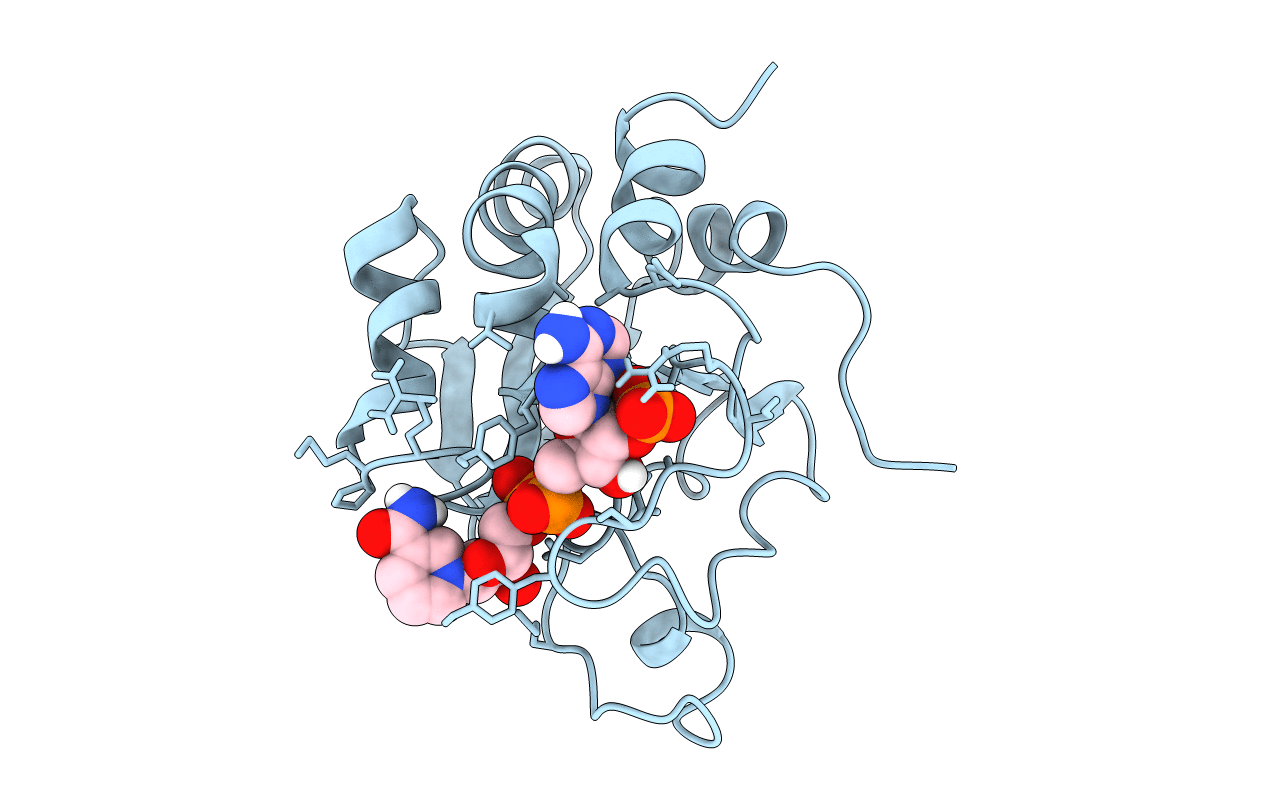
PDB ID:
1E3T
Keywords:
Title:
Solution Structure of the NADP(H) binding Component (dIII) of Proton-Translocating Transhydrogenase from Rhodospirillum rubrum
Biological Source:
Source Organism(s):
RHODOSPIRILLUM RUBRUM (Taxon ID: 1085)
Expression System(s):
Method Details:
Experimental Method:
Conformers Calculated:
100
Conformers Submitted:
1
Selection Criteria:
AVERAGE OF 10 LOWEST ENERGY STRUCTURES


