Deposition Date
2000-02-16
Release Date
2000-03-29
Last Version Date
2024-05-15
Entry Detail
PDB ID:
1DZ5
Keywords:
Title:
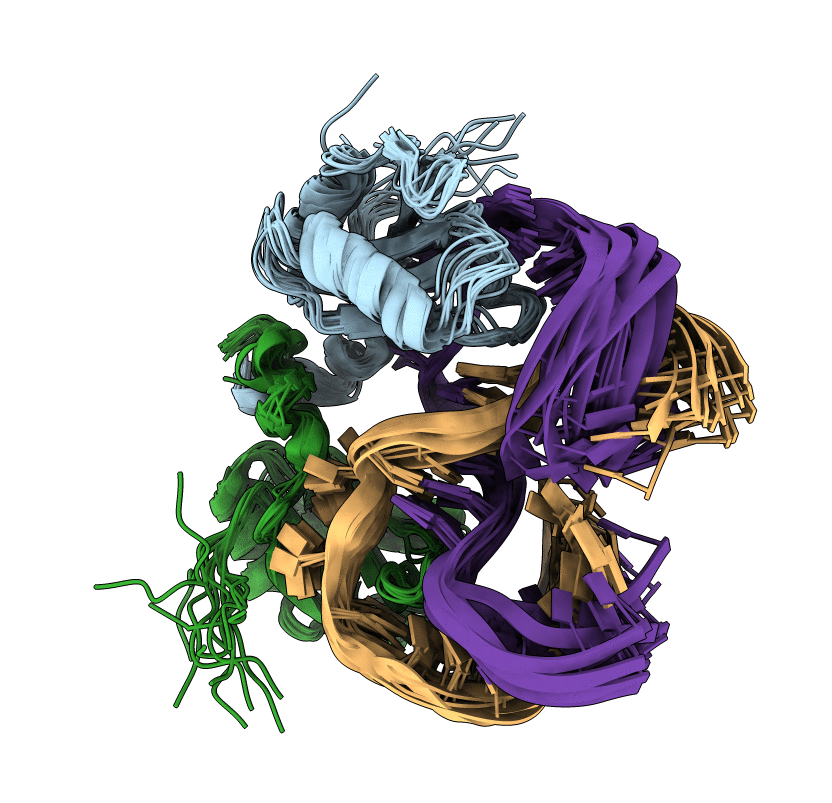
The NMR structure of the 38KDa U1A protein-PIE RNA complex reveals the basis of cooperativity in regulation of polyadenylation by human U1A protein
Biological Source:
Source Organism(s):
HOMO SAPIENS (Taxon ID: 9606)
Expression System(s):
Method Details:
Experimental Method:
Conformers Calculated:
50
Conformers Submitted:
13
Selection Criteria:
AGREEMENT WITH EXPERIMENTAL DATA