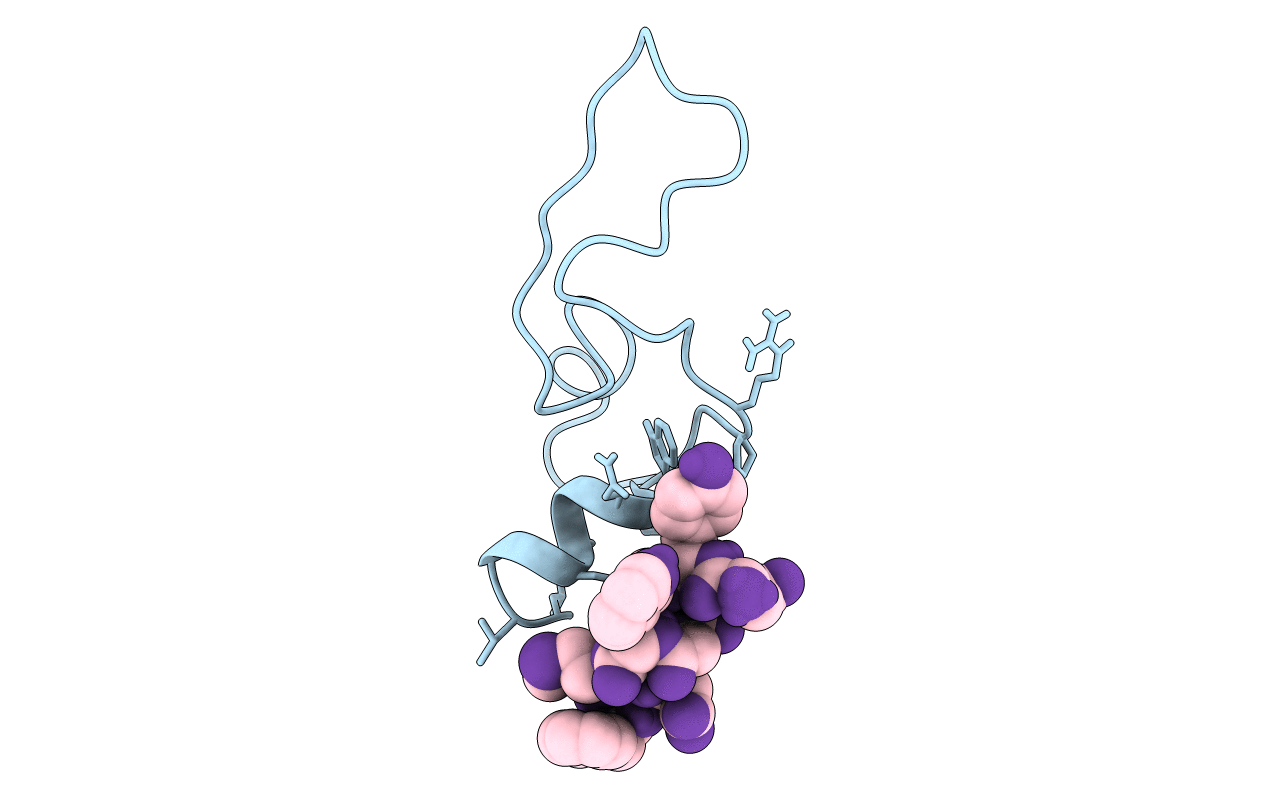
Deposition Date
1999-10-13
Release Date
1999-11-17
Last Version Date
2024-10-16
Entry Detail
PDB ID:
1D6G
Keywords:
Title:
MOLECULAR COMPLEX OF CHOLECYSTOKININ-8 AND N-TERMINUS OF THE CHOLECYSTOKININ A RECEPTOR BY NMR SPECTROSCOPY
Biological Source:
Source Organism(s):
Homo sapiens (Taxon ID: 9606)
Method Details:


