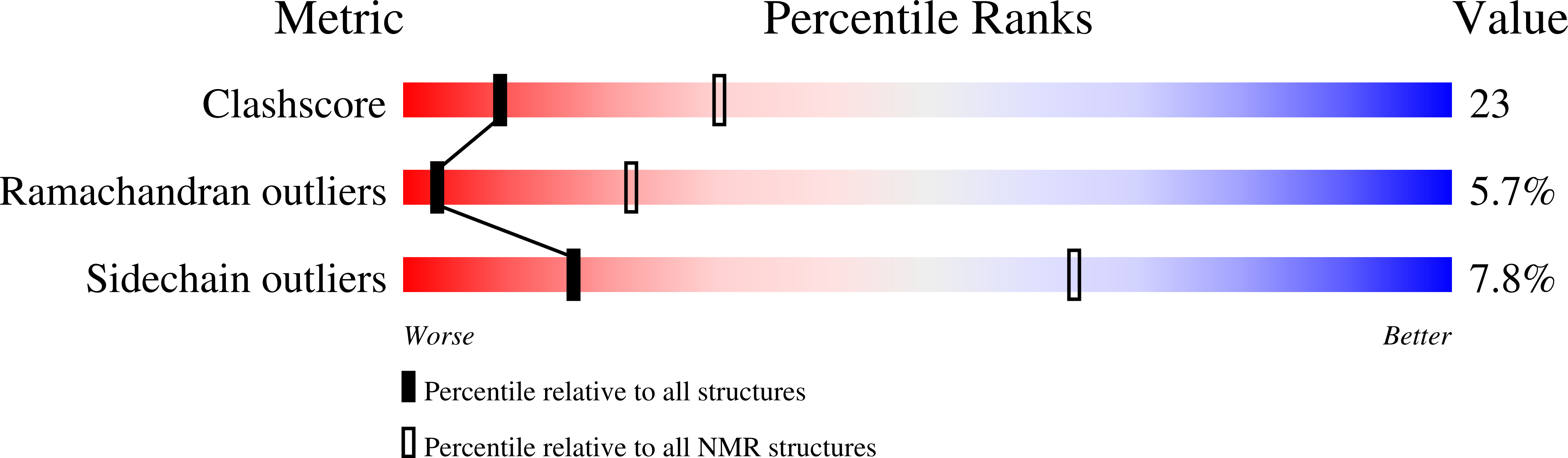
Deposition Date
1999-05-11
Release Date
2000-01-05
Last Version Date
2023-12-27
Entry Detail
PDB ID:
1CMO
Keywords:
Title:
IMMUNOGLOBULIN MOTIF DNA-RECOGNITION AND HETERODIMERIZATION FOR THE PEBP2/CBF RUNT-DOMAIN
Biological Source:
Source Organism(s):
Homo sapiens (Taxon ID: 9606)
Expression System(s):
Method Details:
Experimental Method:
Conformers Calculated:
300
Conformers Submitted:
43
Selection Criteria:
structures with the least restraint violations