Deposition Date
1995-07-31
Release Date
1995-12-15
Last Version Date
2024-10-23
Entry Detail
PDB ID:
1CXH
Keywords:
Title:
COMPLEX OF CGTASE WITH MALTOTETRAOSE AT ROOM TEMPERATURE AND PH 9.6 BASED ON DIFFRACTION DATA OF A CRYSTAL SOAKED WITH MALTOHEPTAOSE
Biological Source:
Source Organism(s):
Bacillus circulans (Taxon ID: 1397)
Method Details:
Experimental Method:
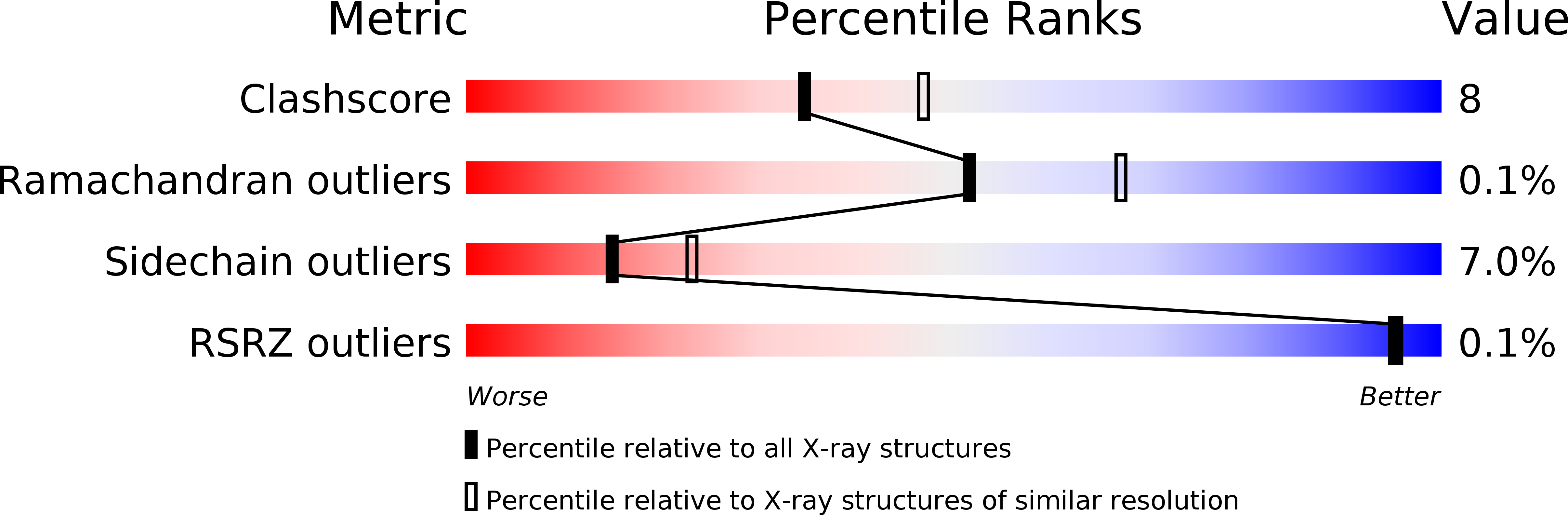
Resolution:
2.41 Å
R-Value Free:
0.2
R-Value Observed:
0.18
Space Group:
P 21 21 21