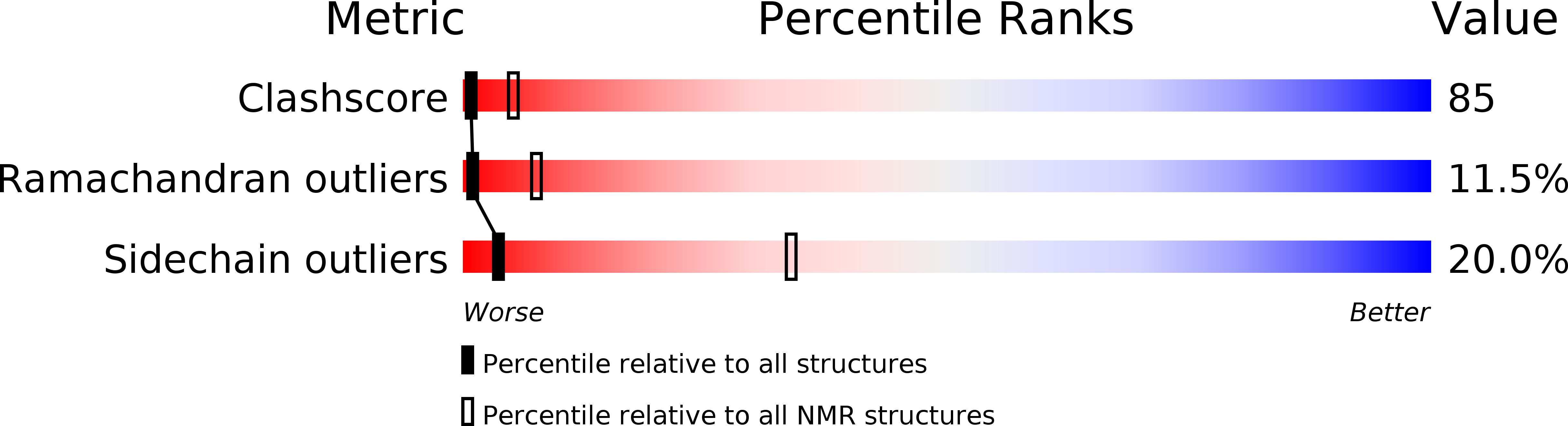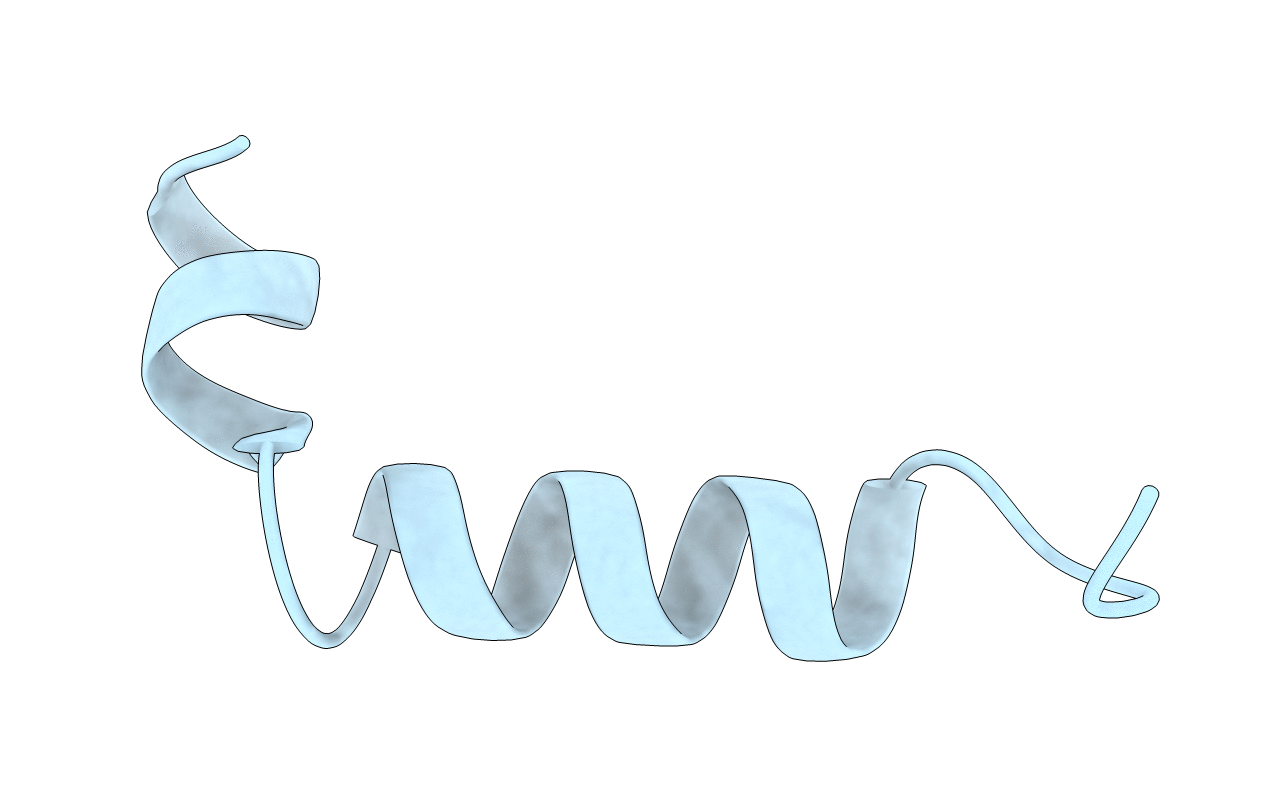
Deposition Date
1999-08-04
Release Date
2000-01-10
Last Version Date
2024-04-10
Entry Detail
PDB ID:
1CQ0
Keywords:
Title:
SOLUTION STRUCTURE OF A HUMAN HYPOCRETIN-2/OREXIN-B'SOLUTION STRUCTURE OF A HUMAN HYPOCRETIN-2/OREXIN-B '
Biological Source:
Source Organism(s):
Homo sapiens (Taxon ID: 9606)
Method Details:
Experimental Method:
Conformers Calculated:
25
Conformers Submitted:
1
Selection Criteria:
REM AVERAGE CONFORMATION