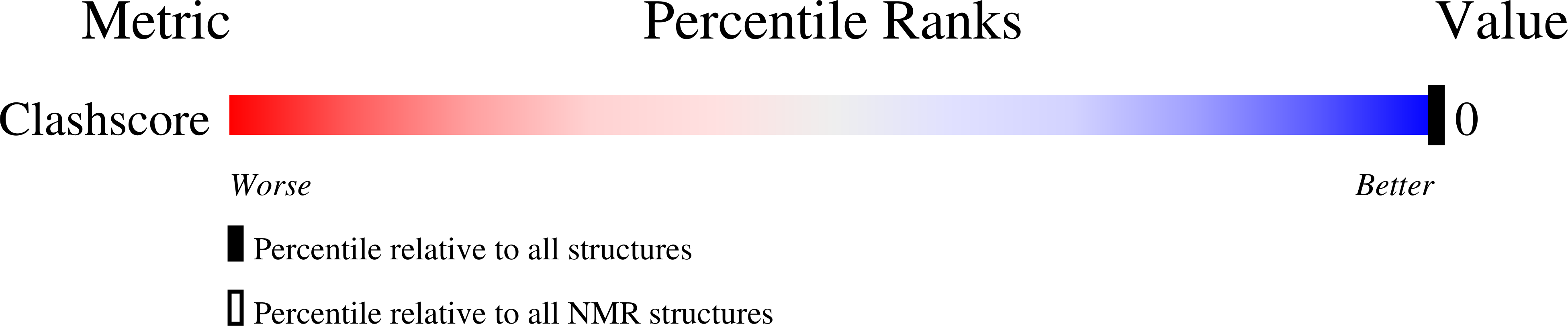
Deposition Date
1998-11-12
Release Date
1998-11-18
Last Version Date
2024-10-09
Entry Detail
PDB ID:
1B0Q
Keywords:
Title:
DITHIOL ALPHA MELANOTROPIN PEPTIDE CYCLIZED VIA RHENIUM METAL COORDINATION
Method Details:
Experimental Method:
Conformers Submitted:
1