Deposition Date
1998-08-30
Release Date
1999-08-10
Last Version Date
2024-10-23
Entry Detail
PDB ID:
1BU3
Keywords:
Title:
REFINED CRYSTAL STRUCTURE OF CALCIUM-BOUND SILVER HAKE (PI 4.2) PARVALBUMIN AT 1.65 A.
Biological Source:
Source Organism(s):
Merluccius bilinearis (Taxon ID: 79698)
Method Details:
Experimental Method:
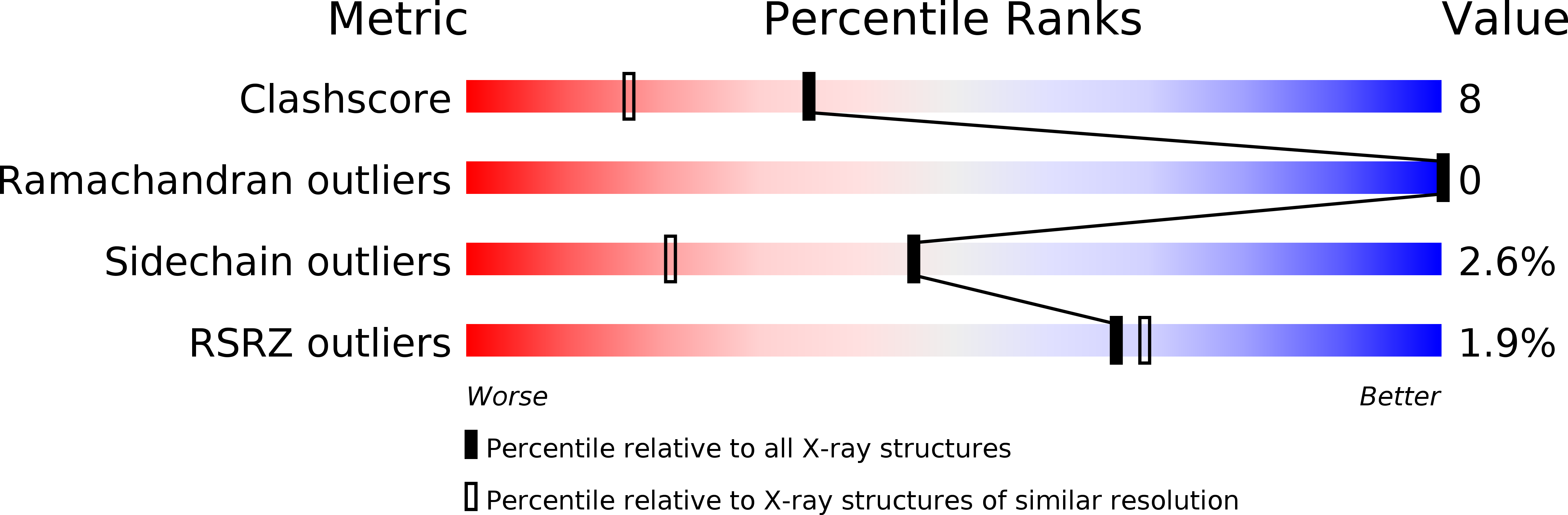
Resolution:
1.65 Å
R-Value Free:
0.25
R-Value Work:
0.21
R-Value Observed:
0.21
Space Group:
C 2 2 21