Deposition Date
1999-09-14
Release Date
1999-12-29
Last Version Date
2024-11-06
Entry Detail
PDB ID:
1D0V
Keywords:
Title:
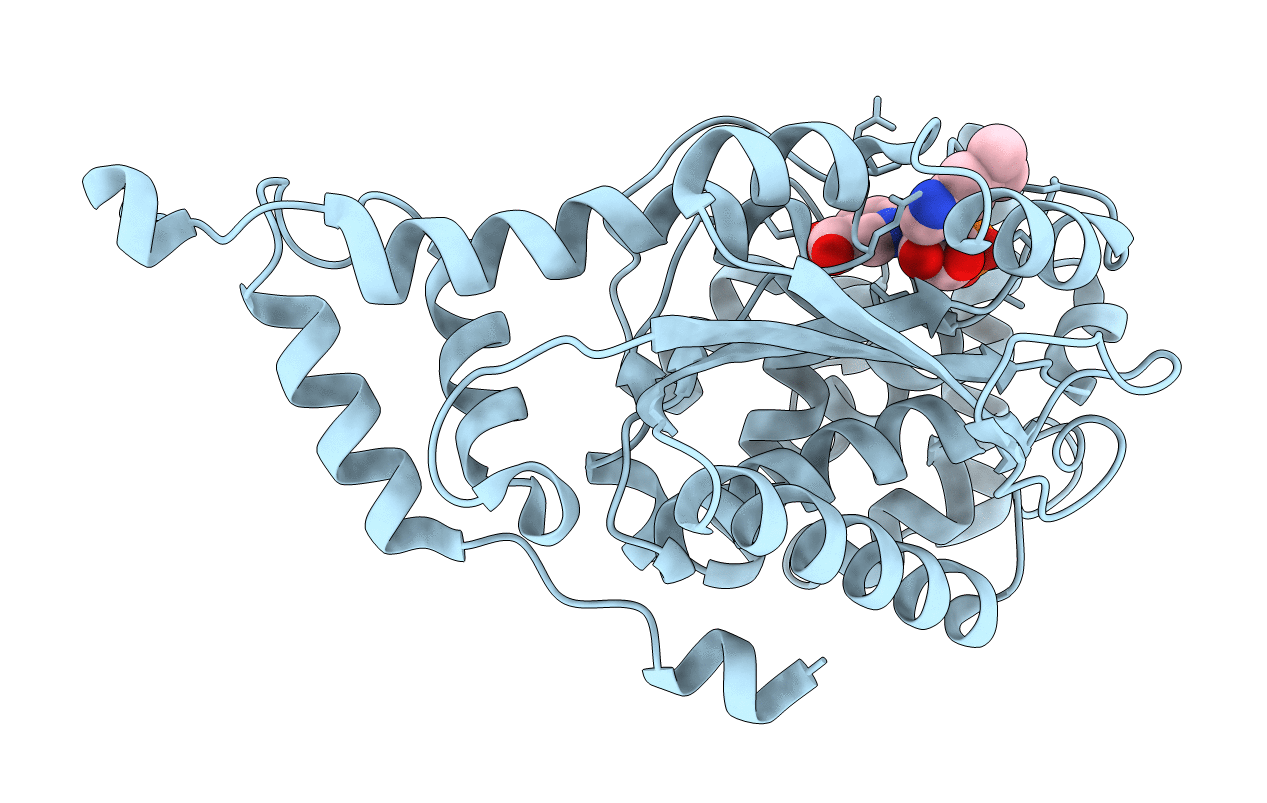
CRYSTAL STRUCTURE OF NICOTINATE MONONUCLEOTIDE:5,6-DIMETHYLBENZIMIDAZOLE PHOSPHORIBOSYLTRANSFERASE (COBT) FROM SALMONELLA TYPHIMURIUM COMPLEXED WITH ITS REACTION PRODUCTS DETERMINED TO 1.9 A RESOLUTION
Biological Source:
Source Organism(s):
Salmonella typhimurium (Taxon ID: 602)
Method Details:
Experimental Method:
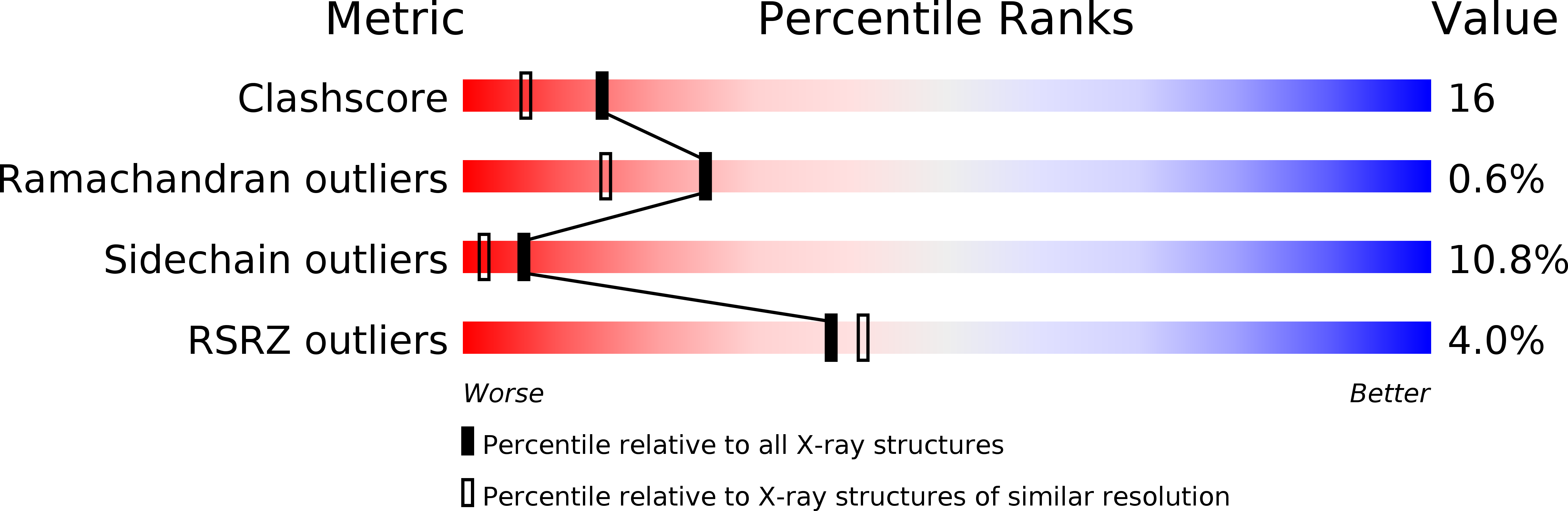
Resolution:
1.90 Å
R-Value Free:
0.24
R-Value Work:
0.16
Space Group:
P 21 21 2