Deposition Date
2000-05-08
Release Date
2003-06-19
Last Version Date
2023-12-06
Entry Detail
PDB ID:
1E1H
Keywords:
Title:
Crystal Structure of recombinant Botulinum Neurotoxin Type A Light Chain, self-inhibiting Zn endopeptidase.
Biological Source:
Source Organism:
CLOSTRIDIUM BOTULINUM (Taxon ID: 1491)
Host Organism:
Method Details:
Experimental Method:
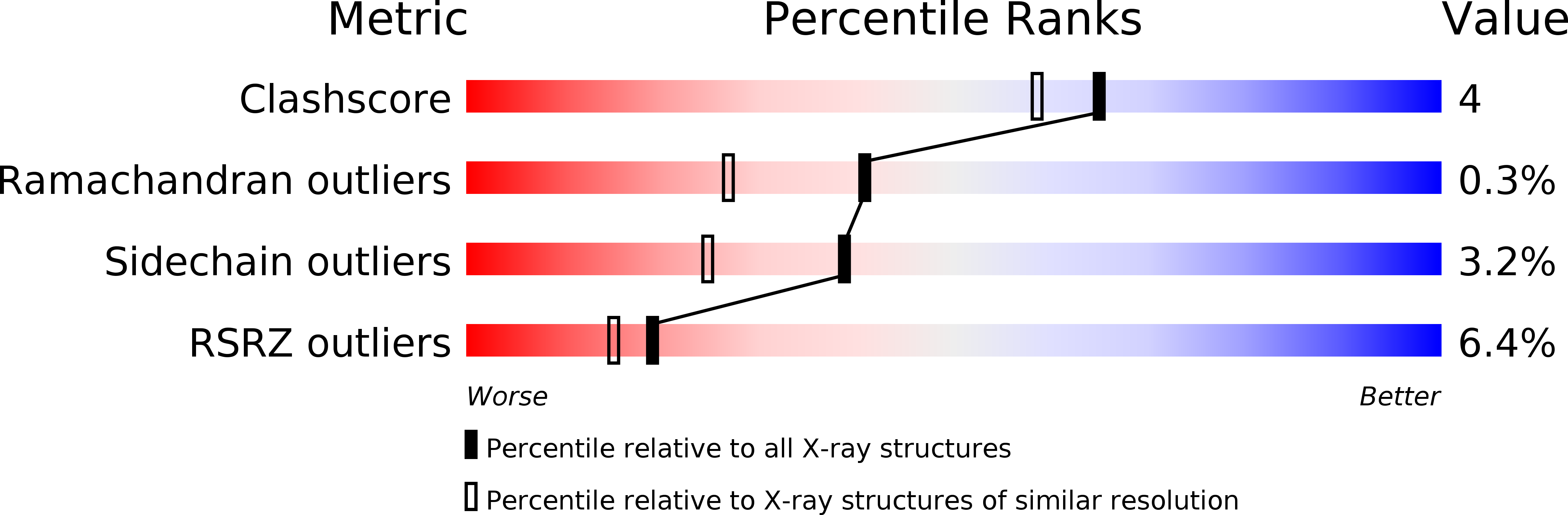
Resolution:
1.80 Å
R-Value Free:
0.23
R-Value Work:
0.19
Space Group:
P 1 21 1