Deposition Date
1997-04-22
Release Date
1997-10-22
Last Version Date
2024-11-13
Entry Detail
PDB ID:
1AIP
Keywords:
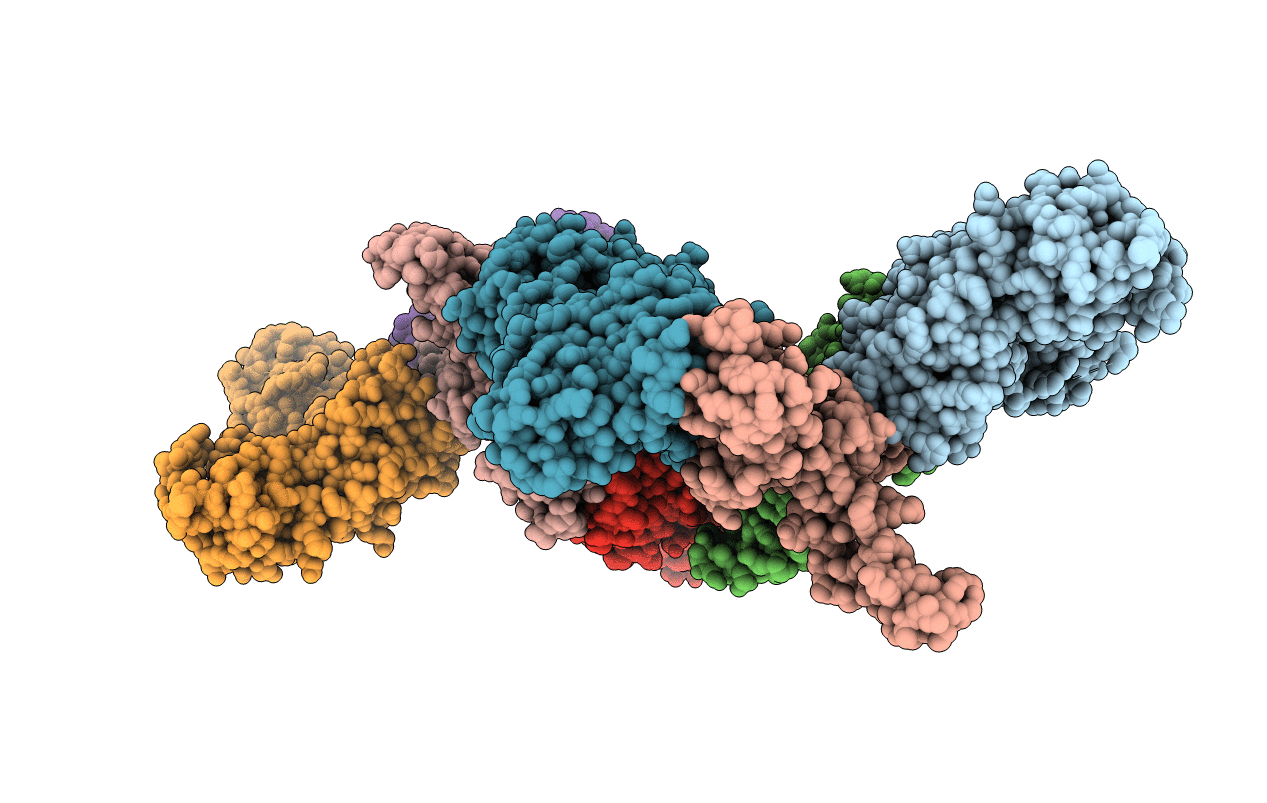
Title:
EF-TU EF-TS COMPLEX FROM THERMUS THERMOPHILUS
Biological Source:
Source Organism(s):
Thermus thermophilus (Taxon ID: 274)
Expression System(s):
Method Details:
Experimental Method:
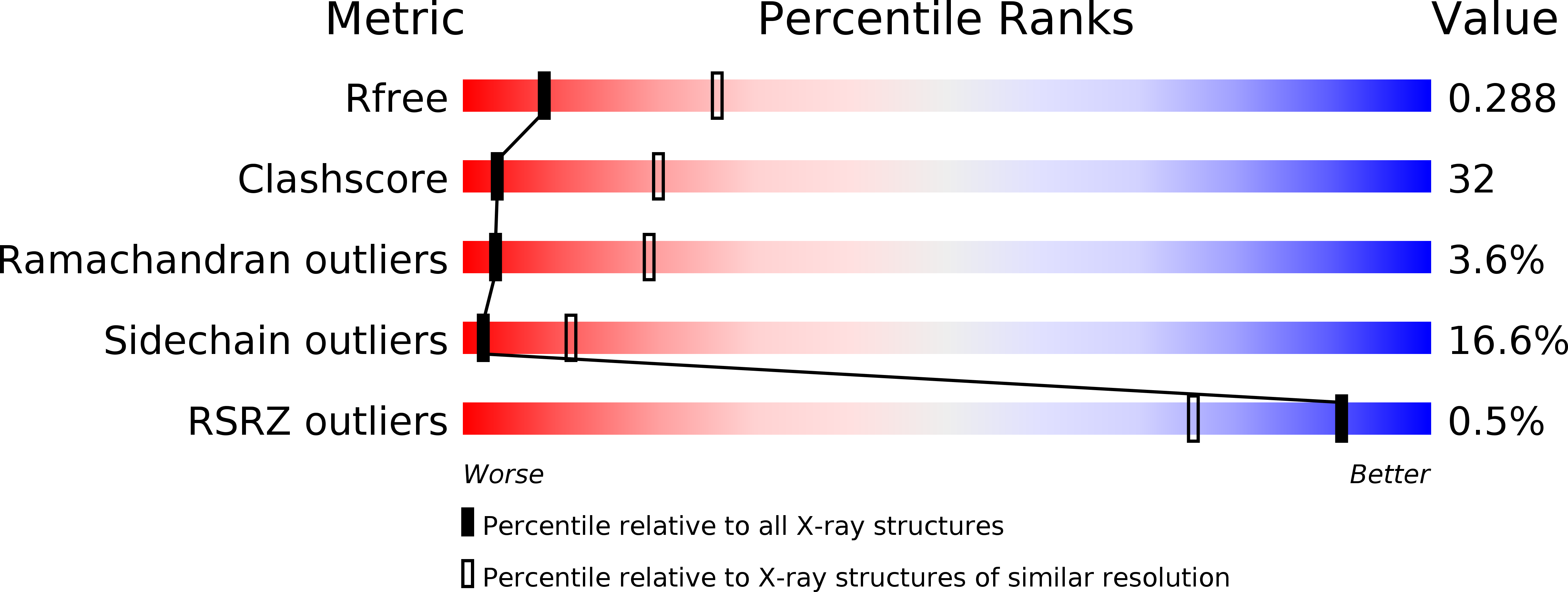
Resolution:
3.00 Å
R-Value Free:
0.28
R-Value Work:
0.21
R-Value Observed:
0.21
Space Group:
P 1 21 1