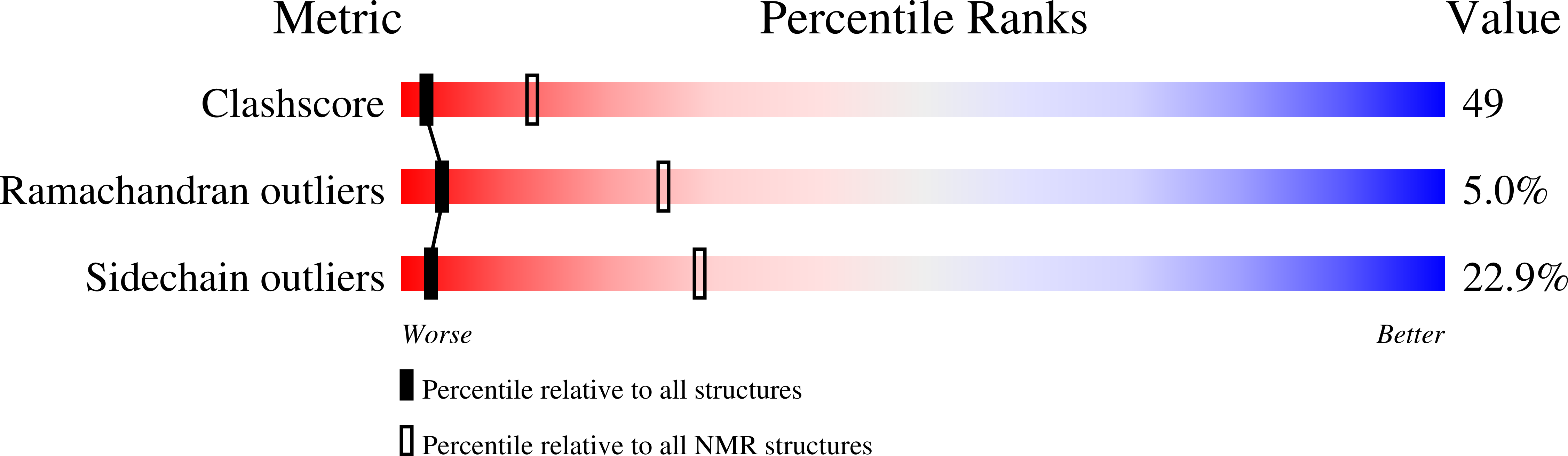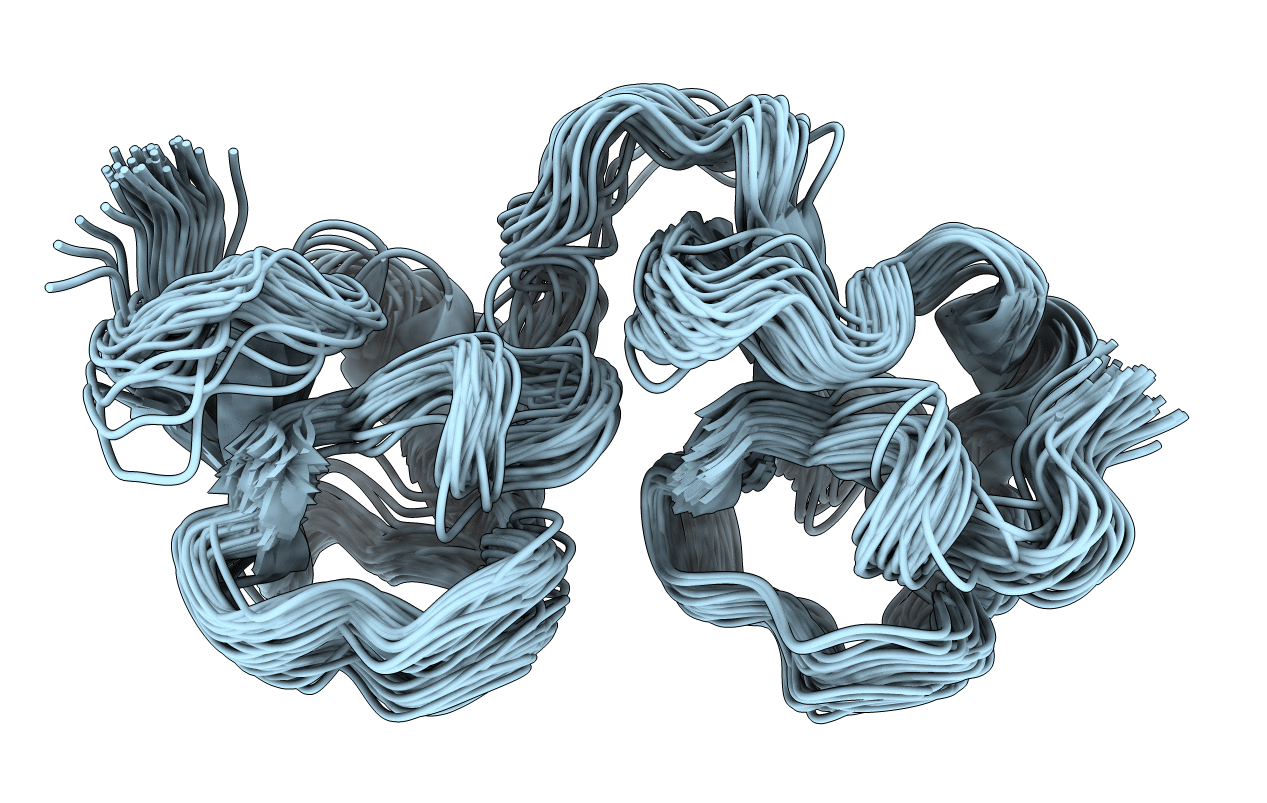
Deposition Date
2000-05-04
Release Date
2001-02-28
Last Version Date
2023-12-27
Entry Detail
PDB ID:
1C89
Keywords:
Title:
NMR STRUCTURE OF INTRAMOLECULAR DIMER ANTIFREEZE PROTEIN RD3, 40 SA STRUCTURES
Biological Source:
Source Organism(s):
Pachycara brachycephalum (Taxon ID: 36221)
Expression System(s):
Method Details:
Experimental Method:
Conformers Calculated:
40
Conformers Submitted:
40
Selection Criteria:
AVERAGE