Abstact
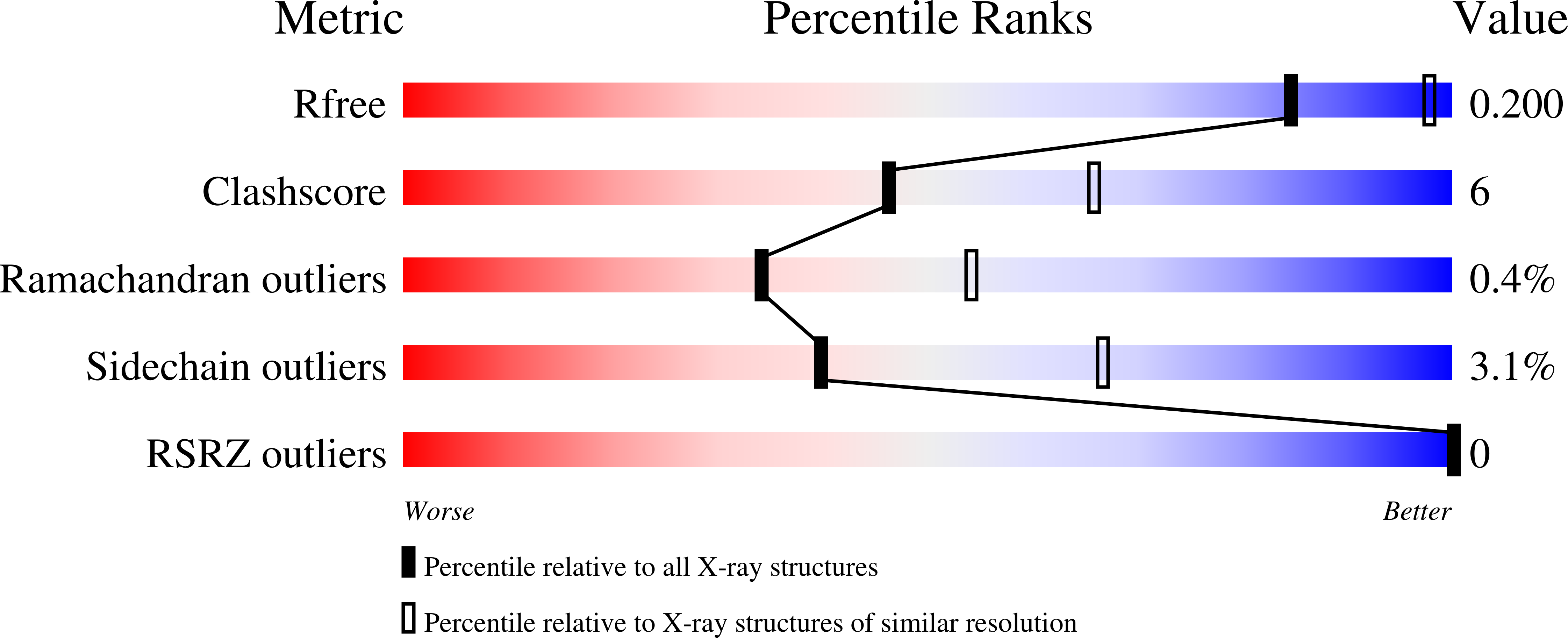
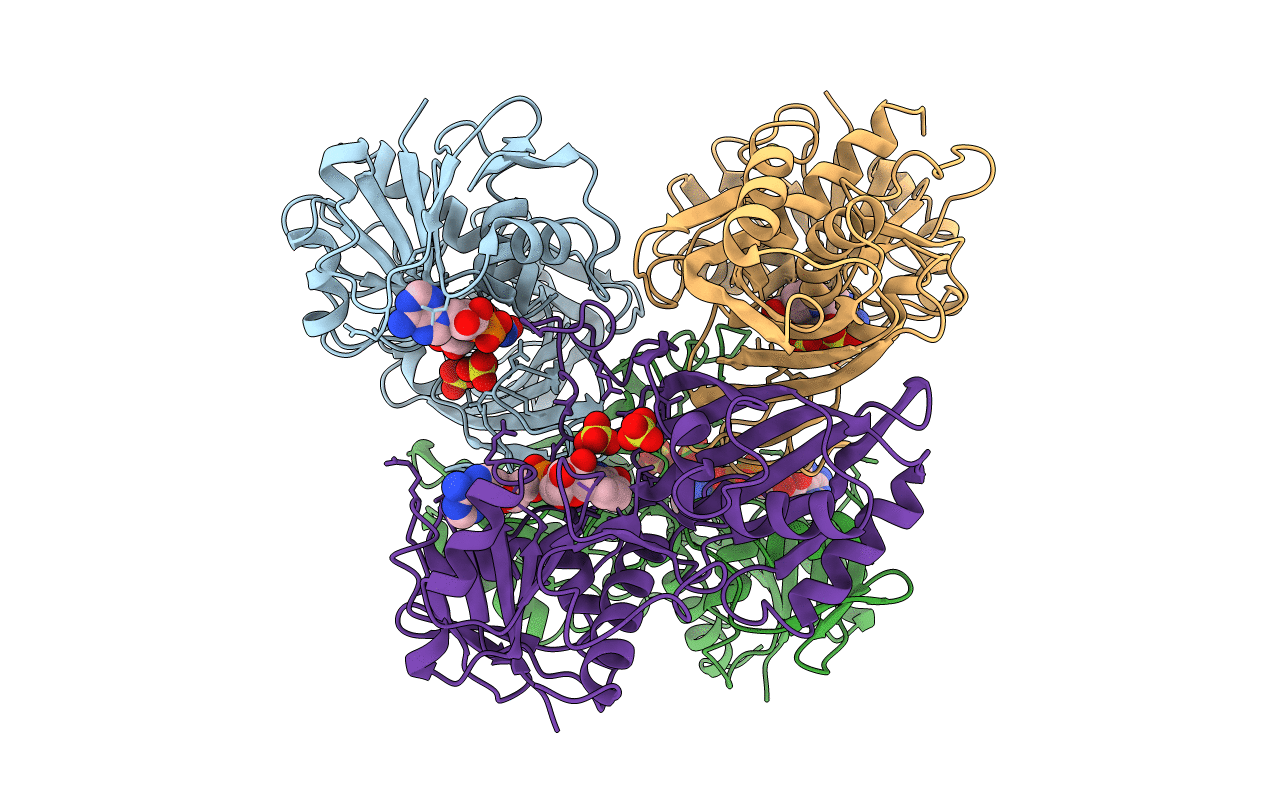
Mutations have been introduced in the cytosolic glyceraldehyde-3-phosphate dehydrogenase (GAPDH) from Bacillus stearothermophilus in order to convert its cofactor selectivity from a specificity towards NAD into a preference for NADP. In the B-S mutant, five mutations (L33T, T34G, D35G, L187A, P188S) were selected on the basis of a sequence alignment with NADP-dependent chloroplastic GAPDHs. In the D32G-S mutant, two of the five mutations mentioned above (L187A, P188S) have been used in combination with another one designed from electrostatic considerations (D32G). Both mutants exhibit a dual-cofactor selectivity at the advantage of either NAD (B-S) or NADP (D32G-S). In order to analyse the cofactor-binding site plasticity at the molecular level, crystal structures of these mutants have been solved, when complexed with either NAD+ (D32G-Sn, resolution 2.5 A, R = 13.9%; B-Sn, 2.45 A, 19.3%) or NADP+ (D32G-Sp, 2.2 A, 19.2%; B-Sp, 2.5 A, 14.4%). The four refined models are very similar to that of the wild-type GAPDH and as expected resemble more closely the holo form than the apo form. In the B-S mutant, the wild-type low affinity for NADP+ seems to be essentially retained because of repulsive electrostatic contacts between the extra 2'-phosphate and the unchanged carboxylate group of residue D32. Such an antideterminant effect is not well compensated by putative attractive interactions which had been expected to arise from the newly-introduced side-chains. In this mutant, recognition of NAD+ is slightly affected with