Deposition Date
1999-11-08
Release Date
2000-03-29
Last Version Date
2024-05-22
Entry Detail
PDB ID:
1DD7
Keywords:
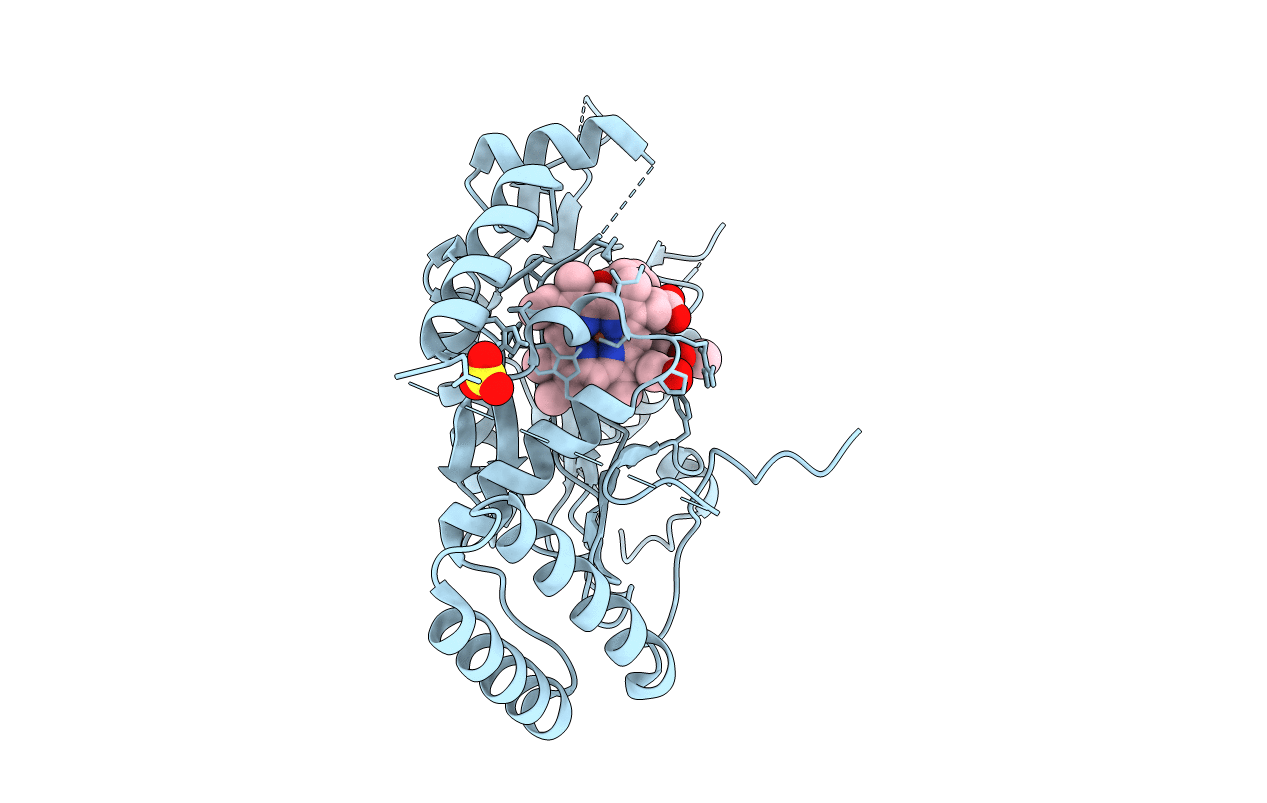
Title:
MURINE INDUCIBLE NITRIC OXIDE SYNTHASE OXYGENASE DOMAIN (DELTA 114) (N-[(1,3-BENZODIOXOL-5-YL)METHYL]-1-[2-(1H-IMIDAZOL-1-YL)PYRIMIDIN-4-YL]-4-(METHOXYCARBONYL)-PIPERAZINE-2-ACETAMIDE COMPLEX
Biological Source:
Source Organism(s):
Mus musculus (Taxon ID: 10090)
Expression System(s):
Method Details:
Experimental Method:
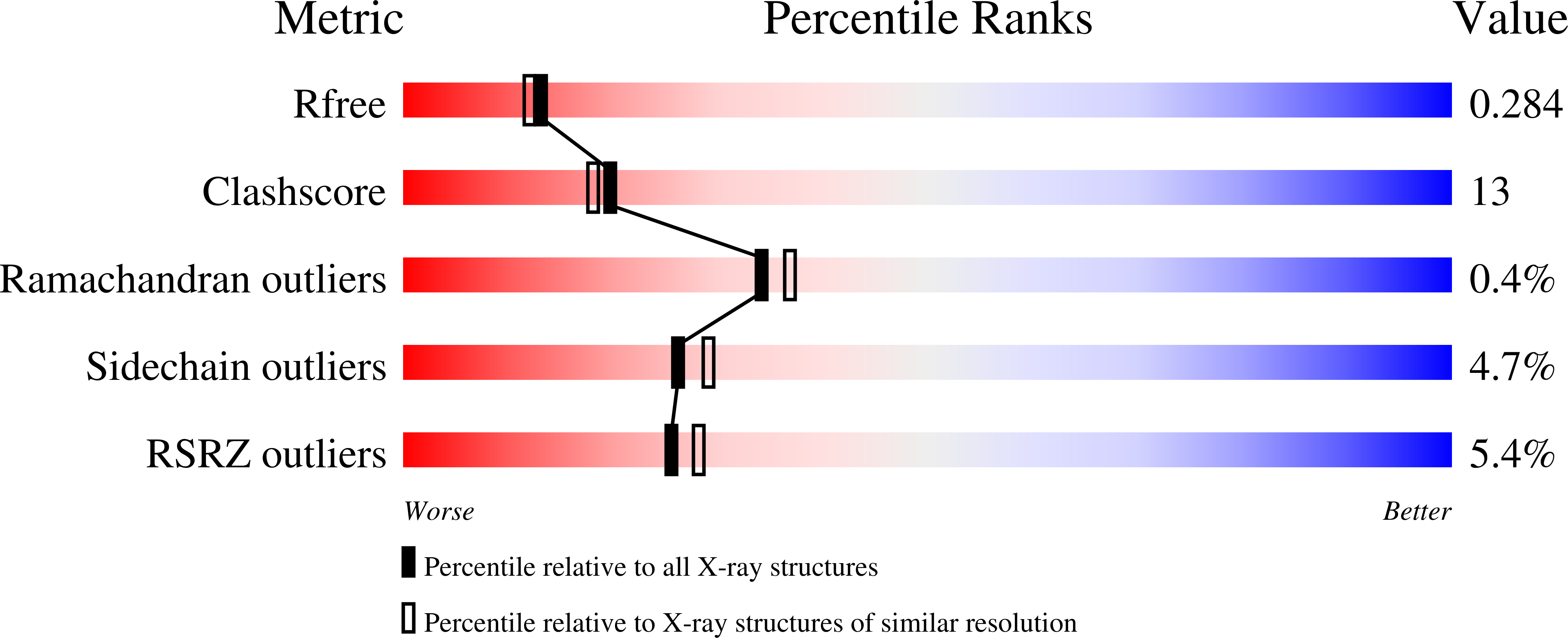
Resolution:
2.25 Å
R-Value Free:
0.28
R-Value Work:
0.19
Space Group:
P 21 21 21