Deposition Date
1999-01-07
Release Date
1999-01-13
Last Version Date
2023-12-27
Entry Detail
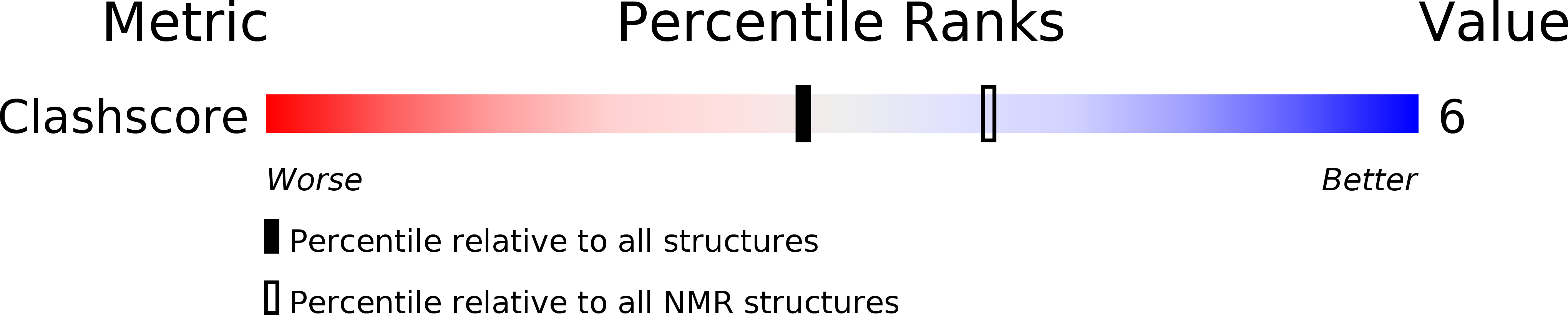
PDB ID:
1B5K
Keywords:
Title:
3,N4-ETHENO-2'-DEOXYCYTIDINE OPPOSITE THYMIDINE IN AN 11-MER DUPLEX, SOLUTION STRUCTURE FROM NMR AND MOLECULAR DYNAMICS
Method Details: