Deposition Date
1998-09-02
Release Date
1999-09-02
Last Version Date
2024-10-16
Entry Detail
PDB ID:
1BT2
Keywords:
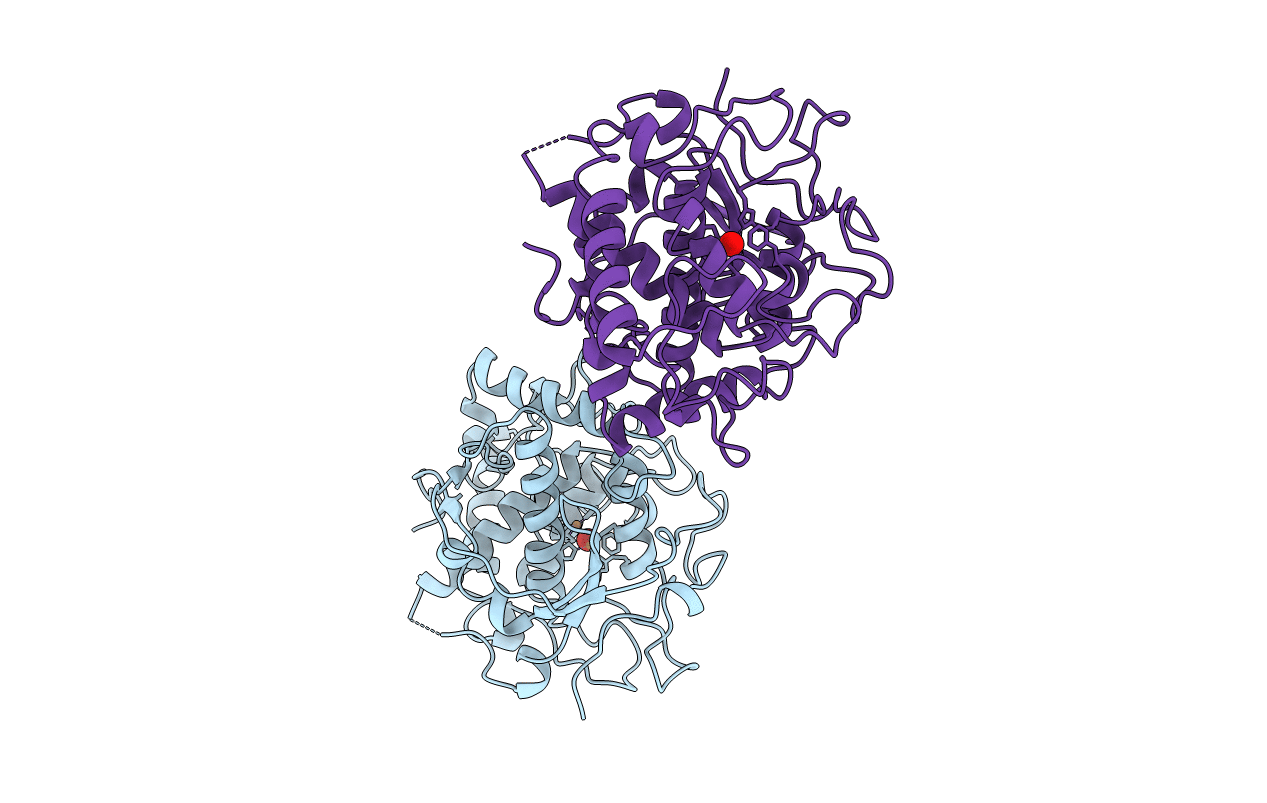
Title:
CATECHOL OXIDASE FROM IPOMOEA BATATAS (SWEET POTATOES) IN THE REDUCED CU(I)-CU(I) STATE
Biological Source:
Source Organism(s):
Ipomoea batatas (Taxon ID: 4120)
Method Details:
Experimental Method:
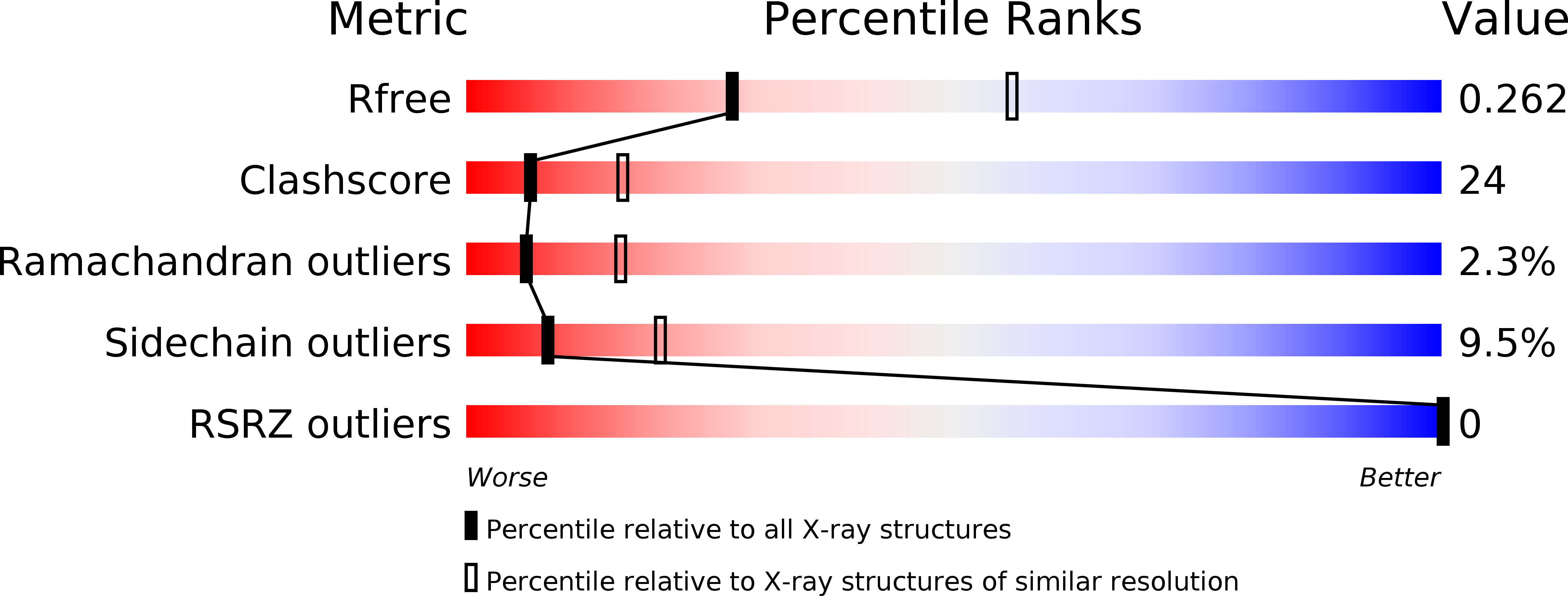
Resolution:
2.70 Å
R-Value Free:
0.27
R-Value Work:
0.18
R-Value Observed:
0.18
Space Group:
P 1 21 1