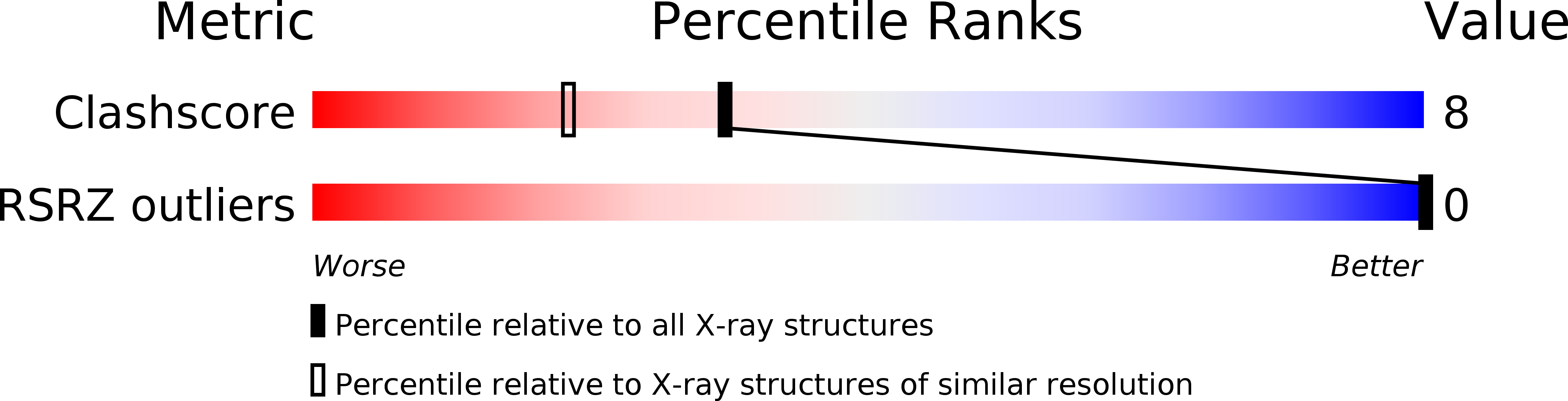
Deposition Date
1993-01-21
Release Date
1993-04-15
Last Version Date
2024-02-07
Entry Detail
PDB ID:
1DA9
Keywords:
Title:
ANTHRACYCLINE-DNA INTERACTIONS AT UNFAVOURABLE BASE BASE-PAIR TRIPLET-BINDING SITES: STRUCTURES OF D(CGGCCG)/DAUNOMYCIN AND D(TGGCCA)/ADRIAMYCIN COMPL
Method Details:
Experimental Method:
Resolution:
1.70 Å
R-Value Observed:
0.21
Space Group:
P 41 21 2