respect to that known on the wild-type, because mutations only weakly destabilize hydrogen bonds and van der Waals contacts originally present in the natural enzyme. Thus, the B-S mutant does not mimic efficiently the chloroplastic GAPDHs, and long-range and/or second-layer effects, not easily predictable from visual inspection of three-dimensional structures, need to be taken into account for designing a true "chloroplastic-like" mutant of cytosolic GAPDH. In the case of the D32G-S mutant, the dissociation constants for NAD+ and NADP+ are practically reversed with respect to those of the wild-type. The strong alteration of the affinity for NAD+ obviously proceeds from the suppression of the two wild-type hydrogen bonds between the adenosine 2'- and 3'-hydroxyl positions and the D32 carboxylate group. As expected, the efficient recognition of NADP+ is partly promoted by the removal of intra-subunit electrostatic repulsion (D32G) and inter-subunit steric hindrance (L187A, P188S). Another interesting feature of the reshaped NADP+-binding site is provided by the local stabilization of the extra 2'-phosphate which forms a hydrogen bond with the side-chain hydroxyl group of the newly-introduced S188. When compared to the presently known natural NADP-binding clefts, this result clearly demonstrates that an absolute need for a salt-bridge involving the 2'-phosphate is not required to switch the cofactor selectivity from NAD to NADP. In fact, as it is the case in this mutant, only a moderately polar hydrogen bond can be sufficient to make the extra 2'-phosphate of NADP+ well recognized by a protein environment.