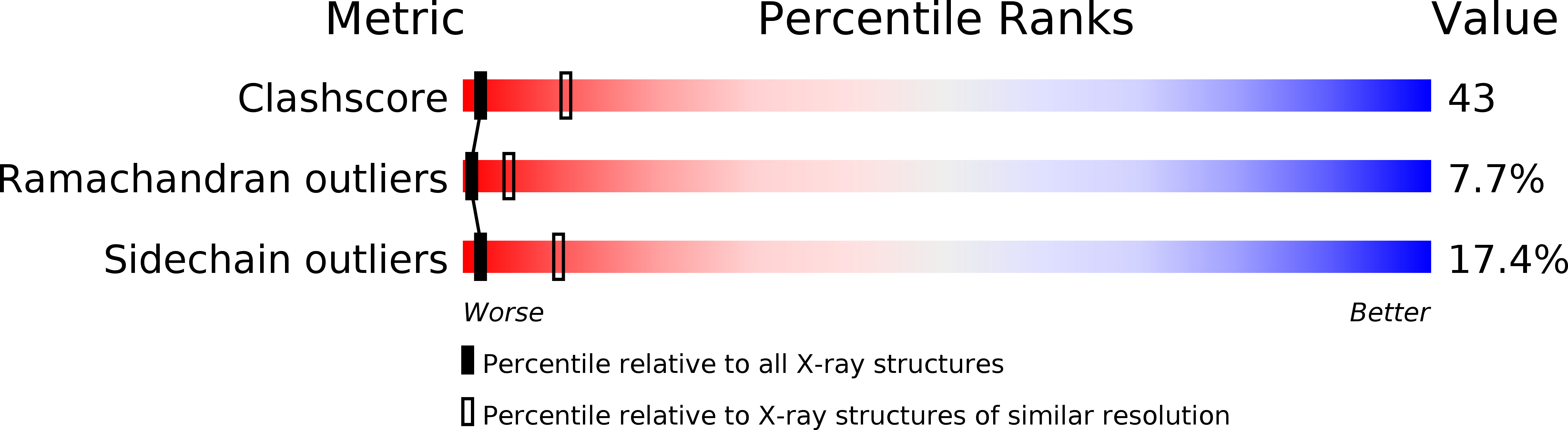Deposition Date
1999-12-21
Release Date
2000-12-27
Last Version Date
2023-08-09
Entry Detail
PDB ID:
1C6V
Keywords:
Title:
SIV INTEGRASE (CATALYTIC DOMAIN + DNA BIDING DOMAIN COMPRISING RESIDUES 50-293) MUTANT WITH PHE 185 REPLACED BY HIS (F185H)
Biological Source:
Source Organism(s):
Simian immunodeficiency virus (Taxon ID: 11723)
Expression System(s):
Method Details:
Experimental Method:
Resolution:
3.00 Å
R-Value Free:
0.36
R-Value Work:
0.20
R-Value Observed:
0.20
Space Group:
P 21 21 21