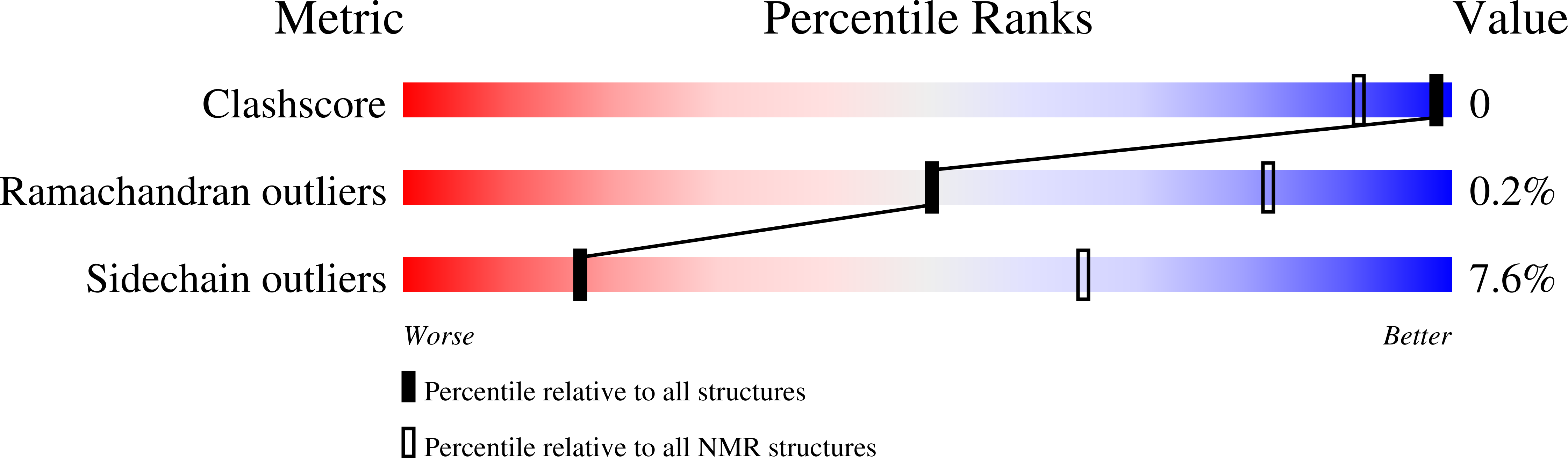
Deposition Date
1999-01-05
Release Date
1999-07-09
Last Version Date
2024-10-09
Method Details:
Experimental Method:
Conformers Calculated:
80
Conformers Submitted:
43
Selection Criteria:
POTENTIAL ENERGIES